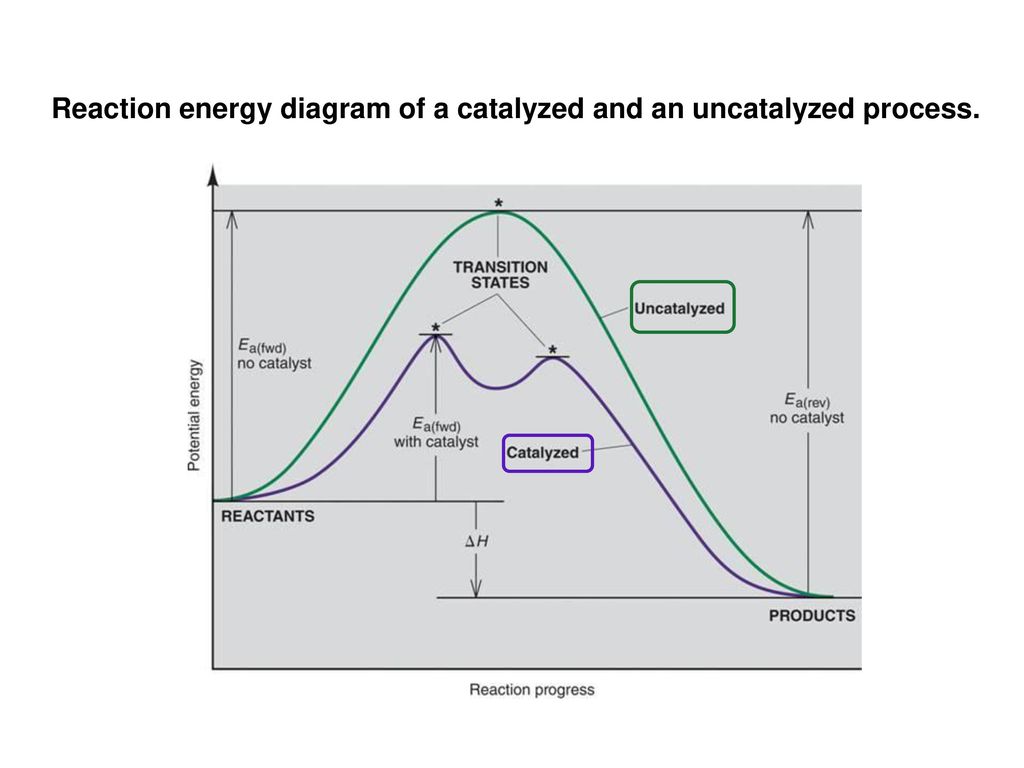
Label The Following Reaction Energy Diagram For A Catalyzed And An Uncatalyzed Process
Below the attached figure shows the energy profile of a reaction carried out in the presence of 1 hour ago #15:
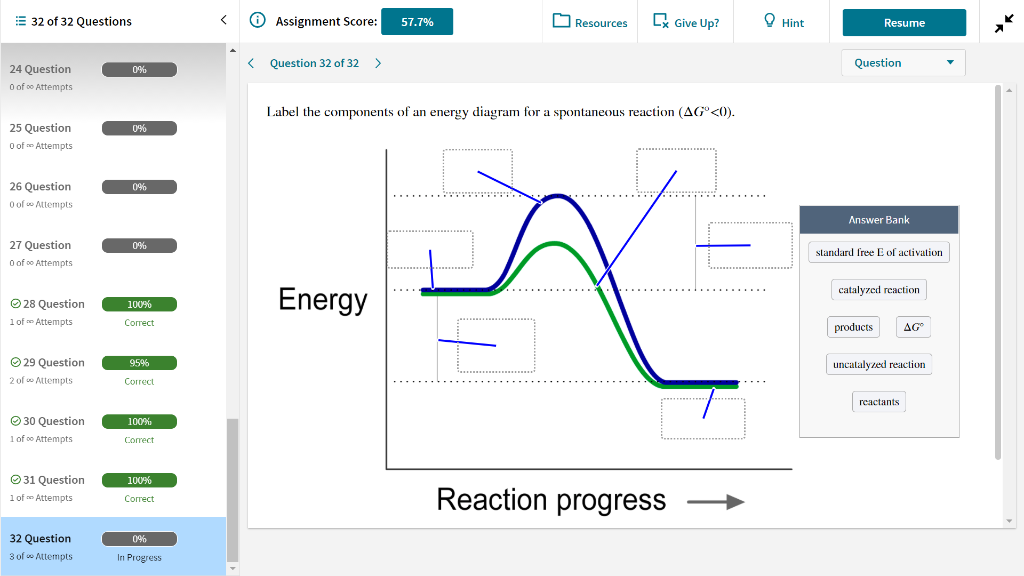
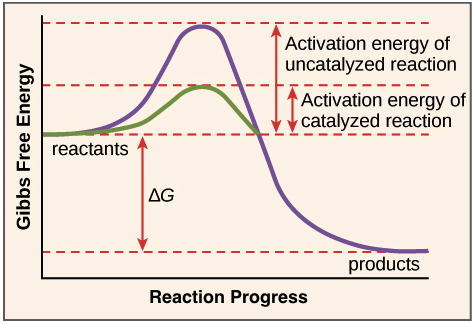
Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Catalysts lower the activation energy for reactions. Figure 1 shows how an enzyme (or any other catalyst) we can express this reaction by the following chemical equation the line labeled uncatalyzed reaction in figure 1 represents changes in energy that take place in the reaction without a catalyst. The following is the primary reaction catalyzed by catalase, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form repeat the steps from exercise 2b, using the uncatalyzed h2o2, to. What apparatus and procedure can you use to investigate catalysts by measuring the rate of reaction?
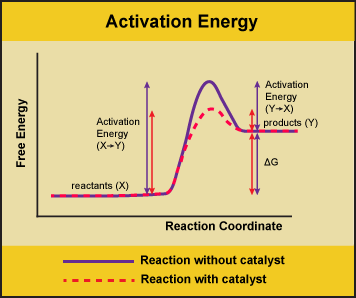
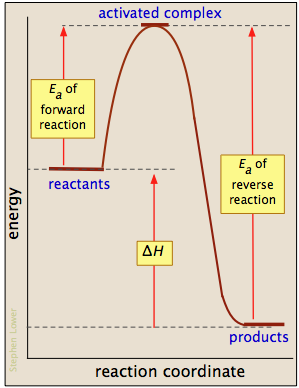
So, of the choices given in this question, the ones that are different from the uncatalyzed reaction would be One without a catalyst and one with a catalyst. Notice that the only effect of the catalyst is the decrease in the energies of activation, ea, for both the forward and reverse reactions. The comparison of catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions using energy diagrams is to be shown.
Transcribed image text from this question. Draw and label a reaction coordinate diagram for an uncatalyzed reaction s p and the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme e. The diagram below shows steps in the exothermic chemical reaction of. How do we process the results from catalysed experiments?
- Pro Comp Pc 2015 Wiring Diagram
- Troy Bilt Pony Deck Belt Diagram
- 2002 Ford Explorer Xlt Fuse Box Diagram
In the diagram below, label the two reaction pathways as either catalyzed or uncatalyzed. Therefore the higher reaction speed is not represented in those diagrams. Complete the following diagram to discuss your experiment with your teacher and classmates. Identify which of the following atoms has the highest electronegativity and choose the.
What is the activation energy for a reverse reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction has a higher activation energy because there is no enzyme present in the reaction. Using reaction diagrams to compare catalyzed reactions the two reaction diagrams here represent the same reaction: Solvent effects in acid catalyzed dehydration of the diels alder.
Watch the video at the link below and answer the following questions Analyzing the potential energy diagram of a regular/uncatalyzed and a catalyzed (adding a catalyst) reaction. A⟶ show the catalyses activation energy which is due to addition of catalyst. Thus enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. It is observed that after washing, weight of each garments has increased from 5% to 36%; The energy relationships of a reaction are explained on the basis of energy diagrams. In an exothermic reaction, the energy of products is lower than that of the reactants.
In other words, why is there a minimum energ. Not all molecules of the same type will possess the same amount of energy 1. The way that a catalyst works is by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction. Which one of the following is not among the six internationally accepted classes of enzymes?
Remember that the 🔼h of reaction remains the. An enzyme catalyzes the reaction a → b. The presence of the catalyst has no impact on the free energies of the reactants or the products or. There are many reactions catalyzed by solid acids in oil processing and petrochemical processes as well as in organic syntheses.
Draw and label a reaction coordinate diagram for an uncatalyzed reaction, s → p, and the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme, e. The following diagram shows an energy diagram for the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid. The following lovely diagram comes from the wikipedia article on catalysis: A generic equation for complex formation is as follows:
Stitch length of the constituted fabric has decreased from 1. Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction The lower the activation energy for a reaction, the faster the rate. Reaction diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed reaction.
O o o o o in water baths set at 55 c, 60 c, 65 c, 70 c by placing a 0.15 ml aliquot of the reaction mixture in a labeled clean test tube and boiling in a water bath activation energies you have determined with the values for other catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. Describe an experiment to measure the speed of a catalysed and uncatalysed. Why does a potential energy diagram showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy not move left on the reaction pathway scale (compared to uncatalysed reaction) if a catalyst speeds up reactions? The activation energy of the uncatalyzed reaction is shown by ea, while the catalyzed reaction is shown by ea'.
The way in which this is accomplished is by providing an alternate mechanism. They are biochemical catalysts meaning they lower the activation energy needed for a biochemical reaction to occur. The initial rate of the reaction was measured as a function of the concentration of a. A mixture containing a solid and a liquid consists of two phases.
The peak representing activation energy is lower for the catalyzed reaction. After the reaction occurs, a catalyst returns to its original state and so catalysts can be used over and over again. Activation energy for the same reaction when catalyzed is 11.9kj. What is the ratio of the rate constant for the catalyzed reaction to that for the uncatalyzed reaction at 25c?
The activation energy is higher for a noncatalyzed reaction (a) than for the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme (b). Energy profiles of the reaction over weak and strong acids. Select the correct options among the following concerning the rate of a chemical reaction increases In a heterogeneous reaction, the catalyst is in a different phase from the reactants.
These revision notes are suitable for gcse reaction? For each of the following reactions decide whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic, then sketch a potential energy diagram. The difference between a homogeneous mixture and a compound a homogeneous mixture can be seperated by physical reactions, but compounds can be seperated by chemical.