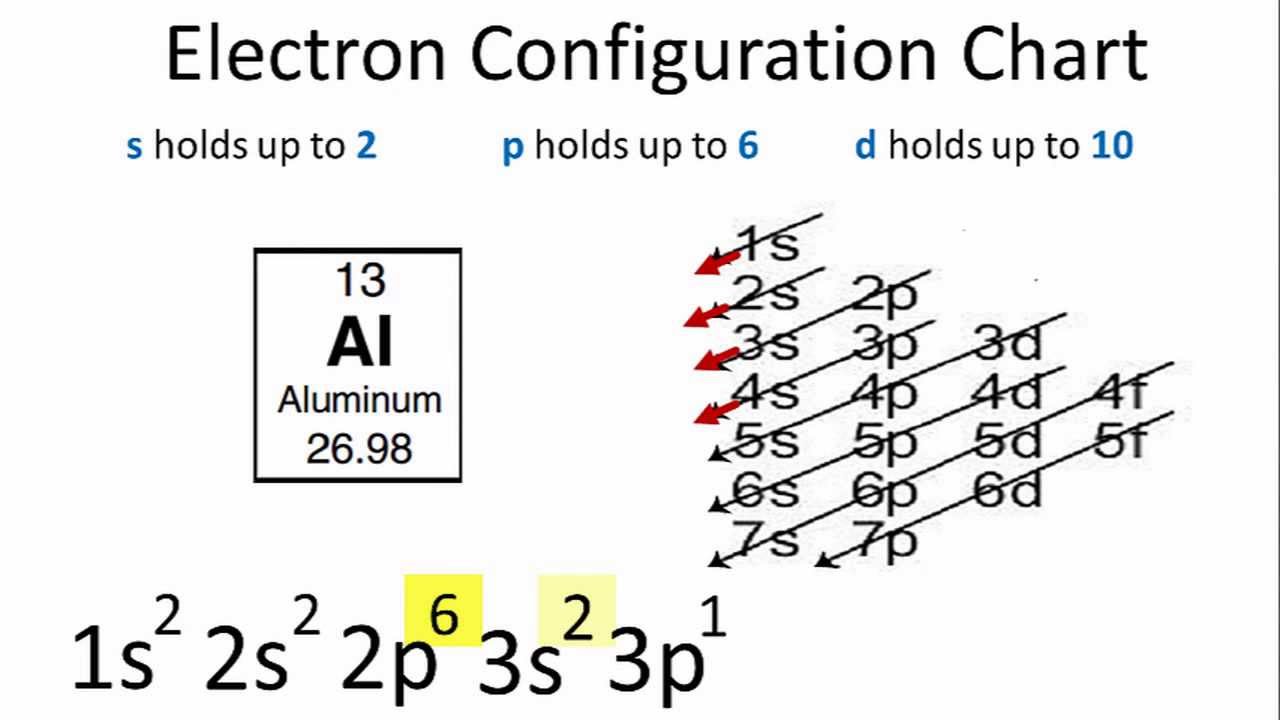
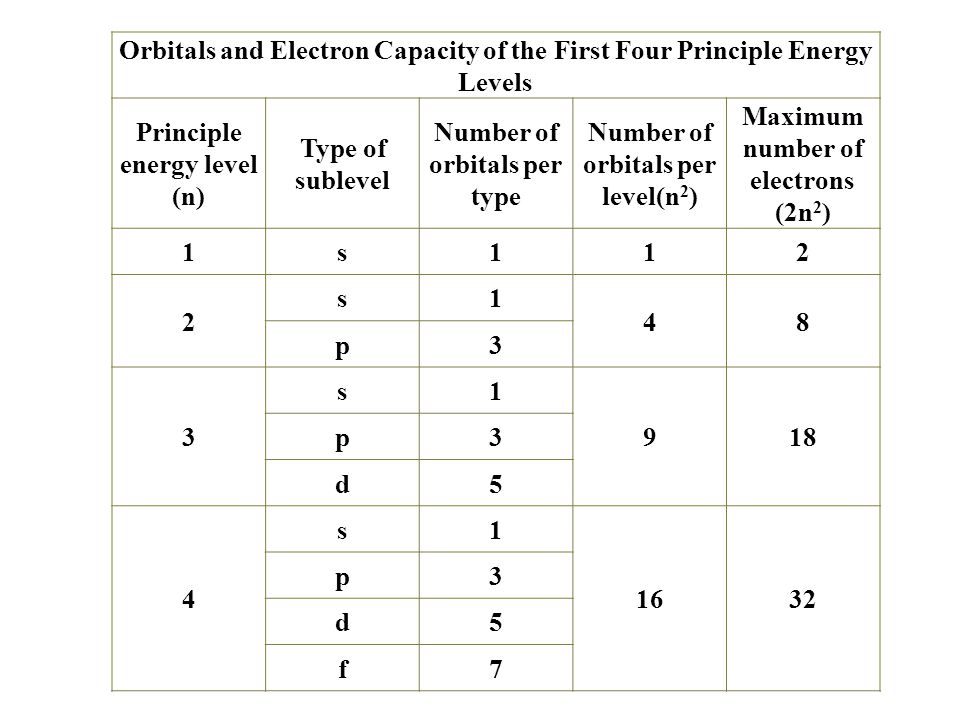
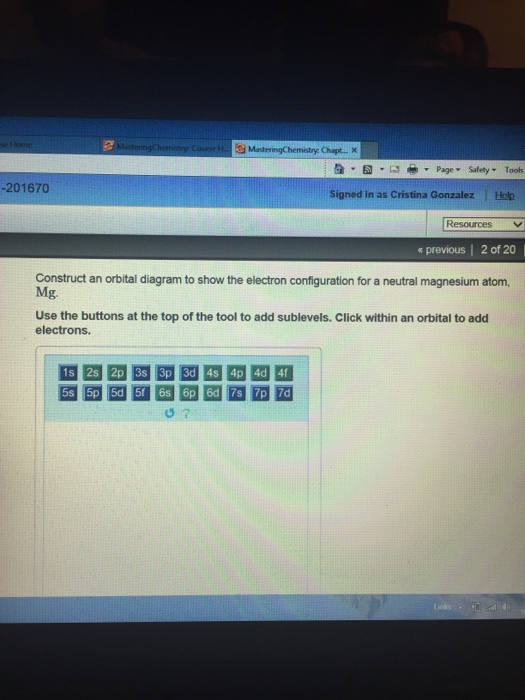
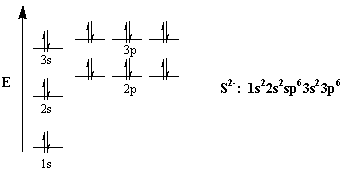Construct An Orbital Diagram To Show The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Magnesium Atom
To show the electron configuration for an atom, what is the advantage of using an orbital notation compared to a dot structure?
Construct an orbital diagram to show the electron configuration for a neutral magnesium atom. These labels contain the shell number (given by the principal quantum the pauli exclusion principle states that a maximum of two electrons, each having opposite spins, can fit in an orbital. Model 1 because it shows an electron. An electron configuration shows the distribution of electrons of an atom or a molecule. Atomic orbital diagrams and electron configuration.— 3 chemical bonds, molecules, and compounds.
Ce electron dot structures chemists use valence electrons to show how atom's are involved in bonding. Electron configurations are written so as to clearly display the number of electrons in the atom as well as the number of electrons in each for instance, if we want to write an electron configuration for an uncharged calcium atom, we'll begin by finding its atomic number on the periodic table. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 or in shorthand [ne] 3s2. Video explanation on the exceptions to electron configuration.
Electronic configuration or electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in different orbitals the atomic number in neutral atom represent the number of electrons 2. Which diagram shows the correct distribution of electrons in the electron shells of a magnesium atom? This principle can also be stated. An atom's electrons exist in discrete atomic orbitals, and the atom's electron configuration can be determined using a set of guidelines.
The electron configuration for magnesium is shown below. Click within an orbital to add electrons. When electrons fill the energy levels, it fills principal energy levels, sublevels, atomic orbitals from lowest energy first. As an atom gains electrons, they fill different orbitals sets according to a specific order.
The electron configuration of any given element follows precise rules regarding the placement of electrons around the atom's each electron follows a path around the center of the atom, or more precisely the term orbital refers to the way a particular electron is moving within a particular shell. The electron configuration of a neutral magnesium atom is: Electron configuration electron configuration is shorthand for the arrangement of electrons in errata: The atomic number is defined as the total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
The electron configuration of an atom is written with the help of subshell labels. In the diagram below, the black circle represents the nucleus of the atom, and each circle represents the boundary of an electron shell. Click within an orbital to add electrons. Neither model is able to show the reactivity of potassium.
Chromium is a transition metal and it has 24 electrons and here is the orbital diagram. Orbital diagrams orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Draw the electronic configuration for potassium using. Orbital diagrams show the arrangement of electrons in orbitals within an atom.
The electrons in an atom fill up its atomic orbitals according to the the outermost orbital shell of an atom is called its valence shell, and the electrons in the valence shell as you move from left to right across the periodic table, the above diagram shows the order in which. Each set of orbitals, when full. Distinguish between outer energy level (valence) electrons and let's begin this section with the orbital box (or the orbital representation diagram) for a neutral atom. It doesn't save much space here, but imagine if you were writing the electron configuration for say well, a neutral helium atom is going to have two electrons.
In all neutral atoms both protons and electrons are numerically equal. There is a specific notation that can quickly show you where the what is an atomic orbital? In writing the electron configuration for magnesium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. The above diagram simplifies how to fill in the electron configuration from lowest to highest.
Electron configurations describe where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. Ground state electron configuration of atoms in periods 1 to 3 in energy levels or shells tutorial for chemistry students. Start filling the question 1 write the electronic configuration for the following atomic numbers (a) 23 (b) 30 (c) 19. To view the order in which the sublevels the table below shows the electron configuration for the first 20 elements on the periodic table.
So instead of just having one electron in. The basis of this prediction is a rule known as the aufbau the energy of an orbital depends on both its size and its shape because the electron spends more of its time further from the nucleus of the atom. The electron configuration of an atom describes the orbitals occupied by electrons on the atom. The electron configuration for cl should be [ne]3s23p5.
The main difference between this diagram and the one we showed before is that now the individual orbitals are. The electron configuration for that of the chromium atom is here's what i have for the electron configuration for chromium with the orbital notation. Magnesium has three electron shell, that is 2.8.2 whereby the first electron shell hold a maximum of two electrons, the second one hold a maximum of eights electrons while the rest two. Use boxes to represent orbitals.
4 lewis dot symbols show valence 6 the octet rule for chemical compounds atoms attempt to attain a noble gas electron configuration in. The ion's configuration would therefore be: Arrangement of electrons in an atom more electron configuration practice • draw orbital notations for a. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add sublevels.
Alright so let's talk about chromium. In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Convert from orbital representation diagrams to electron configuration codes. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms on the white board, i show students the electron configuration for hydrogen and explain how we use the periodic table to.
1s2 2s2 2p6, which is isoelectronic with.