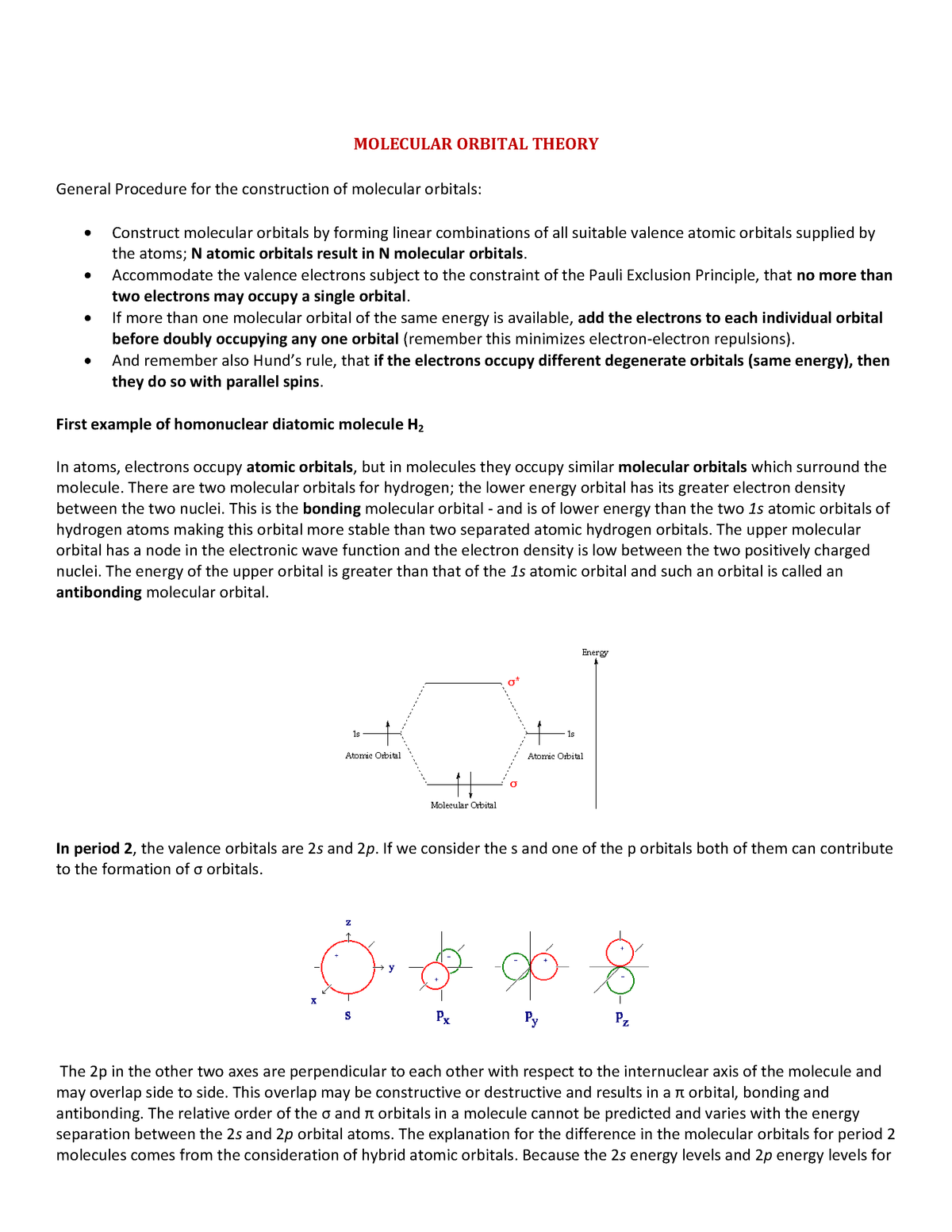
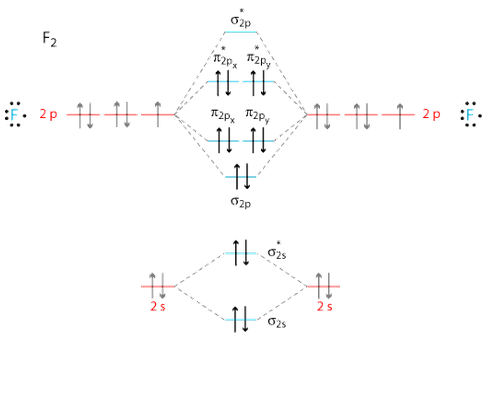
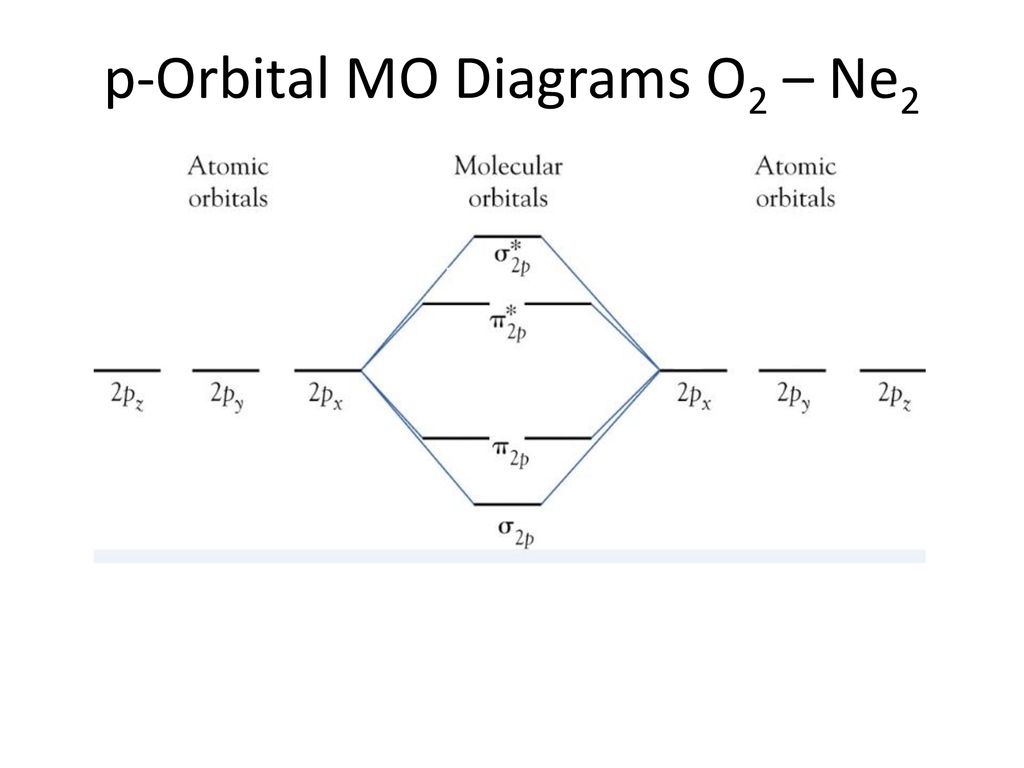
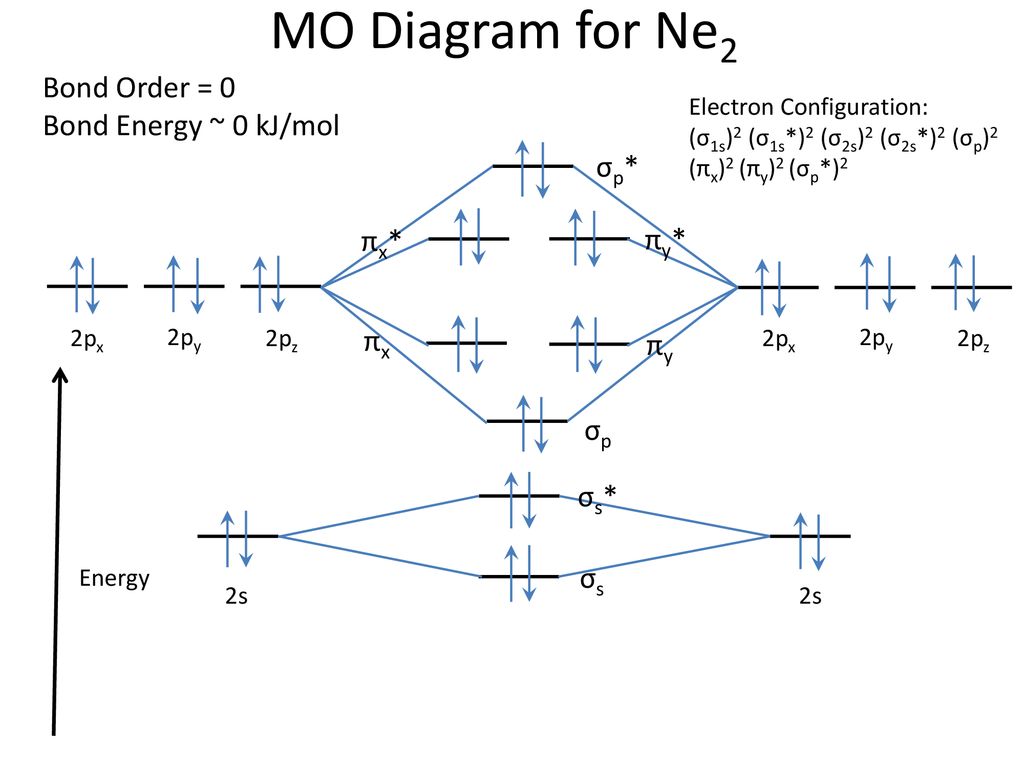
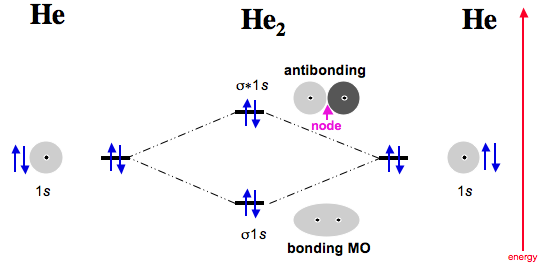
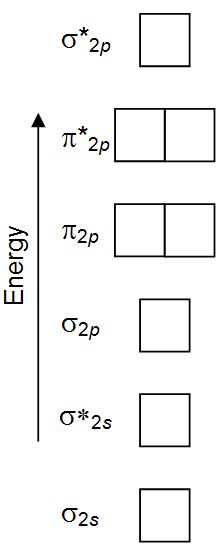
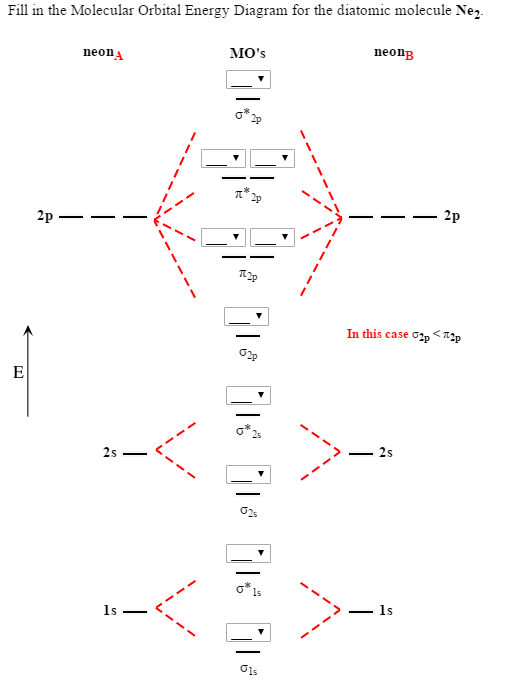
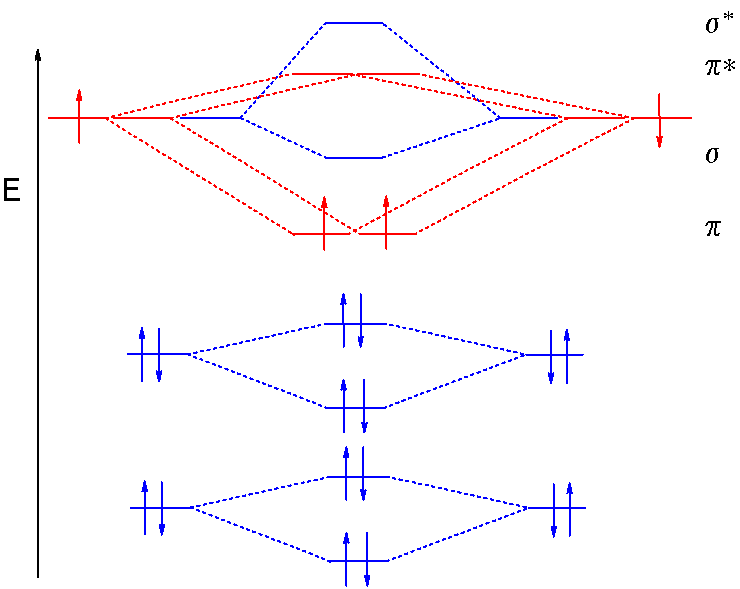
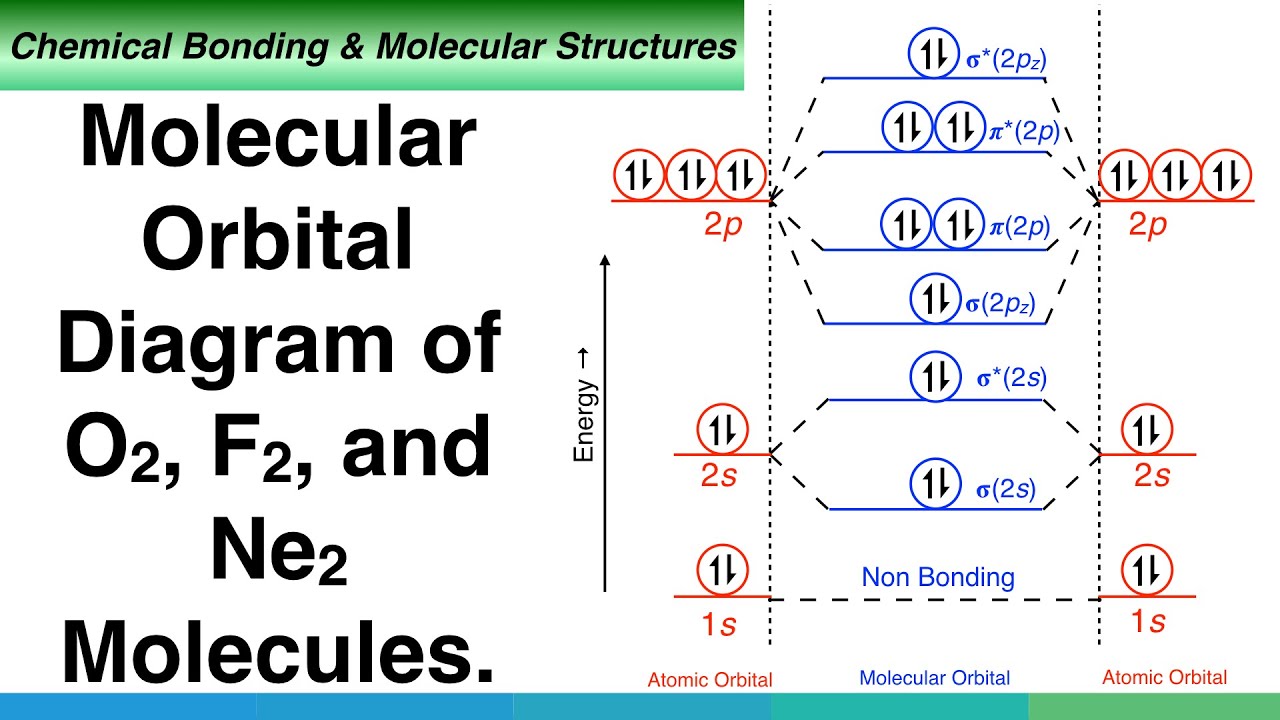
Ne2 Orbital Diagram
Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here.
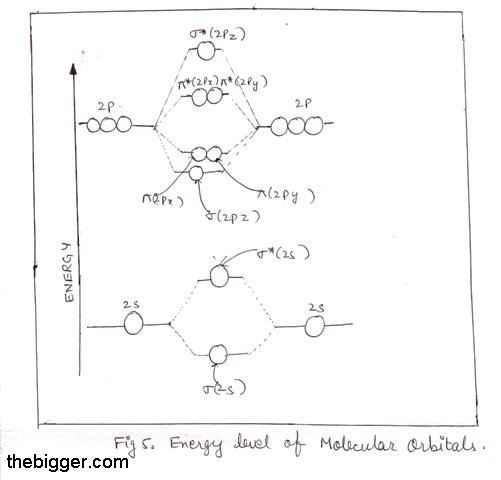
Ne2 orbital diagram. Alright let's talk about orbital diagrams. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas ( 1 ion) (n2( )). Orbitals for which n = 2 are larger than those for which n = 1, for example. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s(2).
How to express the electronic structure of atoms using electron configuration notation? Molecular orbital mo diagram of n2 molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas n2 use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you sigma2s 2 sigma2s 2 pi2p 4 mo diagram for n2 molecular orbital there are two mo. An mo diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each mo. Figure 6.27 orbital energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom shows that the energy levels become closer and closer together as the value of n increases, as expected because of the 1/n2 dependence of orbital energies.
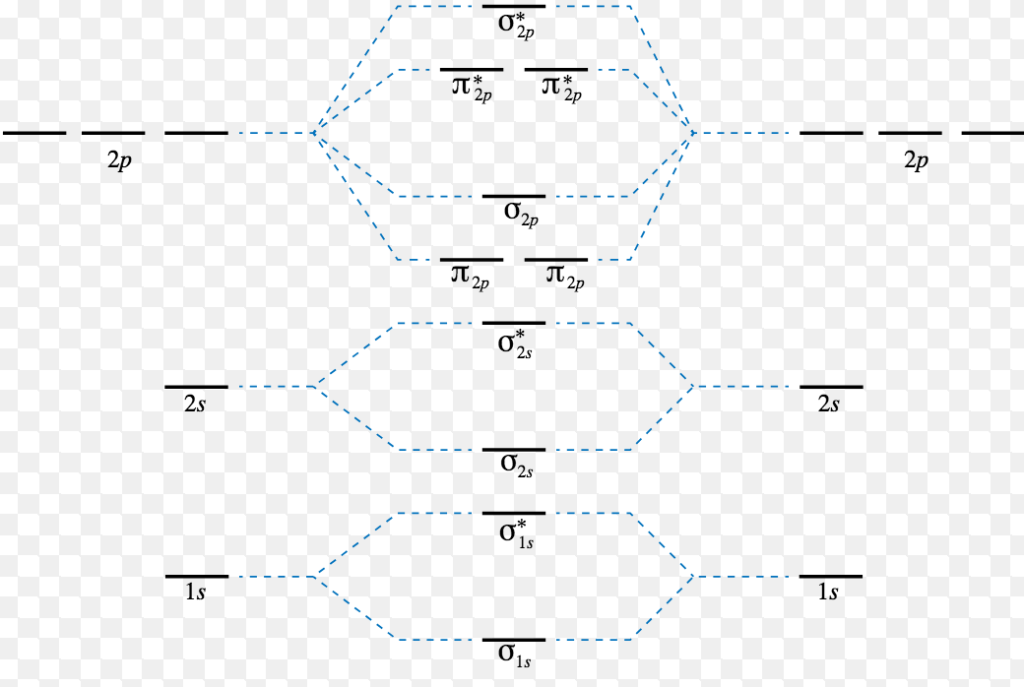
They weren't drawn that way on this diagram, but they should be. Each line in the molecular orbital diagram represents a molecular orbital, which is the volume within which a high percentage of the negative charge generated by we will use this diagram to describe o2, f2, ne2, co, and no. Because they have opposite electrical charges, electrons are attracted to the nucleus of the atom. G means gerade, or even symmetry upon inversion, and u means ungerade, or odd symmetry upon inversion.
- John Deere F525 Wiring Diagram
- 2000 Toyota Sienna Spark Plug Wire Diagram
- Honda 300 Fourtrax Carburetor Diagram
We use the following procedure when drawing molecular orbital diagrams. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2). Neon atom has 10 electrons and its electronic configuration is. The molecular orbital diagram of are shown below.
Here are some orbital diagrams of elements with more electrons to help you understand the rules, electron configuration, orbital diagrams, and also you can't abbreviate a noble gas by using its symbol in brackets; For the first ionization energy for an n2 molecule, what molecular orbital is the electron removed from? The principal quantum number (n) describes the size of the orbital. Now note that even in this advanced molecular orbital theory a bunch of approximations is introduced, and the answer in general depends on at which level of theory calculations are done.
Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. The second rule that we're going to talk about is the pauli exclusion principle which basically states that there are maximum 2 electrons per orbital. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for b₂ and other diatomic molecules from row 2 elements of the periodic.
There are two mo diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (n2, o2, ne2, etc). One atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a n2 molecule will have 14 electrons so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond next 2 in 1s sigma anti bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma bon. Individual atomic orbitals ao are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Transcribed image text from this question.
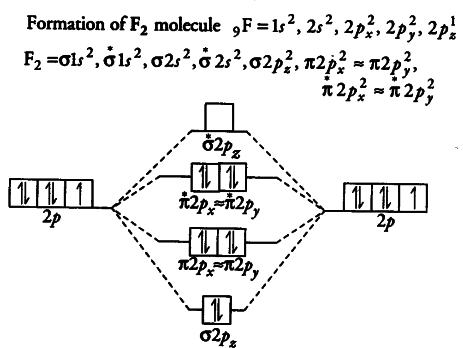
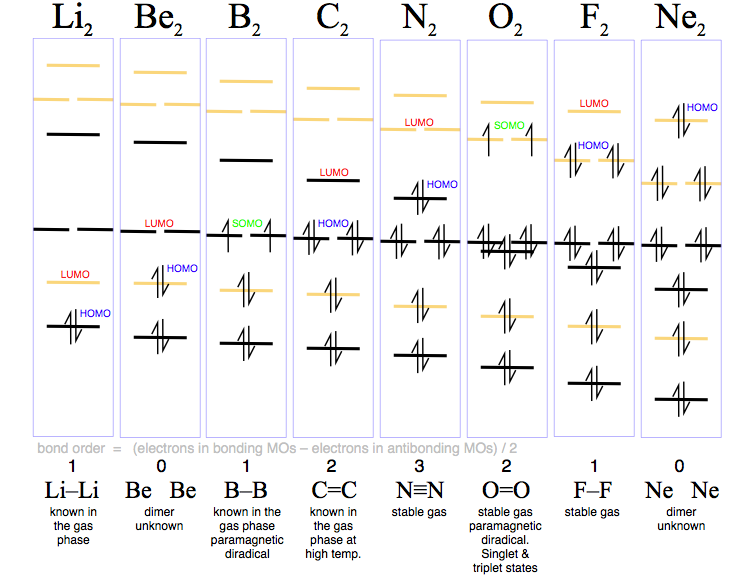
Fill from the bottom up, with 9 valence electrons total. Mo occupancy and molecular properties for b2 through ne2. The two available electrons (one from each h atom) in this diagram fill the bonding σ 1 s molecular orbital. As it can be seen from the mot of o2 , the electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the by using molecular orbital theory, why doesn't the ne2 molecule exist? One is for the elements up to nitrogen. The electron configuration for cl should be [ne]3s23p5. If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the second period (li₂, be₂, b₂, c₂, n₂, o₂ whilst this is the mo diagram for n₂:
Orbital diagrams give you all of the information you need about the electron configuration and occupied spin states for chemistry or see resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Finally, you can still count the number of. Orbital diagrams orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. The bond order of is, 3.
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. Energy difference in n2 2s orbital and 2px orbital is very low due to which they mix with each other.2s give its energy to 2px, 2px gain more energy and became unstable and increase its energy, and. Will the mo diagram be the same as that of $\ce{n2}$ or not? Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of n2 using its diagram.
Seeing a molecular orbital diagram for n2 will clarify what i mean. The orbital correlation diagram in predicts the sa. The other is for after nitrogen. According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be, as there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen.
Ne2 molecular orbital diagram posted on may 15, 2016 by admin a diagram is shown that has an upward facing vertical arrow running along the left mo diagram cyanide molecular orbital diagram of hetero nuclear diatomic molecule 14 mo ne2 molecular orbital diagram elegant mo f 2 trusted wiring. That is, ar is [ne]3s23p6 not [ar]. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p.