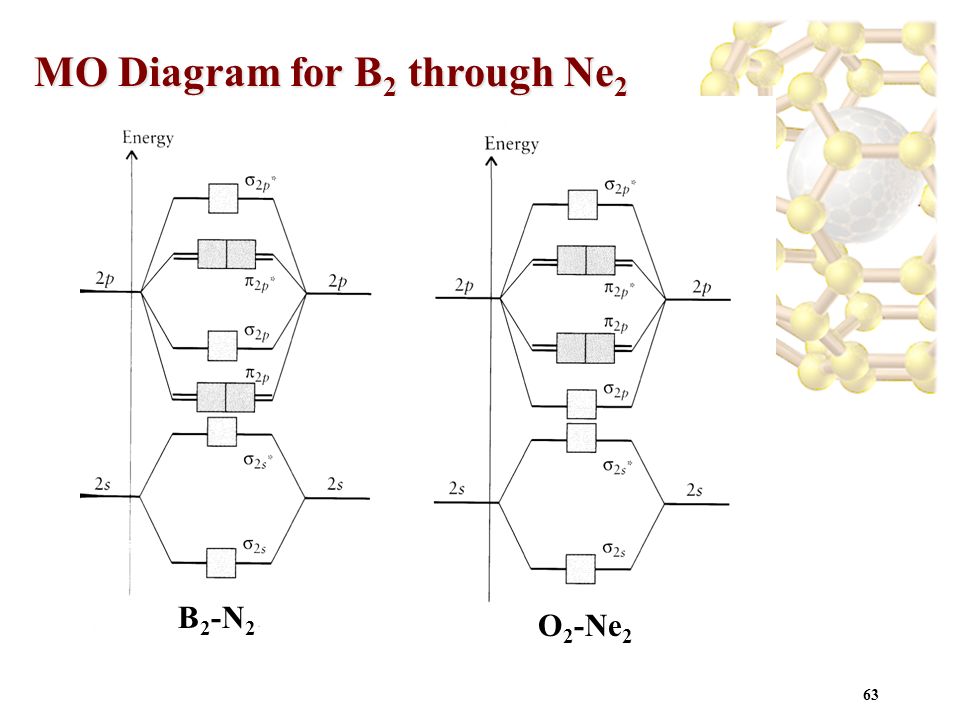
Ne2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Bond Order
A bonding molecular orbital is always lower in energy (more stable) than the component atomic orbitals, whereas an antibonding molecular orbital is always higher in energy (less stable).
Ne2 molecular orbital diagram bond order. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the h2 molecule are in the σ1s bonding orbital; For example, to give you a glimpse at where we are headed. There are two mo diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (n2, o2, ne2, etc).
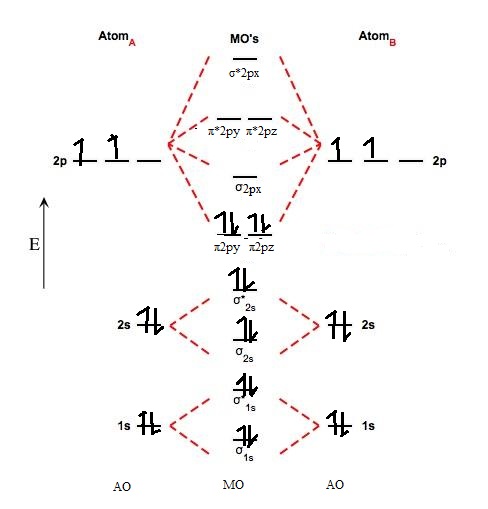
The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a way of looking at the structure of a molecule by using molecular orbitals that belong to the molecule when simple bonding occurs between two atoms, the pair of electrons forming the bond occupies an mo that is a mathematical combination of the. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Label all atomic and molecular orbitals.
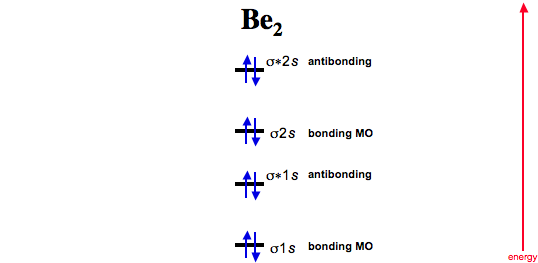
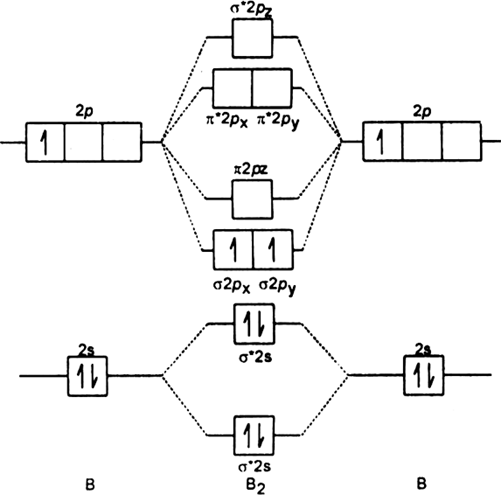
Draw a molecular orbital diagram and determine the bond order expected for the molecule b2. One is for the elements up to nitrogen. We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram (see the figure below) in which a single upward arrow indicates one electron. The electron configuration is (σ1s)2.
- Gmc Stereo Wiring Diagram
- Cummins Isx Ecm Wiring Diagram
- 2008 Toyota Camry Interior Fuse Box Diagram
It is defined as the number of covalent bonds between the two combining atoms of a molecule. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is given by half the difference in number of electrons between bonding and anti bonding molecular orbitals. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Half baked knowledge is dangerous! just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order, doesn't mean that it should exist.
(a) draw a mo diagram for the valence electrons of bc. Li2, be2, b2, c2, n2, o2, f2, and ne2. Explain your answer here in addition to providing the bond order values. Because arguments based on atomic orbitals this diagram suggests that the energy of an h2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated the molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both.
Use the molecular orbital energy diagram below to answer the questions about bond order for the positive ion c2 number of bonding number of antibonding c2 valence 251 d. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. Does the bond order calculated agree with what you would draw for the lewis structures of these molecules? Molecular orbital theory, bond order, bond strength, magnetic properties.
If it doesn't, it means we need to extract more information from the mo diagram. For the elements li to n, the molecular orbital in addition, the bond orders predicted by mo theory for the diatomic molecules of all the second row elements are in agreement with those in lewis. Relationship between electronic configuration and molecular behaviour : The central importance of the electron pair for bonding arises naturally in mo theory via the pauli exclusion principle.
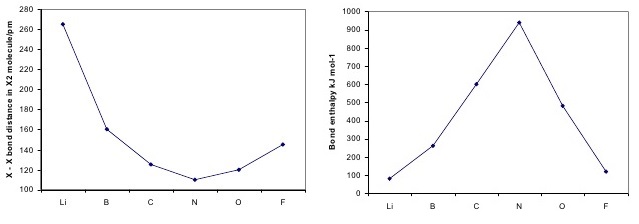
Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Valence bond theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for b₂ and other diatomic molecules from row 2 elements of the. The key difference between the two models is that in valence bond theory, electrons are localized between two specific atoms in the molecule, whereas in.
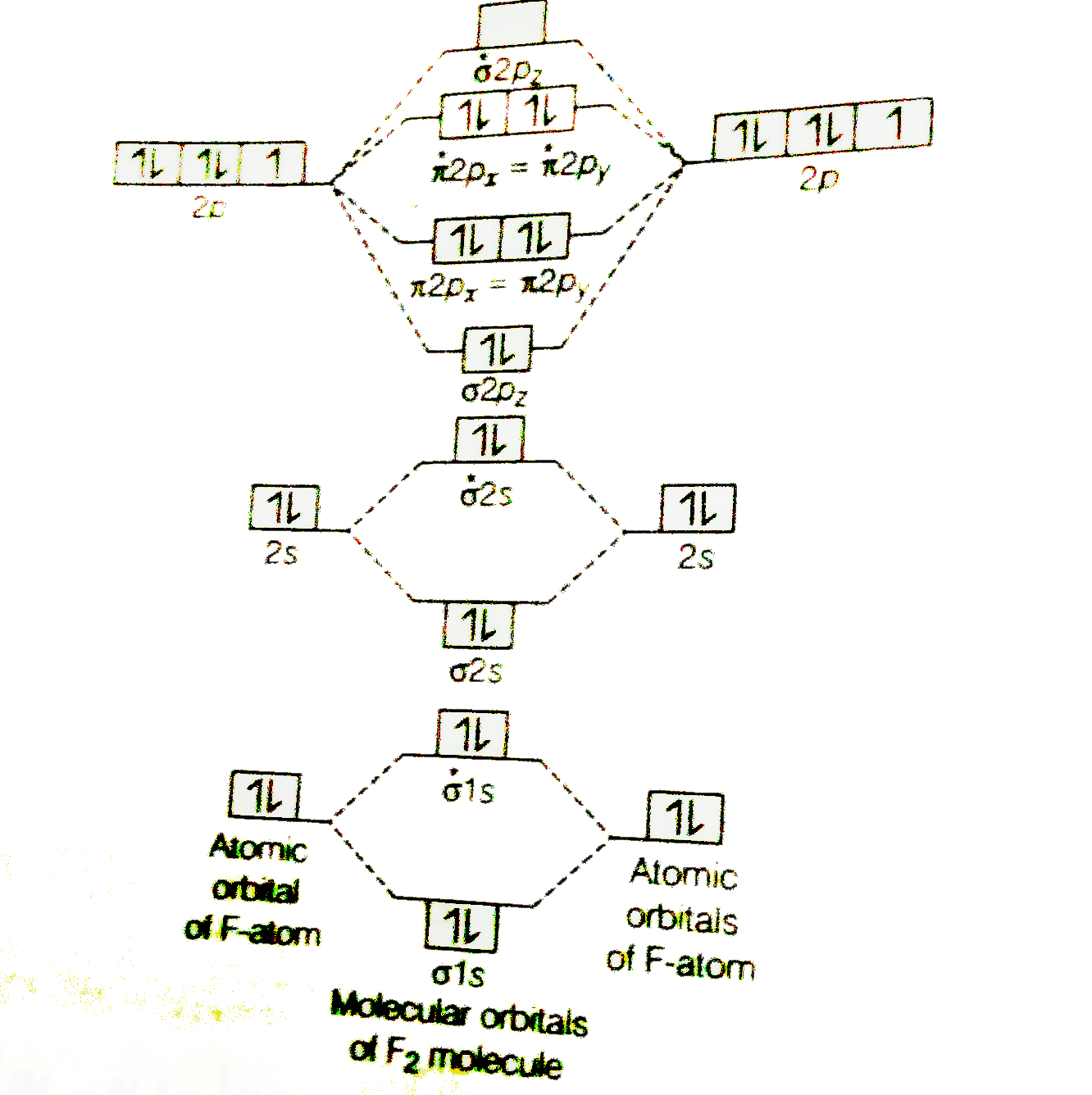
The molecule ne2 is predicted to be unbound (bond order of 0), and has indeed never been observed. A positive bond order indicates a strong bond while a negative or zero bond order indicates that a bond will not form. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f. The second molecular orbital is described by destructive overlap (or destructive interference, if you prefer) where p according to the aufbau principle, these orbitals will fill up in order of stability, which means that for a typical pi bond, we end up with two electrons in the pi orbital and zero in the pi*.
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that he2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons. On the other hand, molecular orbital theory visions the electrons of a covalent bond to be delocalized over the entire molecule. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. As it can be seen from the mot of o2 , the electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
(b) the shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the • the term bond order refers to the number of bonds that exist between two atoms. The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. For full credit on mo diagrams, • label increasing energy with an arrow next to the lecture 13. The molecular orbital energy level diagram has to sigma2p orbital at a higher energy level that the two pi2p orbitals for which of the following species.
According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be, as there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen. We will look first at diatomic molecules and only later move on to polyatomic molecules. Posted 4 years ago by saroj bhatia. Those with positive bonding order are considered stable molecule while those with negative bond order or zero bond order are unstable molecule.
What is the bond order for a molecule with 10 electrons in bonding molecular orbitals and 5 electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals.