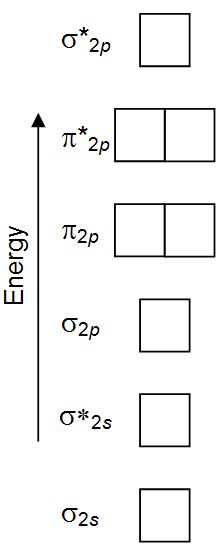
Molecular Orbital For Ne2
Molecular orbital mo diagram of n2 molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas n2 use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you sigma2s 2 sigma2s 2 pi2p 4 mo diagram for n2 molecular orbital there are two mo.
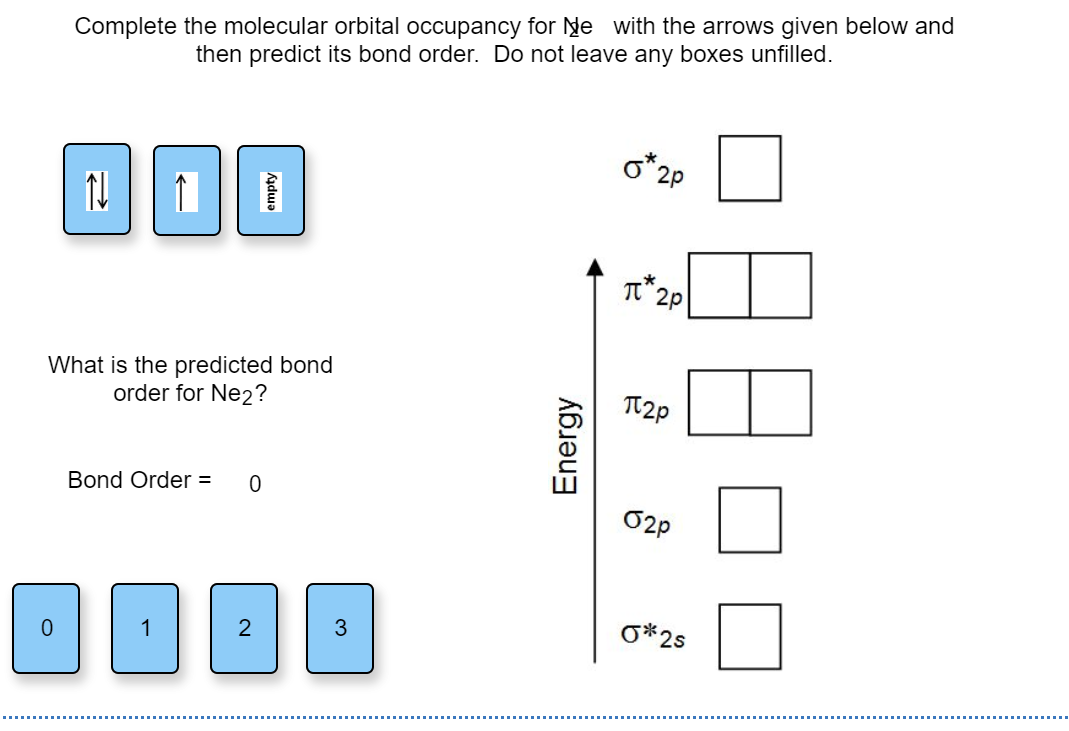
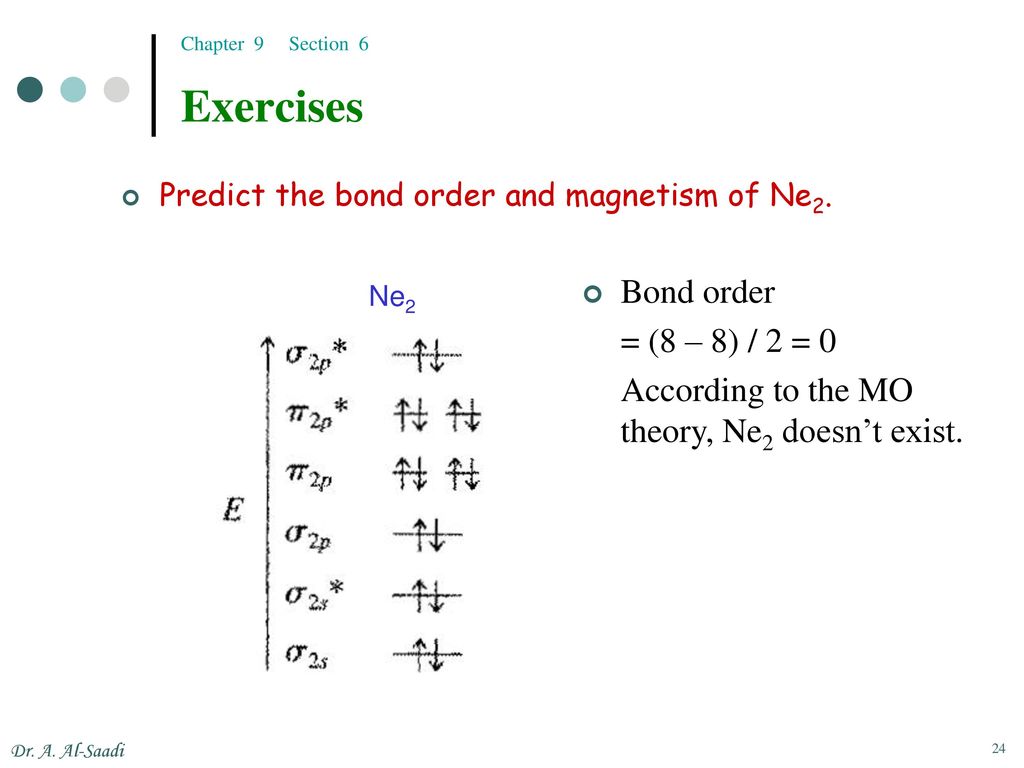
Molecular orbital for ne2. (d) this plot of the square of the antibonding molecular orbital illustrates the node corresponding to zero electron probability density between the two hydrogen nuclei. 2 + draw the molecular orbital (mo) electron diagram for the ne 2 molecular ion. This problem has been solved! Molecular term symbols are of the form 2s +1 !
The molecular orbital theory explains how there are no unpaired electrons in the bonds between the two n atoms. They weren't drawn that way on this diagram, but they should be. Let's look at the correlation diagram that. Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of n2 using its diagram.
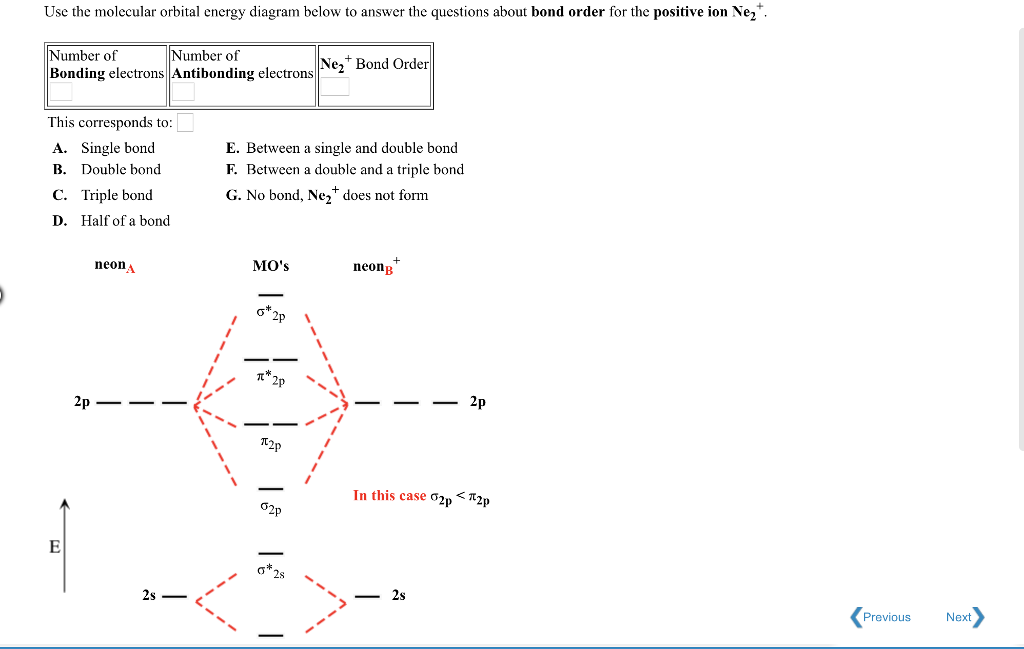
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for ne2+ and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any. Molecular orbital for h2 as the difference of the wave functions (ψ) of two h 1s atomic orbitals. Table 9.1 molecular orbital (mo) configurations and equilibrium bond lengths of n2.
- 2003 Eclipse Radio Wiring Diagram
- 2015 Ford Upfitter Switch Wiring Diagram
- 2013 Nissan Altima Fuse Box Diagram
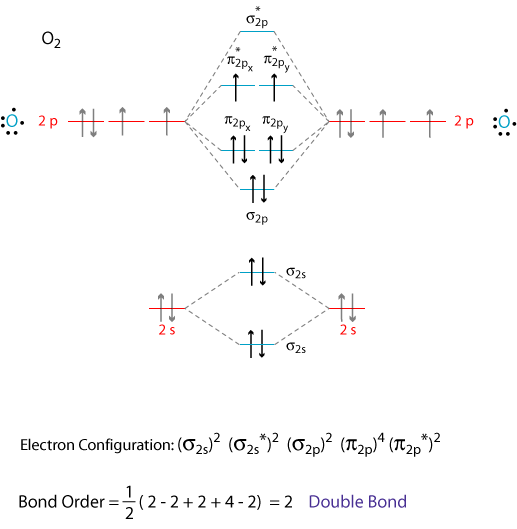
For reduction, electrons must be added to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital of n2 at —7 ev. From the molecular orbital diagram of n2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Like an atomic orbital, a molecular orbital is full when it contains two electrons with opposite spin. The number of electrons present in molecule = 2(7) = 14.
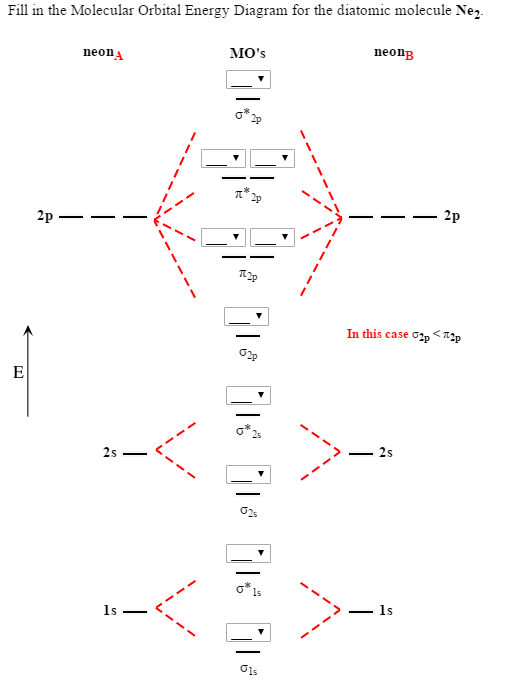
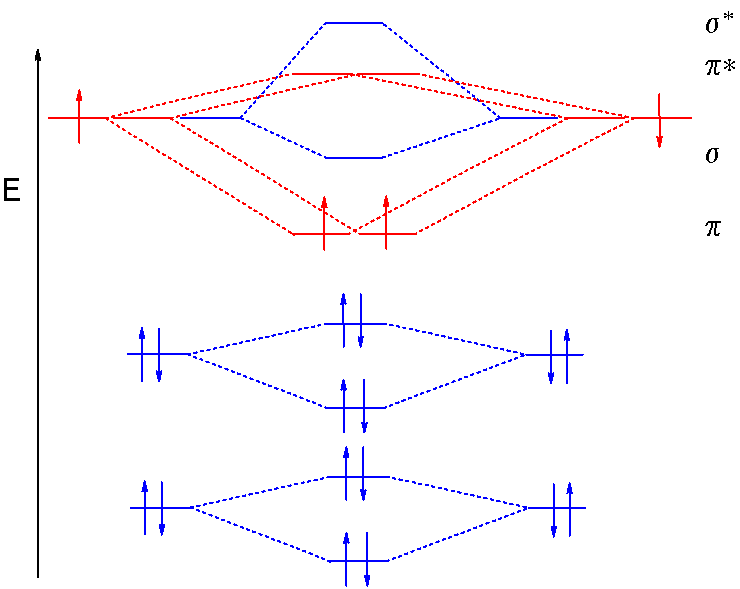
We assume that the electrons would fill the molecular orbitals of molecules like electrons fill atomic for o2, f2, or ne2, the orbital energies are different enough so only orbitals of the same energy interact to a significant degree. The molecular orbital volume encompasses the whole molecule. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2). There are two mo diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (n2, o2, ne2, etc).
The other is for after nitrogen. (b) the shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for mo1 and mo2. Molecular orbital (mo) theory is a more accurate way to use calculations to predict molecular geometries and energies than vb the four molecules mentioned above all use their n=2 valence shell to do the bonding. According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be, as there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen.
Anyways, for the electron configurations, you would use a notation like. Ne2 molecular orbital diagram posted on may 15, 2016 by admin a diagram is shown that has an upward facing vertical arrow running along the left 9 7 ordering question: The bonding molecular orbital concentrates electrons in the region directly between the two nuclei. As it can be seen from the mot of o2 , the electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
Seeing a molecular orbital diagram for n2 will clarify what i mean. If we build the mo diagram for #n_2#, it looks like this: Ignoring weak clusters held together by van der waals interactions, the reason that ne2 does not form a stable covalent molecule can be understood if you construct the molecular orbitals of ne2 using the 2s and. First though, notice that the #p# orbitals are supposed to be degenerate.
One is for the elements up to nitrogen. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. (g/u) , where 2s + 1 is the multiplicity, λ is the quantum number for the total orbital angular momentum about the internuclear axis. Transcribed image text from this question.
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. Molecular orbital theory (mo theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. This occurs only in the presence of highly electropositive metals such as lithium. The p orbitals combine to produce a sigma and two perpendicular pi.
Neon atom has 10 electrons and its electronic configuration is.