Molecular Orbital Diagram For B2
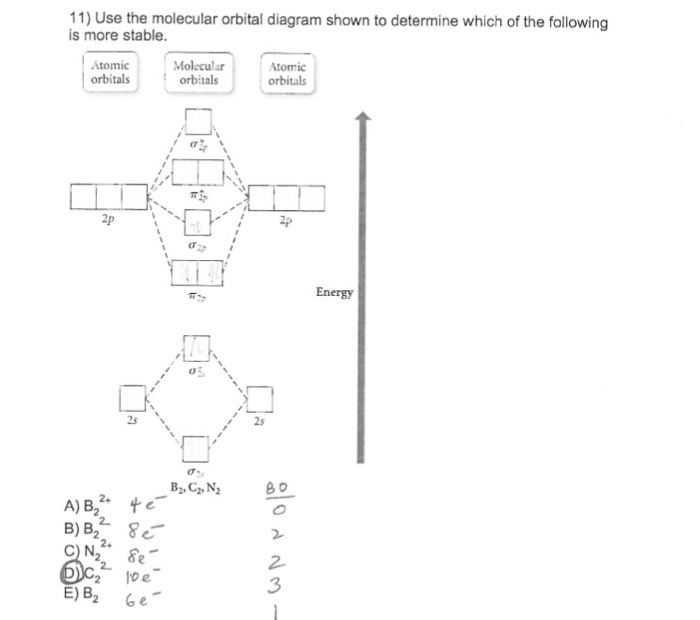
Li2, be2, b2, c2, n2, o2, f2, and ne2.
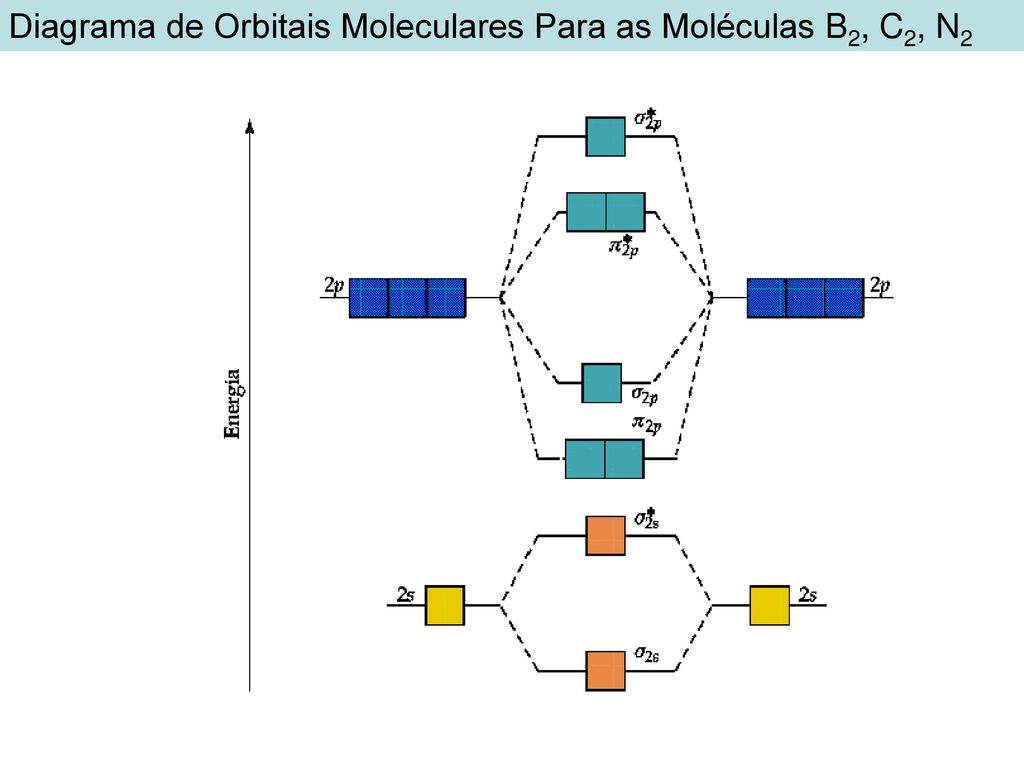
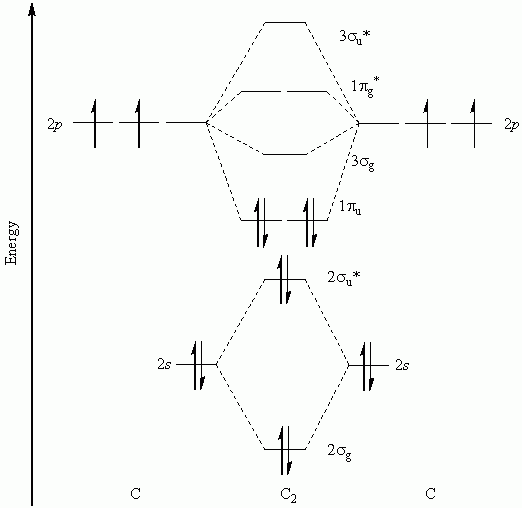
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. The molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions experiments have shown that o2 and f2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but b2, c2, and n2 are best described by a model that. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the. Draw a cartoon energy level.
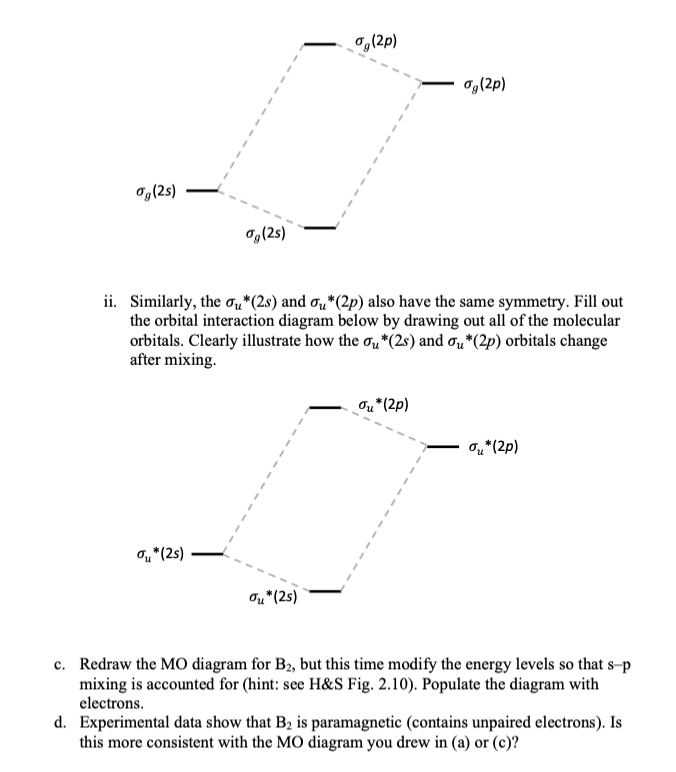
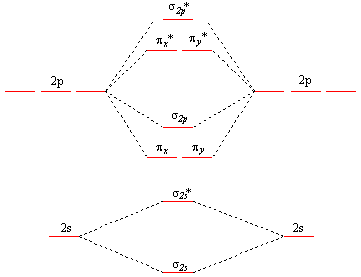
The subscripts g and u refer to the parity of the orbitals g (german gerade, even). Figure 19.14 molecular orbital diagram for an octahedral complex of a first series transition metal (only a interactions are considered in this simplified figure b a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for ferrocene. Molecular orbital theory provides an alternative model to valence bond theory that better describes the electron behaviour and physical/chemical properties of. In the h 2 molecule the two hydrogen electrons go into the.
Each hydrogen atom has one 1 s electron. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in latex by means of the package modiagram. For example consider b2 (each atom has an electron configuration of [he]2s22p), which has a total of 6 valence electrons. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12.
It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule : Li2, be2, b2, c2, n2, o2, f2, and ne2. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for:(i) be2(ii) b2 and.
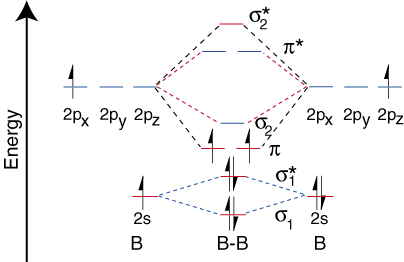
Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of. We have three valence electrons from each b atom, so b₂ will have six valence electrons. Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions.
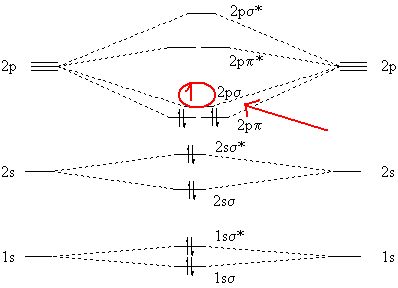
For information about the more traditional molecular structure. The molecular orbital electronic configuration, magnetic property: It appears your instructor either didn't account for the. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table:
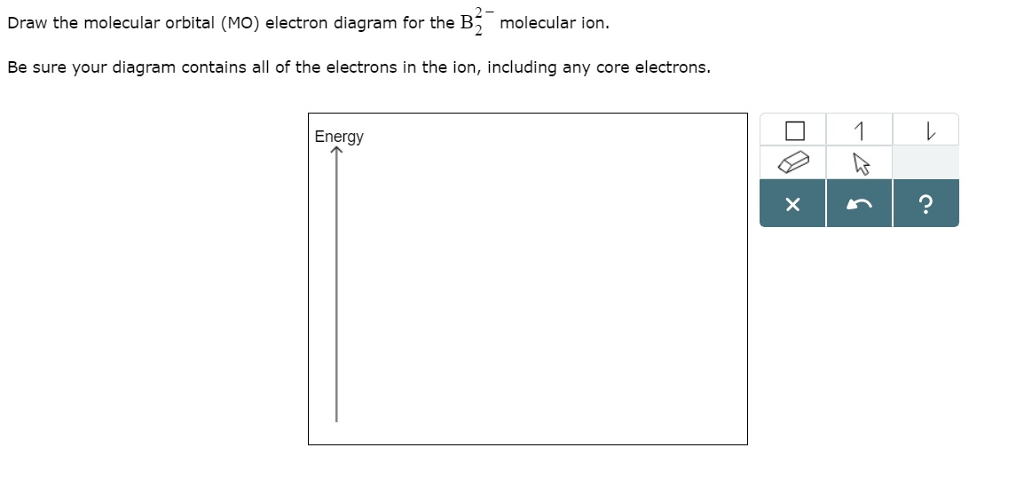
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons energy. 502 x 496 png 50 кб. Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. Molecular orbital theory (mo theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule.
The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a way of looking at the structure of a molecule by using molecular orbitals that belong to the molecule the energy diagrams are shown in figure 2. The number of unpaired electrons in the b2 molecule is _____. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons energy.
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals.
In molecules, atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals which surround the molecule. • the following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. We can ignore the #1s# orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. = 0 unstable diamagnetic σ1∗s.
Since bond order is zero, be2 molecule does not exist. Principles of molecular orbital theory. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories if you can understand the foundation and skeleton of the diagram specific to that molecule, then it will be easier and faster for you to draw it. When two hydrogen atoms are at an infinite distance from each other, there is no interaction between them and therefore, the enthalpy of the system is.
• because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. This video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the mo diagrams for b2. Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations. We use the pauli exclusion principle and hund's rule to fill the orbitals in an aufbau process.
960 x 720 jpeg 91 кб. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. The bh3 molecule exists in the gas phase, but dimerizes to b2h6. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that he2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table:
The orbital correlation diagram for diboron, however, is not generally applicable for all homonuclear diatomic molecules. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for b2. Which of the following options correctly interpret this diagram?