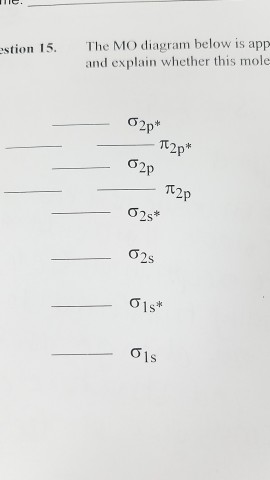Mo Diagram Of B2
Between n2 and o2, the order of the orbitals changes.
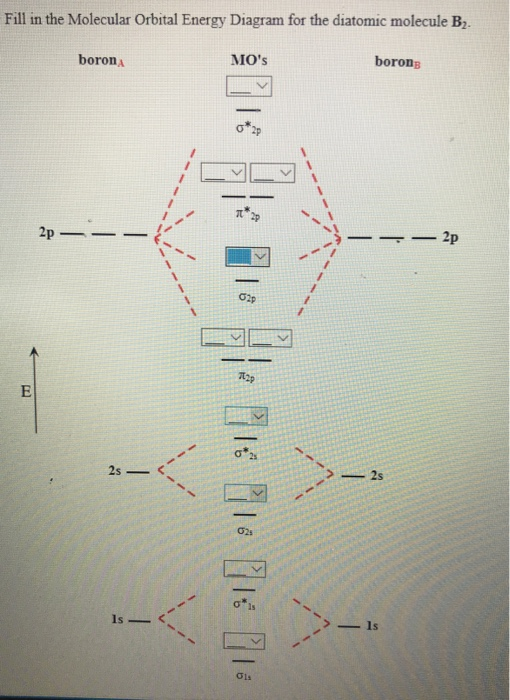
Mo diagram of b2. The 2πg orbiatls are nonbonding because the c 2px,y atomic orbitals are πu. Level diagram for b2,c2 and n2 fsc chemistry book1, ch 6, lec 24: And modified it to be o2 2+ how you basically do these questions is by first drawing the empty ao and mo, then counting the amount of electrons you should have for each atom & filling according to aufbau principle & hund's rule. They're not as intimidating as they may seem.
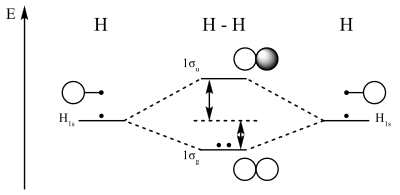
Molecular orbital structures do he2, he2(+), he2(2+) exist, stable? For h2 we have two aos, χ1 and χ2 each mo, φ, will be approximated: Mo diagrams look like this: • explain how to determine the relative phases of the atomic orbitals used to construct the molecular orbitals for molecules with more than two atoms.
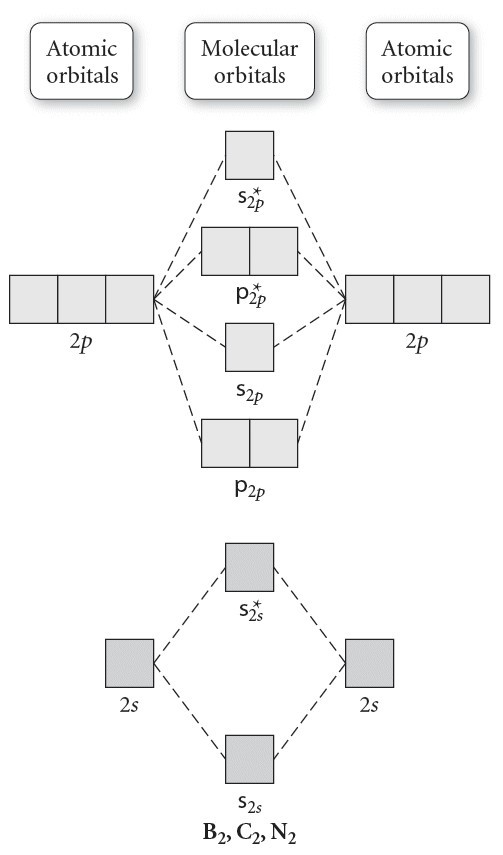
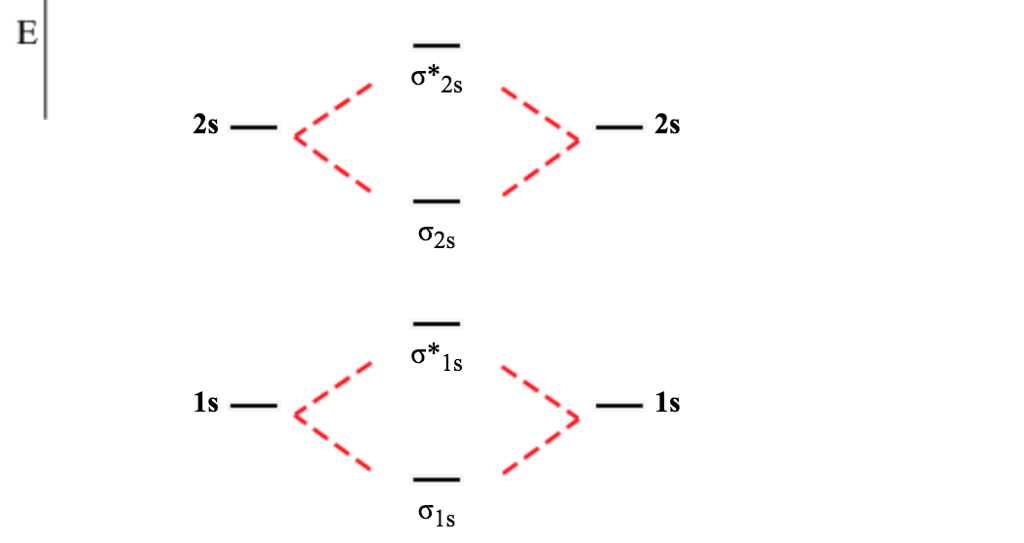
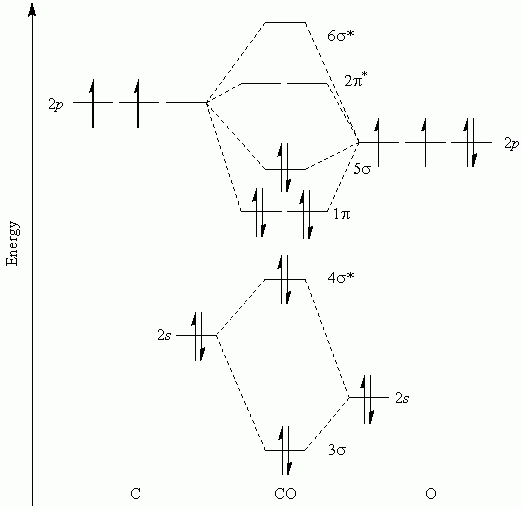
This shows the mo diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. Note that by convention we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how mo diagrams are. Atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals of a molecule can be shown in a molecular orbital diagram. For $\ce{n2}$ the orbitals in increasing energy are
- Msd 7al 3 Wiring Diagram
- Chevy S10 Body Parts Diagram
- Label The Following Reaction Energy Diagram For A Catalyzed And An Uncatalyzed Process
The diagram below shows the atomic orbitals, aos, on a pair of adjacent atoms interacting with each other. I have been taught that the mo diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. The mo diagram for co2 is more complicated than the diagram for b2. Mos are approximated as linear combinations of atomic orbitals.
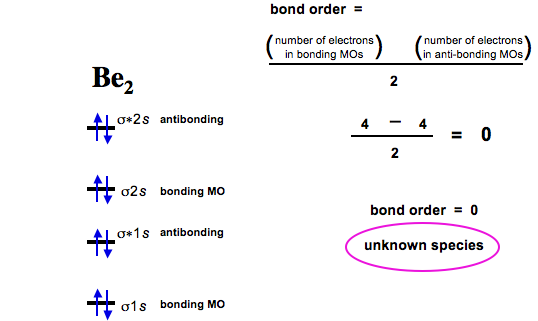
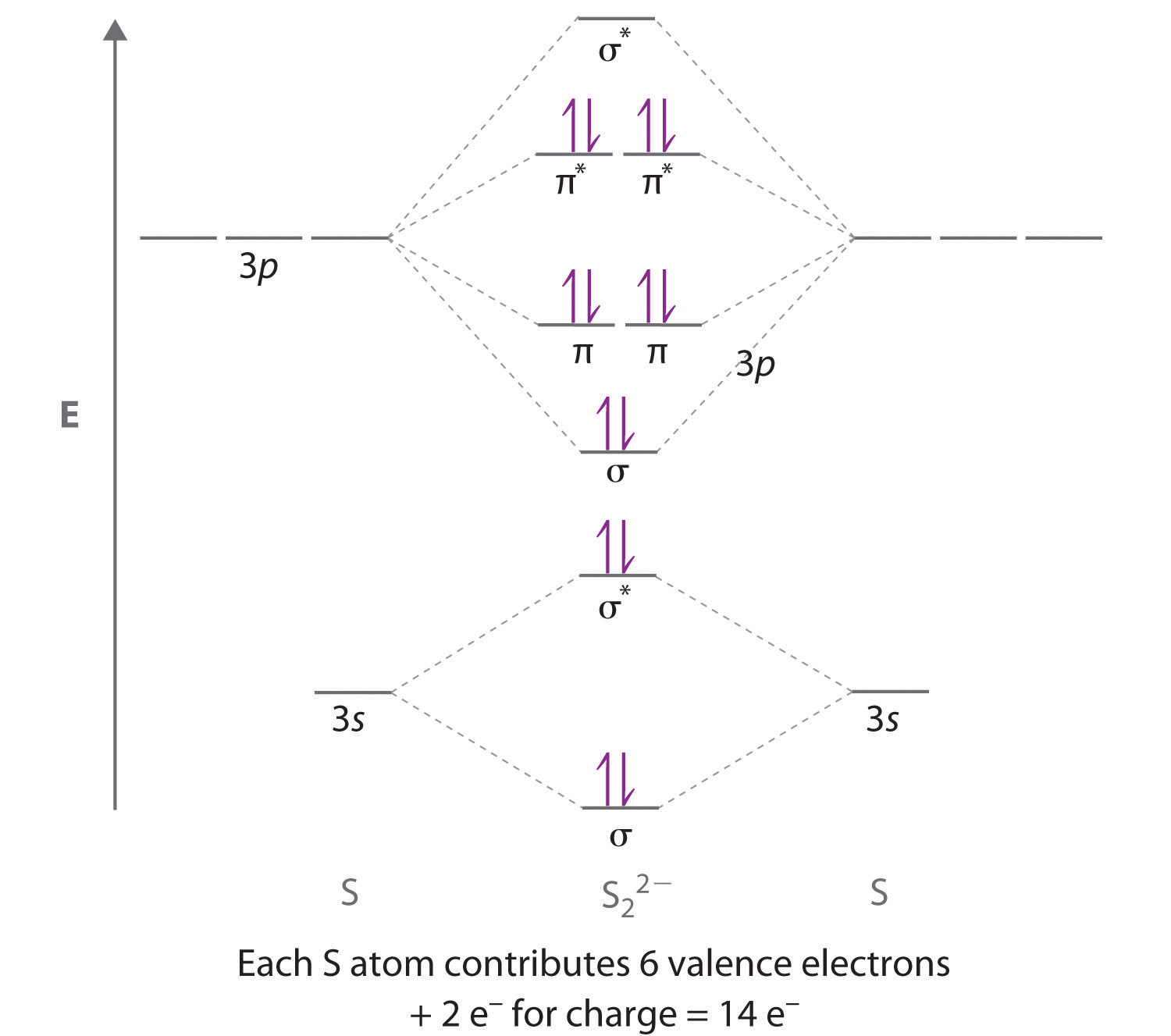
Mo diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram for short is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of dihydrogen mo diagram. My book shows the mo diagram for the bridging interactions in #b_2h_6#, but it neglects to include the influence of the terminal hydrogen orbital interactions with the boron orbitals (it does mention it, but does not incorporate the information into the images). Mot diagrams for be2, b2 and n2. The co2 molecule is defined as l5ung on the z axis.
The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. And draw in the mo energy levels and mos: (adapted from bc open textbooks). Derive the symmetries of the valence orbitals and symmetries for the ligand group orbitals (lgos) to derive a qualitative mo diagram for bf3.
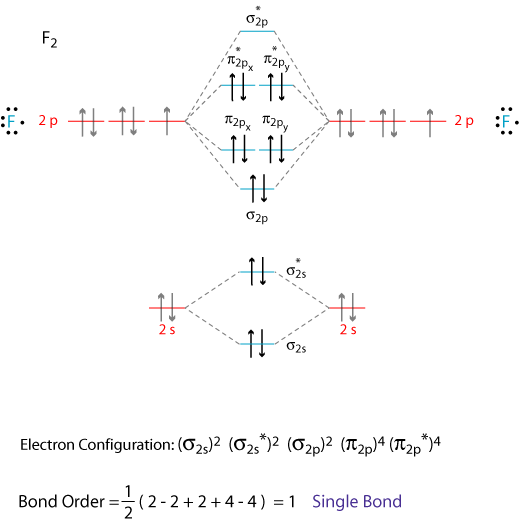
• use an mo diagram to predict the number of unpaired electrons in a molecule. B2g b3g b1u b1u 6. Below is an mo energy level diagram for the diatomic entities of #b, c# and #n#. The f 2s is nonbonding.
Φ = c1χ1 + c2χ2 by symmetry, the electrons have equal probability of being near either h c12 = c22 ∴ c1 = ±c2. I modified the picture from this post: The follwing diagram fails to label orbital symmetries but the lgo 2px,y particpate in the formation of π double bonds. Combine aos from central atom with those group orbitals of same symmetry and similar energy to make the mo diagram.
For now, we're only covering homonuclear mo diagrams which involve the diatomic molecules composed of the same the molecules we'll be dealing with in mo diagrams are all homonuclear moleculars e.g `b_2`, `o_2`, etc. Mo diagram is constructed by allowing interactions between orbitals of the same symmetry. We will predict their bond order and see how the energies of the different orbitals change. We will also compare our predictions to experimental evidence.
(a) the mo diagram for water (bent) is found in a class handout. Mo diagram for hf the ao energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. There will be nothing to attract the nuclei together and the mo is (said to be) antibonding: A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular.
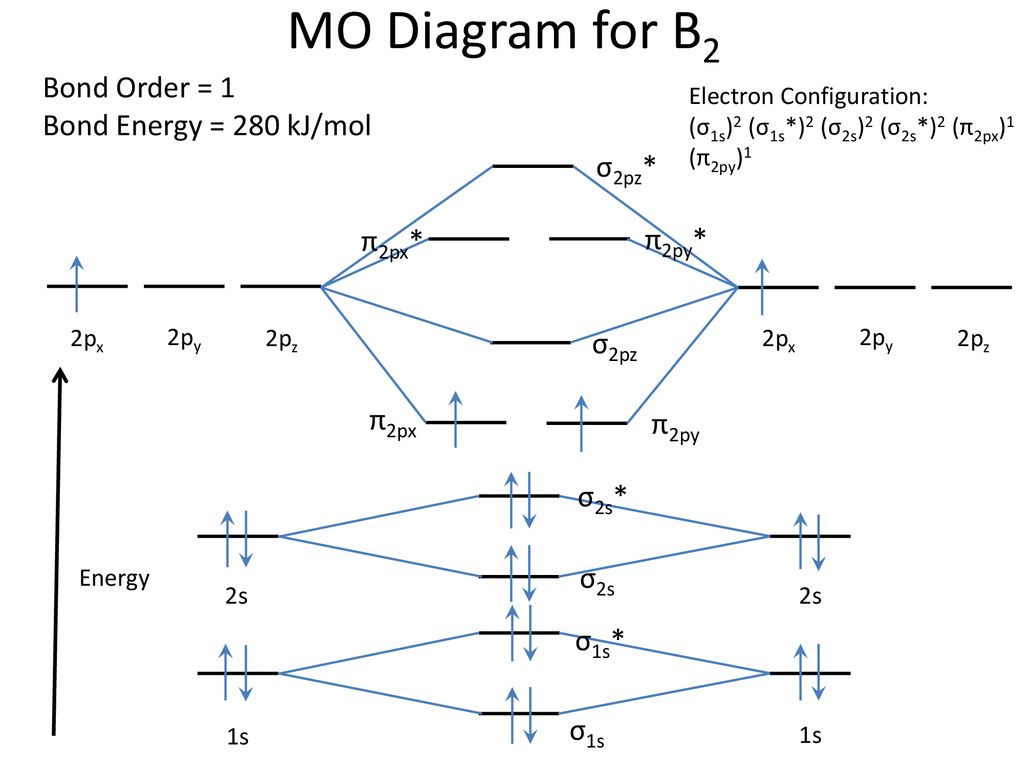
As discussed in class the mo diagram for b2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. O for example the h2o diagram can be used as a basis for all molecules of the form ah2 where a is a main • a socrative quiz o why is the 2su+ (goes to 2b1) mo stabilised (go down in energy)? Subscribe to our youtube channel. We fill the boxes following the aufbau principle and hund's rule until we have added 14 electrons.
21) the mo diagram below is appropriate for b2. What's the mot diagram of o2 +2 ion? [this should be ok qualitatively since the strong geometric preference of 2a1 typically controls the geometry in these ah2 molecules.]