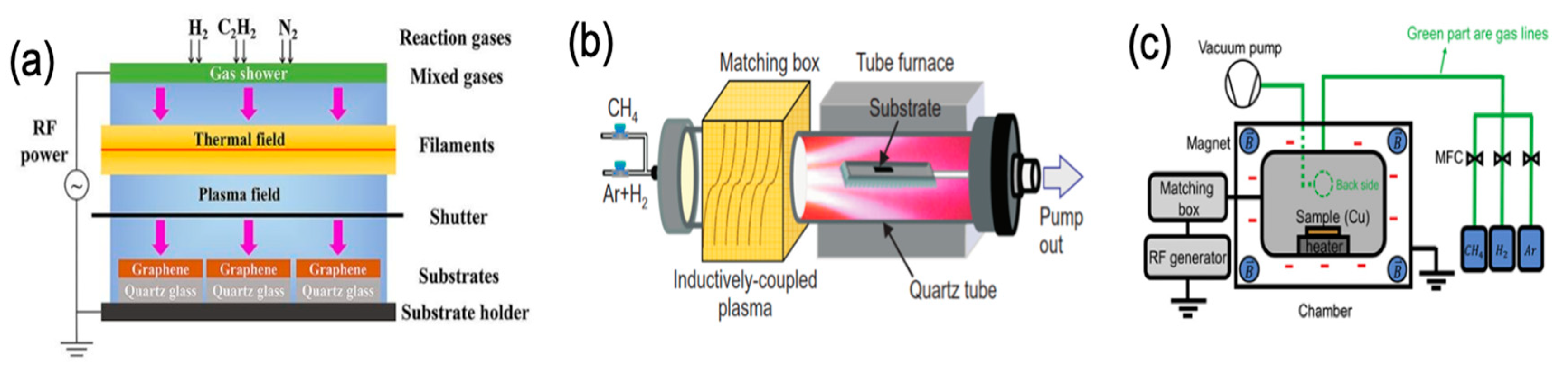
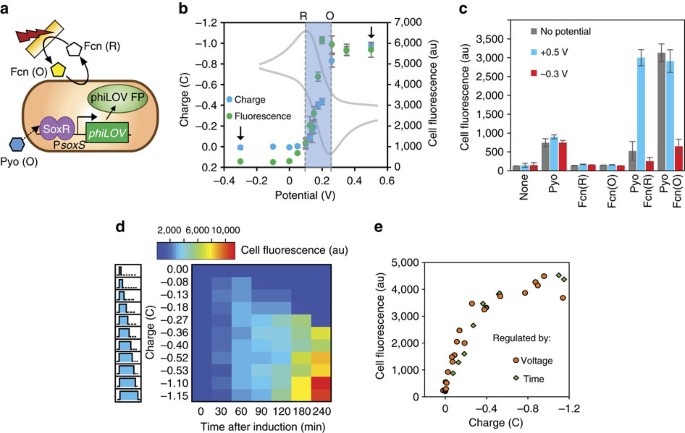
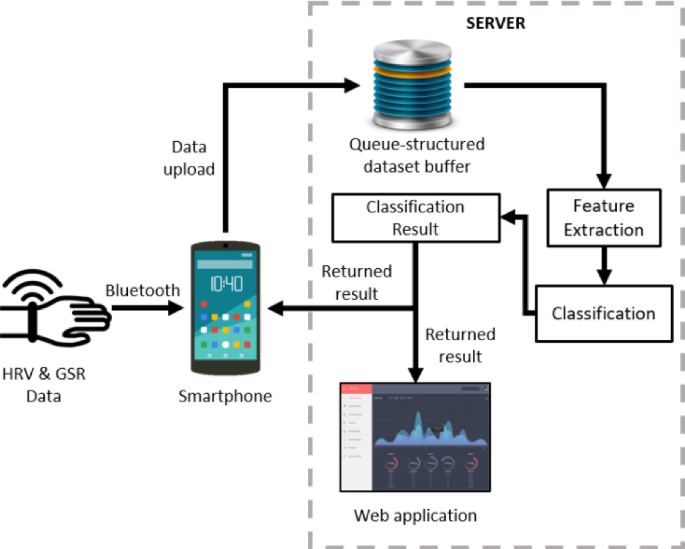
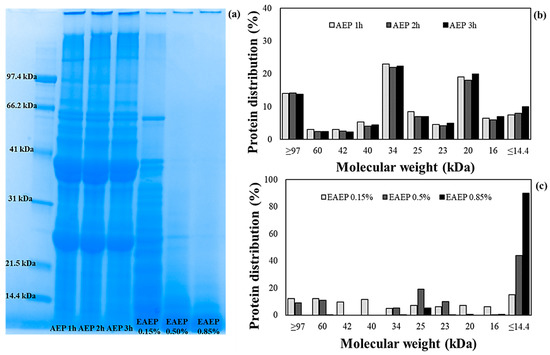
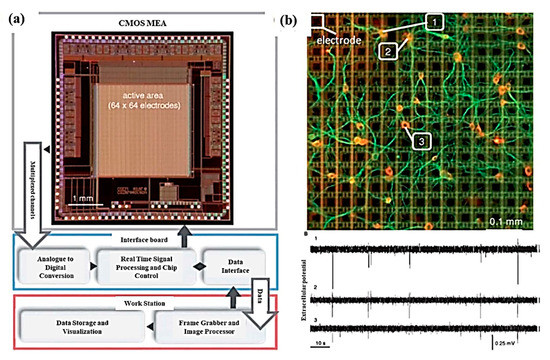
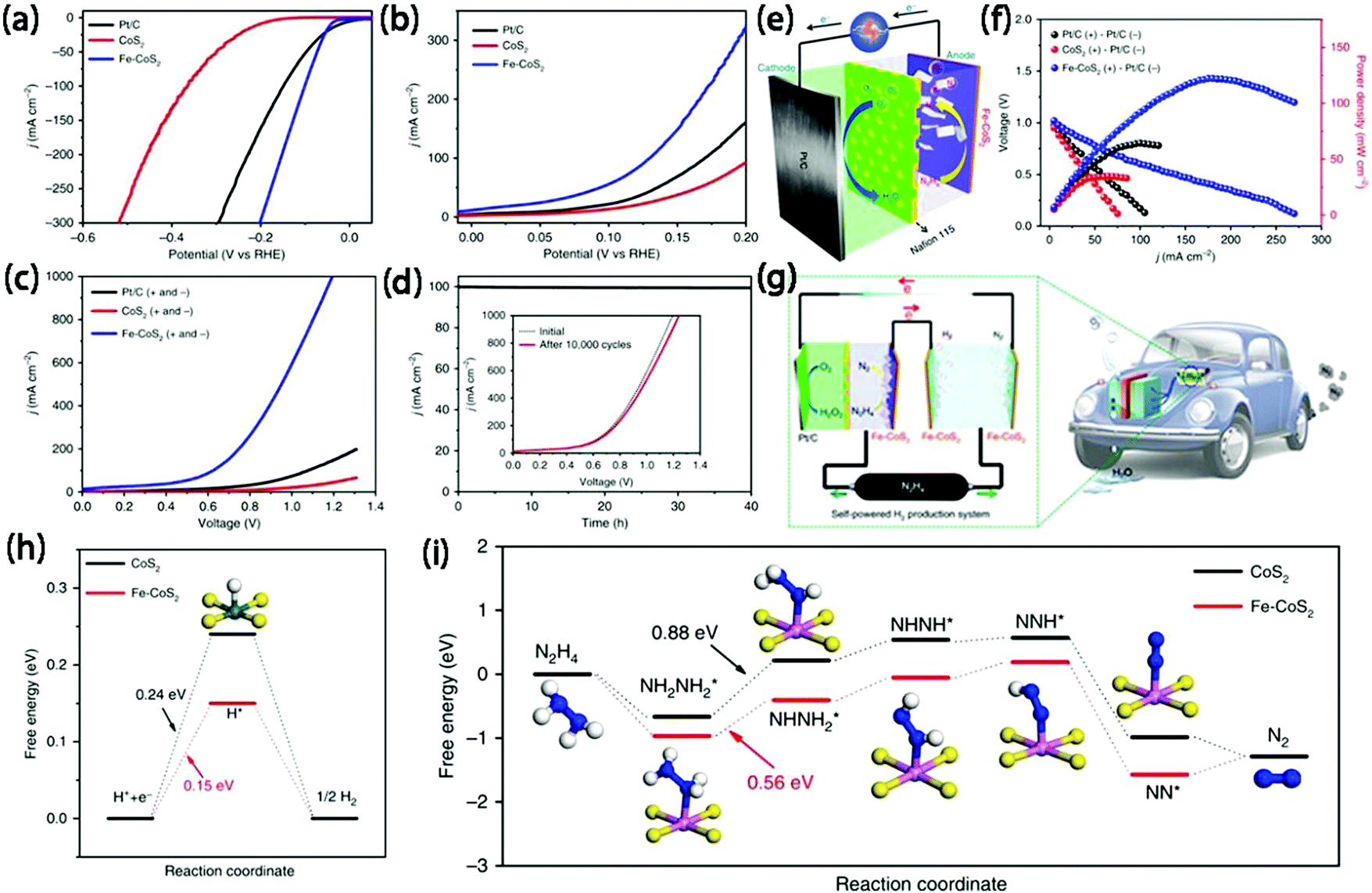
Label The Diagram According To The Components And Processes Of A Voltaic Cell
To avoid this, cancel and sign in to youtube on your computer.
Label the diagram according to the components and processes of a voltaic cell. For detailed discussions on different cells like a galvanic cell or voltaic cell, or about the gibbs energy change spontaneity of a process visit byju's. The voltmeter shows a reading. Which process occurs in the structures that are labeled x? Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) diagram.
Anode, cathode, salt bridge, wire, and two reaction vessels. The redox reaction in a galvanic cell is a spontaneous reaction. A second type of electrochemical cell is the electrolytic cell. Electrochemical cells are devices that convert between chemical and electrical energy.
This additional layer which surrounds the cell membrane is necessary for offering the requisite protection to the plants. In order for the transfer of electrons in a redox reaction to produce an electric current and be useful, the electrons are made to each electrode is connected to the voltmeter by clips and wires. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Voltaic cells, or electrochemical cells, make use of the electrons that are transferred from the species that releases electrons and undergoes oxidation to the species label the diagram according to the components and processes of a voltaic cell.
The chemical reactions that take place inside the cell cause the flow of electrons the flow of electrons from the zinc plate to the copper plate produces an electric current. Embedded proteins and peripheral proteins that function in providing shape and allowing the movement of particles in and. Voltaic cell is a device in which a redox reaction spontaneously occurs and produces an electric current. Glycolysis, krebs cycle and electron transport chain.
Voltaic cells device that changes chemical energy into electrical energydevice that changes chemical energy into electrical energy involves a redox reactioninvolves a redox reaction reducing agent transfers electrons to the oxidizing agentreducing presentation on theme: A half cell is one half of the voltaic cell and consists of an electrode and an electrolyte. A voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that uses a spontaneous redox reaction to produce electrical energy. The anode is always placed on.
In the case of the plant cells, besides the cell membrane, there is also an outer thick layer that is known as the cell wall. Cells are microscopic building blocks of unicellular and multicellular living organisms. 14.2a voltaic cells basic function. Another example of a voltaic cell is the lead acid battery, most commonly used as car batteries.
To determine the overall voltage of a particular voltaic cell, simply combine the voltages of the oxidation and reduction half reactions. According to my notes and many sources on the internet, electrons and cations both travel from the anode (a in the image) to the cathode (b in the image). A dry cell has a voltage of about 1.56 v. Nearly all voltaic cells have the same basic components:
Figure 2 the layout of this cell is the same as a voltaic cell except the anode is now positive and the cathode negative. During operation of a voltaic cell, the zinc late is at a lower potential with respect of the solution film adjacent to it as shown in the figure below. When drawing a cell diagram, we follow the following conventions. A voltaic cell (also known as a galvanic cell) is an electrochemical cell that uses spontaneous redox reactions to generate electricity.
Voltaic or galvanic cells and electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells. Electrodes and voltage of galvanic cell. Not understood how they worked until 100 years after they were invented. As described above, a voltaic cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Structurally, it consists of a phospholipid bilayer along with two types of proteins viz. Given here is a simple voltaic cell diagram. The nucleus and the chloroplast have been labelled the wrong way round. Volta's original batteries, which he called voltaic piles, were made of several in a voltaic cell, zinc ions dissolve at the anode, and copper ions precipitate onto the cathode.
In this way, unlike a galvanic cell, which produces current from a redox. A simple voltaic cell is made by immersing one zinc plate and one copper plate inside a water diluted sulfuric acid solution. The wire allows the electrons freed during oxidation to travel from the anode to the cathode, where they are consumed. These use lead (pb) as the anode and lead.
Cell membrane offers shape and rigidity to the cell. A voltaic cell is a device which converts chemical energy to electrical energy. While common and useful, dry cells have relatively short lifetimes and contain acidic components. The designs vary, but the basic idea is the same.
Plant cells do not contain mitochondria. As you can see in the diagram on screen, if you connect a wire to both. This video shows how to sketch a diagram of a voltaic cell and explains what is going on during the discharge of the cell. The sodium ions migrate toward the cathode, where they are reduced to sodium metal.
The phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water attracting) heads and two hydrophobic (water repelling) tails. As cations are taken out of solution by this process additional metal atoms on the anode are oxidized to fresh cations. What is wrong with this diagram of a plant cell? A useful shorthand notation describes the components of a voltaic cell.
A voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that produces electrical energy using a chemical reaction. A voltaic cell is a cell which converts chemical energy of oxidants and reductants into electrical an example of a voltaic cell; Videos you watch may be added to the tv's watch history and influence tv recommendations. Calculate cell potential e cellodraw a diagram of the galvanic cell for the reaction and label.
A combined name given to anode and cathode where oxidation and reduction. After watching the video, please complete the diagram below to identify the key components in a voltmeter is used to measure the potential, or voltage, of an electrochemical cell. The two electrolytes are separated by a porous boundary. Similarly, chloride ions migrate to the anode and are oxidized to form chlorine gas.
A galvanic or voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The electrons then flow from the copper strip to the zinc strip, such that copper is now oxidized, and zinc is reduced.