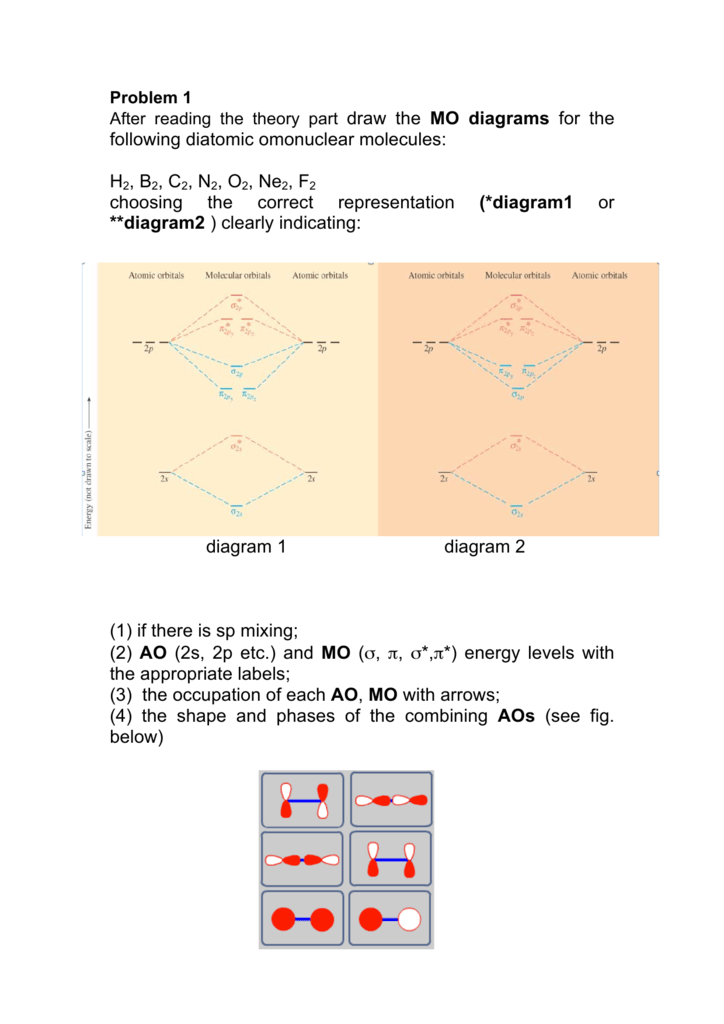
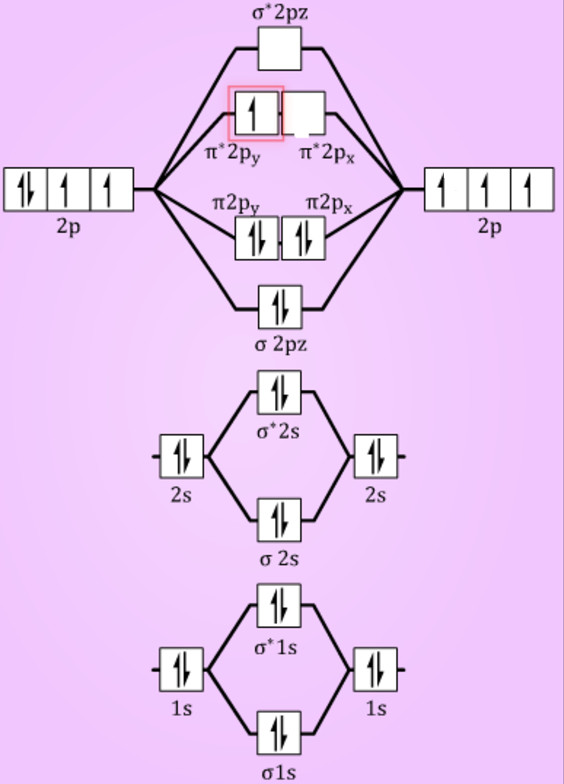
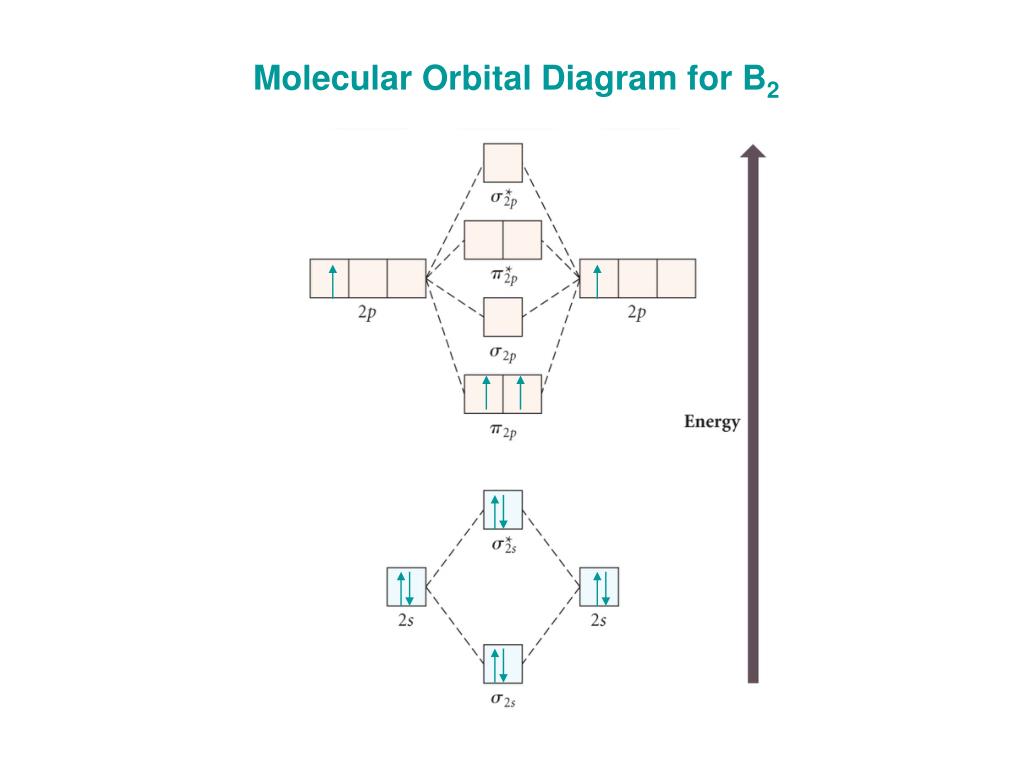
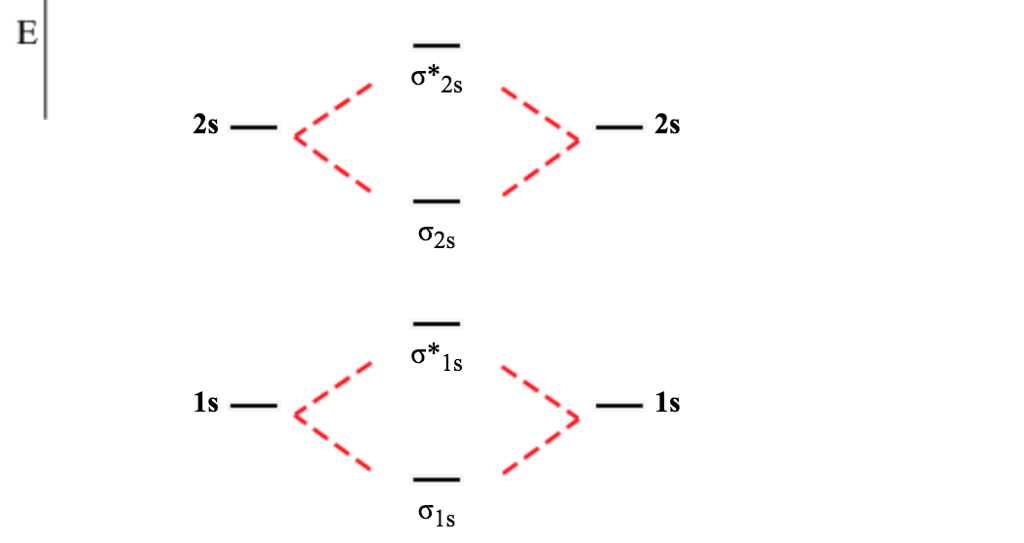
B2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
He2 ∗ σ1s σ1s ∗ σ1s c.
B2 molecular orbital diagram. Why is it that the number of atomic orbitals used to generate molecular orbitals is equal to the number of molecular. Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations. Valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory. Eight electrons from each oxygen atom add up to 16 electrons in the o 2 molecule.
= 2 stable paramagnetic π ∗2p ∗ σ2p π 2p σ1s. In the formation of b2 molecule, three. Determine how many valence electrons you have on each atom (you can ignore the core electrons as core orbitals contribute little to molecular for example consider b2 (each atom has an electron configuration of [he]2s22p), which has a total of 6 valence electrons. This video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the mo diagrams for b2.
365 molecular orbital diagram key draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. The molecular orbital diagram for $\ce{o2}$ says that the sigma 2p bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than the pi 2p bonding molecular orbital. What will be the molecular orbital diagram for nitrite ion? The orbital correlation diagram for diboron, however, is not generally applicable for all homonuclear diatomic molecules.
- 2014 Silverado Stereo Wiring Harness
- 2000 F250 Fuse Panel
- Bending Moment Diagram For Triangular Load
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons energy. Last time you learned how to construct molecule orbital diagrams for simple molecules based on the symmetry of the atomic orbitals. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy.
B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: 502 x 496 png 50 кб. We have three valence electrons from each b atom, so b₂ will have six valence electrons.
Mo energy diagram for o 2. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule we draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in figure 12. For information about the more traditional molecular structure.
For example, to give you a glimpse at where we are headed. • because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram. Total # of bonding electrons.
A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. Li2, be2, b2, c2, n2, o2, f2, and ne2. Molecular orbital diagram of b2. = 1 stable diamagnetic b.
It turns out that only when the bond lengths are relatively short (as in b2, c2, and n2) can. Molecular orbital theory provides an alternative model to valence bond theory that better describes the electron behaviour and physical/chemical properties of. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f. Determine whether each is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
Since bond order is zero, be2 molecule does not exist. The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a way of looking at the structure of a molecule by using molecular orbitals that belong to the molecule as a figure 4. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons energy. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3.
Valence bond theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that he2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in latex by means of the package modiagram.
Draw a molecular orbital diagram and determine the bond order expected for the molecule b2. (b) the shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for mo1 and. The bh3 molecule exists in the gas phase, but dimerizes to b2h6. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules.
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. The molecular orbital electronic configuration, magnetic property: Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. We use the pauli exclusion principle and hund's rule to fill the orbitals in an aufbau process.
Molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms, that is, in terms of orbitals, orbital diagrams, and electron configurations. How does the directional nature of orbitals affect the bond strength? (c) which of the molecular orbitals in bc do not have a planar node along the. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for:(i) be2(ii) b2 and.
Is h2 a viable molecule for the molecular orbital theory? | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule :