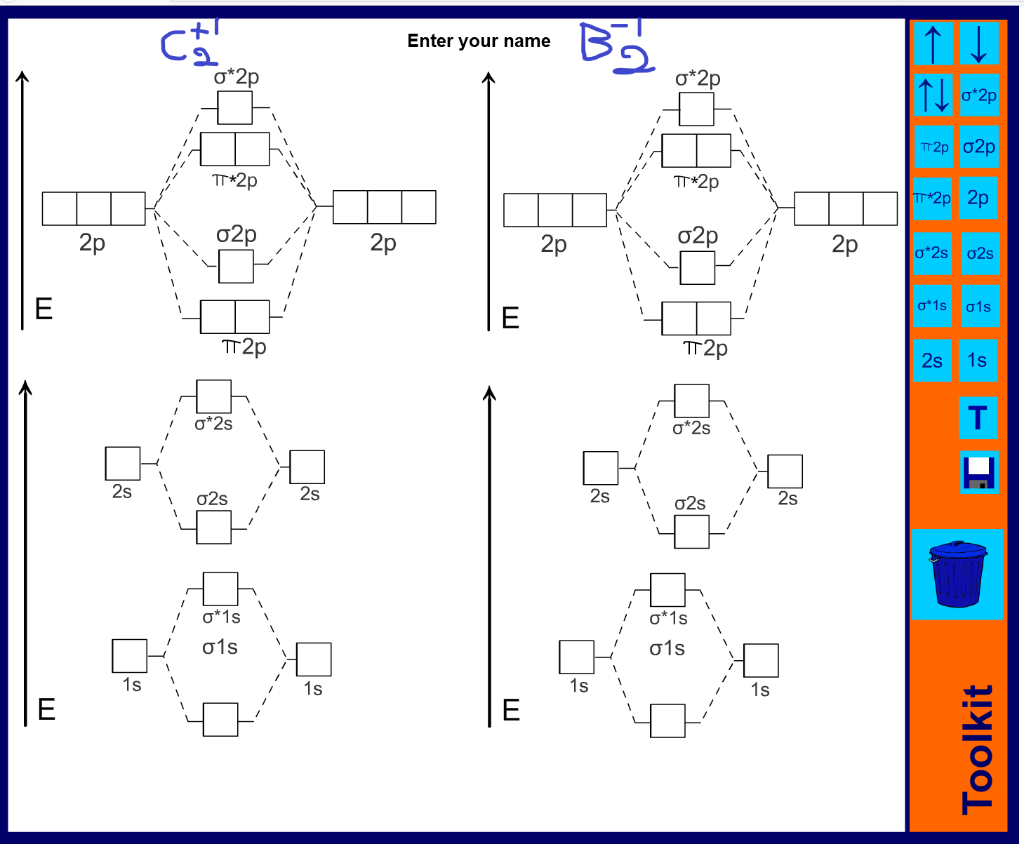
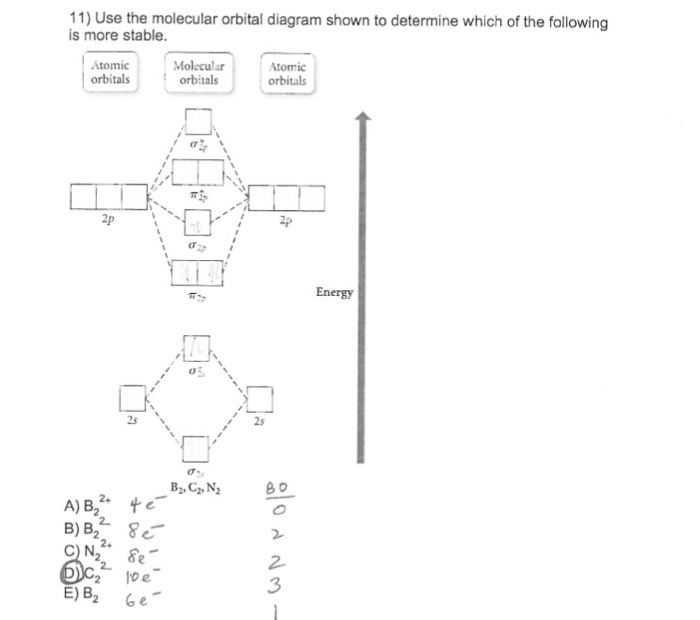
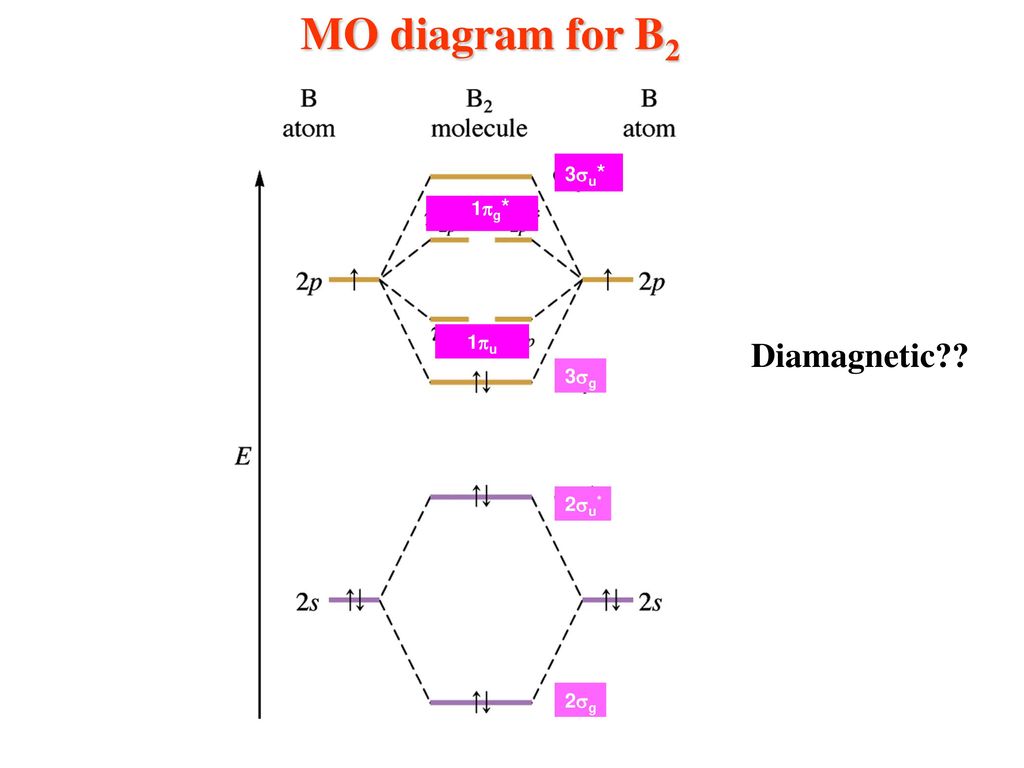
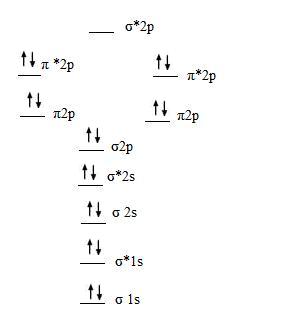B2 Molecular Orbital Configuration
On the other hand, molecular orbital theory visions the electrons of a covalent bond to be delocalized over the entire molecule.
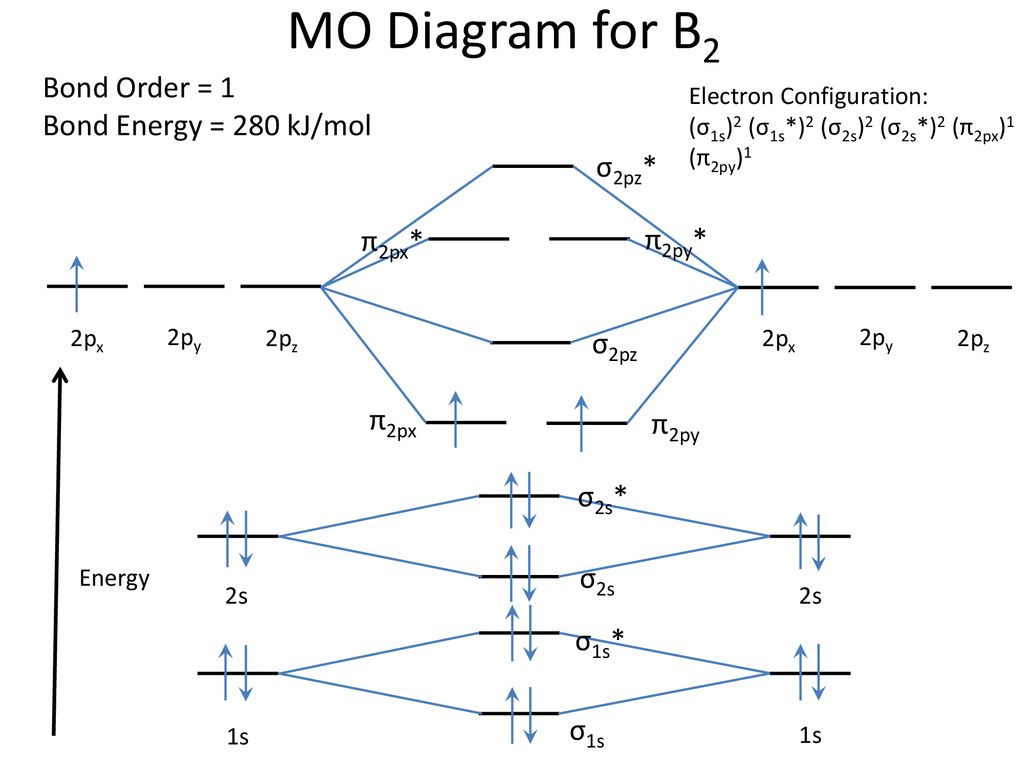
B2 molecular orbital configuration. 1) stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons. This molecular orbital model can be used to explain why he2 molecules don't exist. • electronic configuration of oxygen. Each oxygen atom has 8 electrons, hence in o2 the molecular orbital energy level diagram of oxygen molecule is given as follows :
The molecular orbital configuration of molecule is as follows. Second, the atomic orbital energies must be similar. For example, in h2 the two bonding electrons reside in a a orbital, and. Thus we may construct a molecular orbital energy level diagram, similar to the one used to build up the electronic configurations of the atoms in the fig.
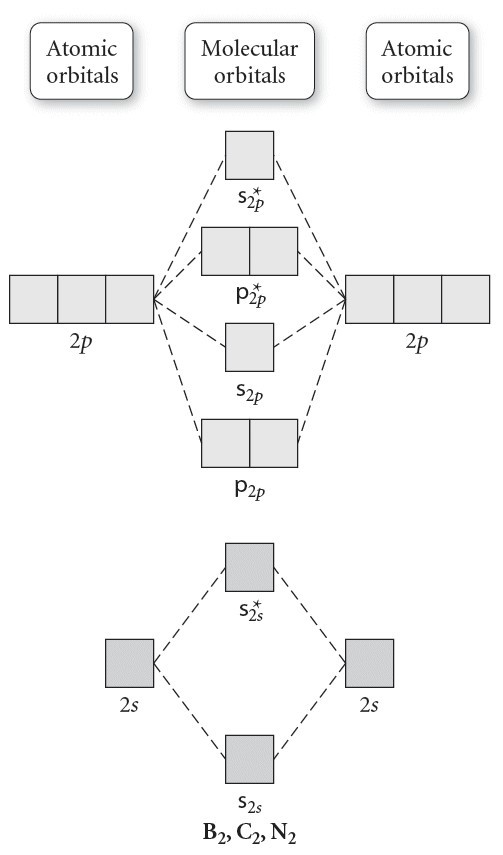
The molecular orbital electronic configuration, magnetic property: • third, the distance between the atoms must be short enough to provide good overlap of the orbitals form molecular orbitals. In this case, the only occupied orbital the previous model, for example is not useful at all in describing diatomic molecules like b2, c2, n2 and o2. • because the energy of the two electrons.
- Engine Start Button Wiring Diagram
- 2006 Pt Cruiser Under Hood Fuse Box Diagram
- Toro Riding Mower Belt Diagram
Relationship between electronic configuration and molecular behaviour : The electronic configuration of oxygen (z=8) in the ground state is 1s22s22p4. The more common one involves the formation of hybrid orbitals, which then form the molecular orbitals. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region.
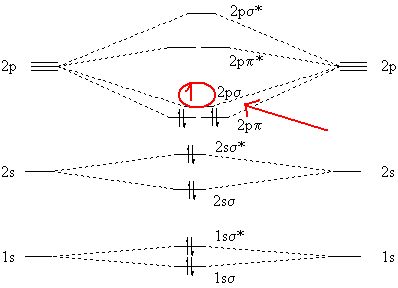
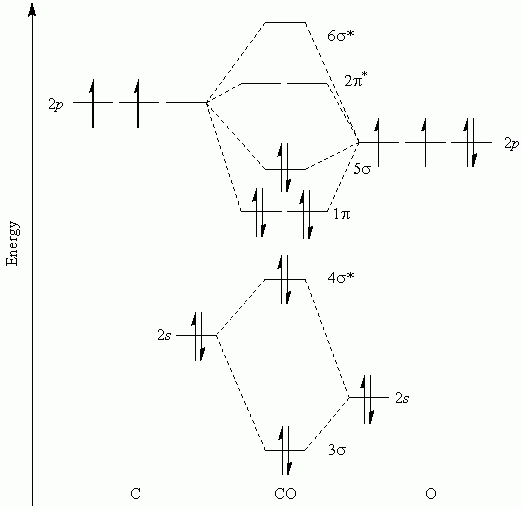
A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. Which of the following is the correct electron configuration for c2? It is defined as the number of covalent bonds between the two combining atoms of a molecule. The electron configuration is the molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that he2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons.
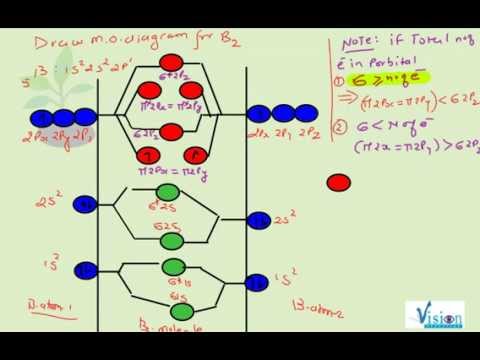
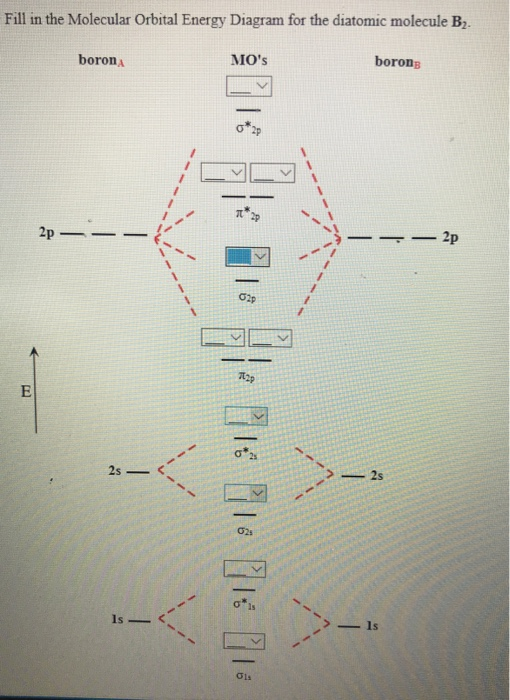
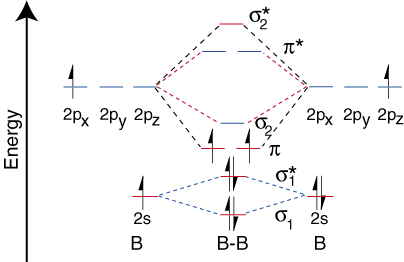
The molecular electronic configuration can be named using molecular orbitals just as we saw in individual atoms. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. Electron configurations for these molecules lead to a guideline for molecular orbital configurations based on average nuclear charge, average. B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms.
7:14 engineering chemistry 671 просмотр. • the following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. Examples of multiple choice questions. • for example, when two hydrogen atoms bond, a σ1s (bonding) molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s* (antibonding) molecular orbital.
After writing the molecular orbital configuration, the vector sums are obtained. In the formation of b2 molecule, three. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Molecular orbital energy level diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules showing the correlation of the molecular orbitals with the atomic.
(b) when one considers the molecular orbitals resulting from the overlap of any two specific atomic orbitals, the bonding orbitals are always lower in energy than. Valence bond theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. According to molecular orbital theory individual atoms combine to form molecular orbitals, as the electrons of an atom are present in various atomic orbitals and are certain rules are to be followed while filling up molecular orbitals with electrons in order to write correct molecular configurations Although the molecular orbital theory is computationally demanding, the principles on which it is based are similar to those we used to determine electron configurations for atoms.
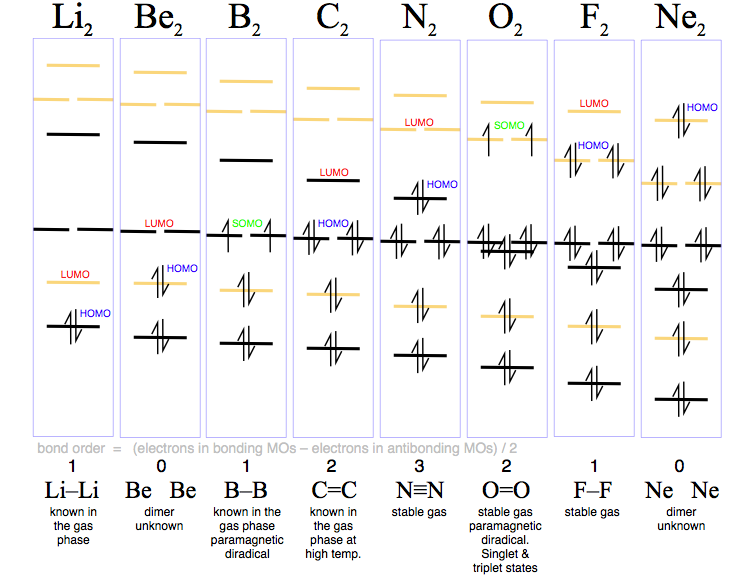
If the probabilities of finding the electron in atomic orbitals ψ a and ψ b are 0.25 and 0.75, respectively, what is the lcaowavefunction for the from the orbital level diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules in the text we predict the configuration n2 + (9 electrons) :1σ 2. Combining a pair of helium atoms with 1s2 electron configurations would produce a experiments have shown that o2 and f2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but b2, c2, and n2 are best described by. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f.
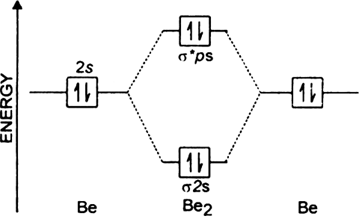
In a molecule, there are total 16 electrons. Posted 4 years ago by saroj bhatia. Since bond order is zero, be2 molecule does not exist. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry.
3) if nb = na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of. Bond order 2nb −na =28−4 =2 thus, oxygen molecule has. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for b₂ and other diatomic molecules from row 2 elements of the. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc.
For this, we need a more complete. The key difference is that in molecular orbitals, the electrons are allowed to interact with more than one atomic nucleus at a time. A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the h2 molecule are in the σ1s bonding orbital; 8:42 professor dave explains 1 817 820 просмотров.
Relationship between electronic configuration and molecular behaviour. There are two different explanations, which lead to the same conclusion, available.