Trapezoidal Distributed Load Shear And Moment Diagram
This is the currently selected item.
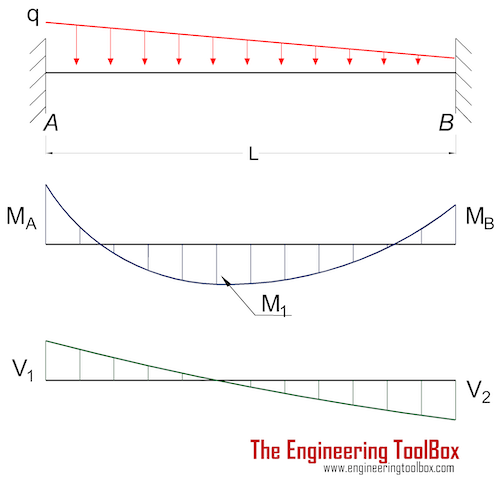
Trapezoidal distributed load shear and moment diagram. Therefore, the distributed load q(x) is statically equivalent to a concentrated load of magnitude q placed at the centroid of the area under the q(x) diagram. In simply supported beams, it occurs at mid span because the bending moment at the supports obviously will be zero hence the positive bending moment occurs in the mid span. Problem 414 cantilever beam carrying the load shown in fig. Draw the shear and bending moment diagram for.
Points of zero shear (v = 0) — for moment. I've been attempting this fundamental shear force diagram problem for several days, but can't seem to get the correct result. Calculate the deflection of steel, wood and other materials. Ø consider the beam shown below subjected to an arbitrary loading.
American institute of steel construction. To construct a moment diagram. For maximum shear force to obtain we ought to multiply load and distance and it surely occurs at the fixed end (w×l). Solving distributed loads and triangular loads by spoonfeedme.
- 2019 Chevy Silverado Fuse Box Location
- 2012 Jetta Under Hood Fuse Box Diagram
- Yamaha Outboard Gauges Wiring Diagram
I'm trying to calculate the shear force diagram in i'd appreciate if someone could explain intensity loads for situations similar to above and where i went wrong in my calculations. Trapezoid is generally form with the combination of uniformly distributed load (udl) and triangular. Shear and moment diagrams are a statics tool that engineers create to determine the internal shear force and moments at all locations within an object. The distributed loads can be arranged so that they are uniformly distributed loads (udl), triangular distributed loads or trapezoidal distributed loads.
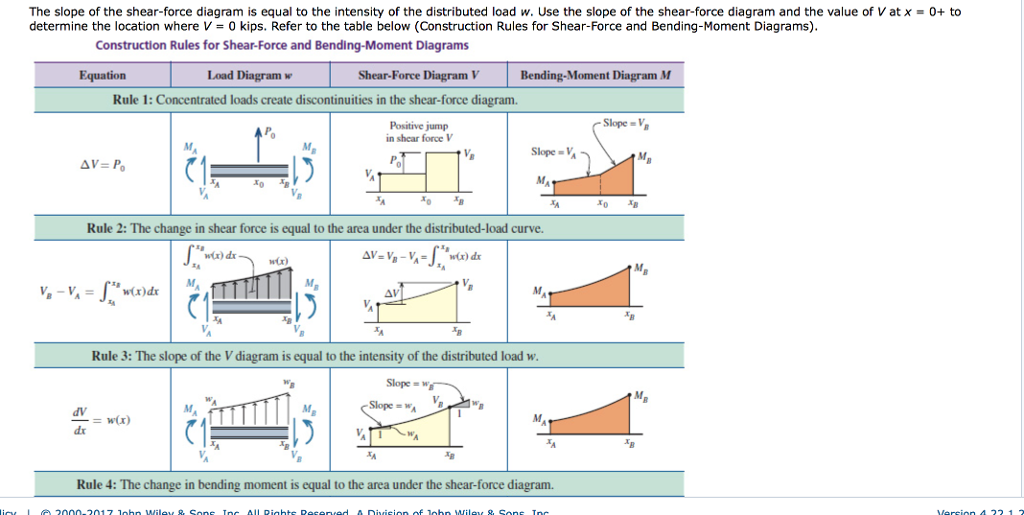
Trapezoidal load is that which is acting on the span length in the form of trapezoid. For a distributed load, q, the forces can be summed in the y direction to give for beams with several different loads, it is often easier to solve for the shear and moment diagrams for the individual loads and then combine them to find the total. For design purposes, it is common to assume the soil pressure is linearly distributed. The slope of the line is equal to the value of the distributed load.
Constructing shear and moment diagrams areas and centroids. Bending moment diagram (bmd) shear force diagram (sfd) axial force diagram. For the distributed load to show select: Axial, shear and bending diagrams 27:
Moment diagram shear diagram shear and moment diagrams uniformly distributed load cantilever beam uniformly varying load trapezoidal load. Relationship between shear force and distributed loads. Input initial boundary value, final boundary value and length of interval. Trapezoidal method is based on the principle that the area under the curve which is to be calculated is divided into number of small segments.
Therefore, a horizontal line connects the end points. Walk through an example using the trapezoid rule, then try a couple of practice problems on your own. Displayà show load assign à frame/cable/tendon on the pop up window click make sure that show joint loads with span loads and show span loading values are selected then press ok. ◀ ← video lecture 16 of 83 → ▶.
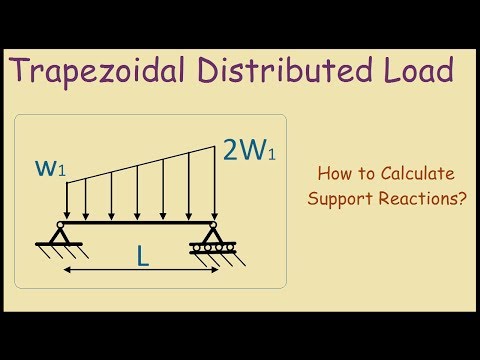
Parallelogram law and triangle 25: How to calculate the support reactions of a beam under a trapezoidal distributed load. 3 basic bending moment diagram. The moment reaction at b is negative.
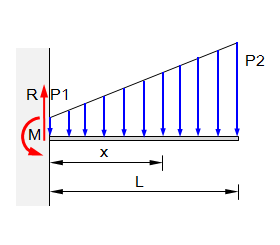
Ø we will assume that distributed loadings will be positive shear and moment diagrams. Relations between distributed loads and internal shear forces and bending moments. Start and stop of distributed loads. Introduction to axial & shear forces and bending moments 26:
Shear and bending moment diagrams are analytical tools used in conjunction with structural analysis to help perform structural design by determining the value of shear force and bending moment at a given point of a structural element such as a beam. 5 uniformly distributed load (udl). Also, draw shear and moment diagrams, specifying values at all change of loading positions and at points of zero. It can e seen that for a uniformly varying distributed load, the shearing force diagram consists of a series of parabolic curves and the bending moment diagram is made up of cubic discontinuities occurring at.
The function of a footing or a foundation is to transmit the load of the structure to the. Uniformly distributed load is usually represented by w and is pronounced as intensity of udl over the beam, slab etc. Using the principle of superposition a trapezoidal load on a beam can. Equals the area under the load distribution diagram.
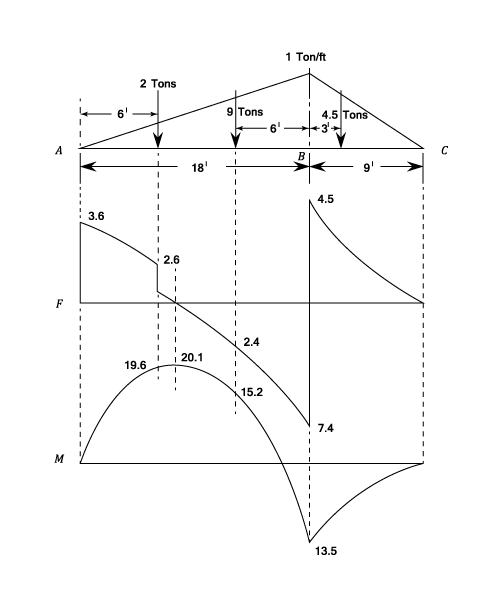
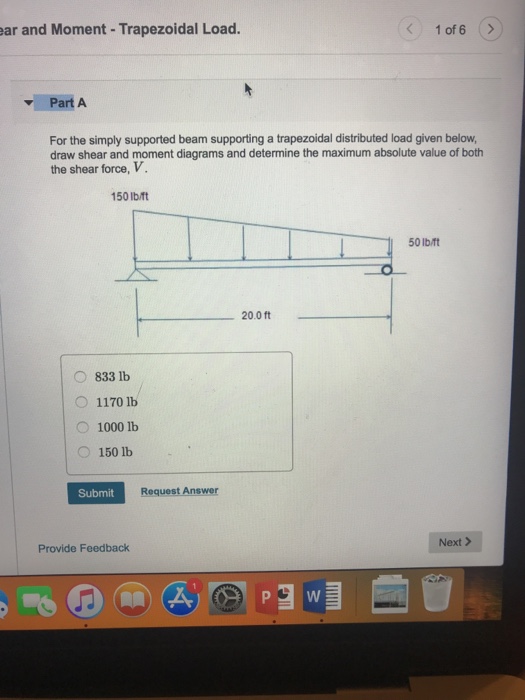
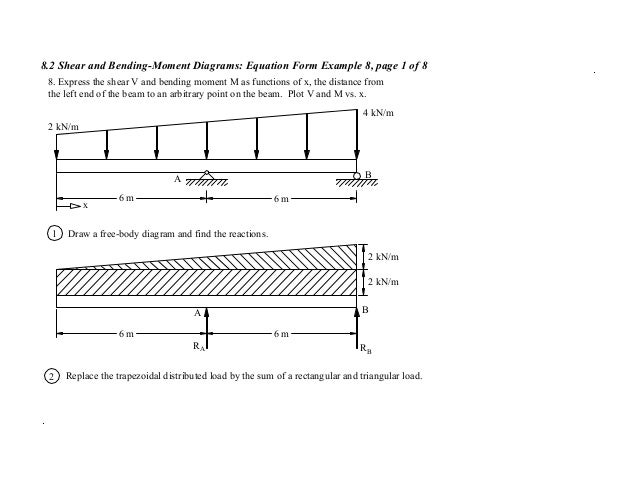
The complete diagrams are shown. Resolve the trapezoidal loading into a uniformly distributed load and a uniformly varying load.) in each problem, let x be the distance measured from left end of the beam. Calculate the reactions at the supports of a beam. Thus after you finish passing over the width of a distributed load, the value of the shear diagram will have changed by the magnitude of the distributed load, and in the direction that load is.
We have already noted in eqn. As you would have noticed when working out the bending moment and shear force at any given point, sometimes you just work it out at the point, and.