This Diagram Shows How The Body Keeps Blood Glucose
The integration of hepatic glycogen anabolic.
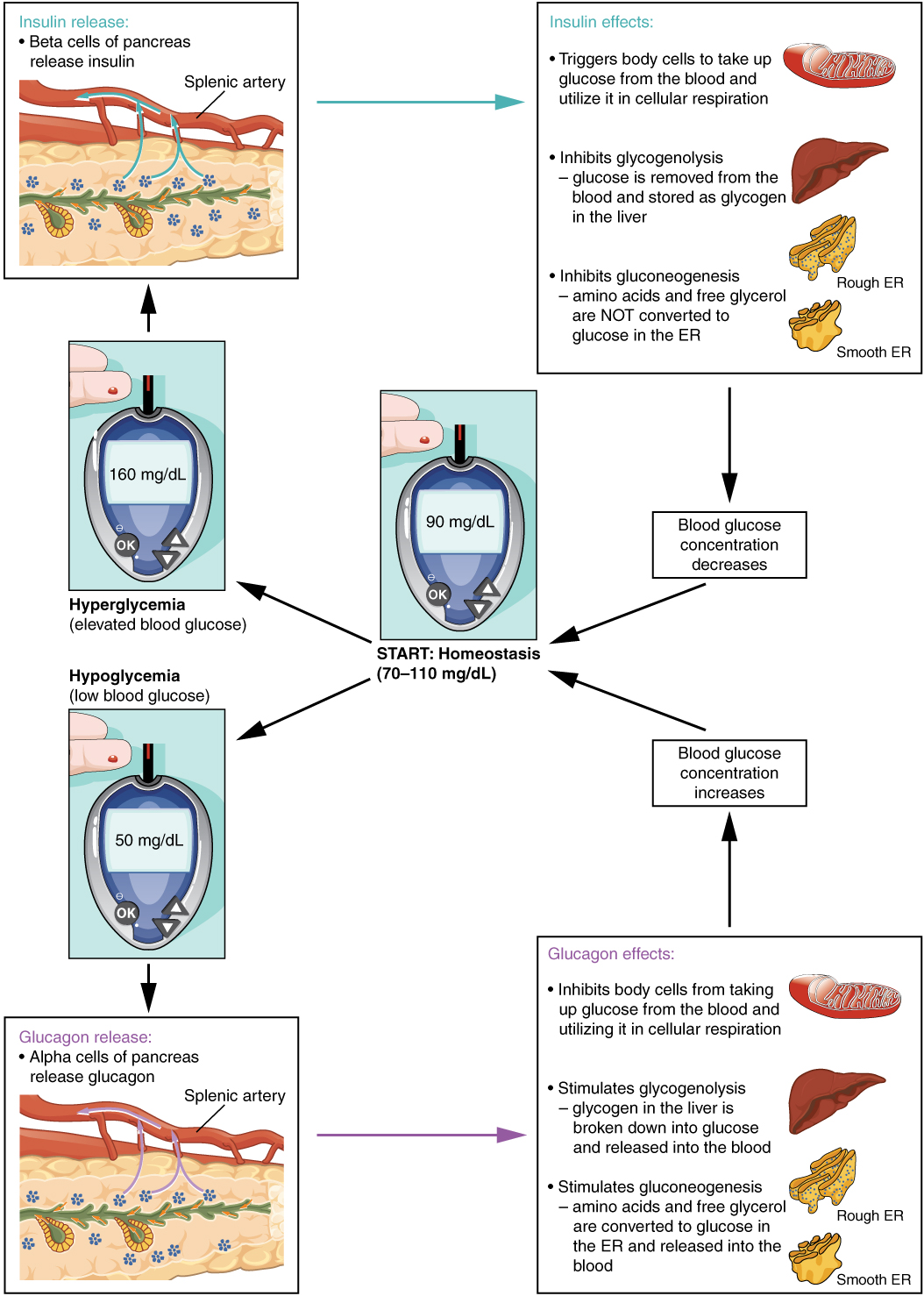
This diagram shows how the body keeps blood glucose. What happens to blood glucose (blood sugar) when you eat? This tight regulation is referred to as glucose homeostasis. A person can test their blood glucose levels with a glucometer. Blood glucose levels tend to be more stable in the morning, so morning appointments are preferable for diabetic patients.
Keep a log of each glucose. The heart constantly receives signals from the rest of the body that direct how hard it. Glucose molecules are delivered to cells by the circulating blood and therefore, to ensure a constant supply of glucose to cells, it is essential that blood negative feedback systems are processes that sense changes in the body and activate mechanisms that reverse the changes in order to restore. Beta cells in your pancreas monitor your blood sugar level every few seconds.
The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the concentration of glucose present in the blood of humans and other animals. Glucose levels are measured most commonly to diagnose or to monitor diabetes. This diagram shows how the body keeps blood glucose at a normal level. Not only does the circulatory system keep our cells healthy, but it also keeps us alive.
- Club Car 48 Volt Battery Wiring Diagram
- Husqvarna Lgt2654 Drive Belt Routing
- 2000 Buick Century Brake Line Diagram
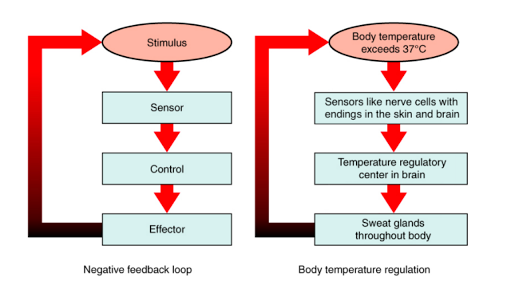
Keeping blood glucose above 4 mmol/l for people on insulin or certain medications for type 2 diabetes is important to prevent hypos occurring, which can be dangerous. Insulin rises with the blood sugar levels and directs it into the cells of the muscle and liver to use for energy. 5.3 describe generally how a negative feedback loop works it comes to the diagram below helps to explain this using the example of body temperature. Your body needs glucose to.
Learn the common symptoms and how to hyperglycemia means high (hyper) glucose (gly) in the blood (emia). They usually come with lancets, or tiny follow your doctor's instructions in line with whichever reading shows on the screen. Children, older people and those at particular risk of hypoglycemia may be given wider targets. Abnormal secretion of some hormones in blood which act as antagonists to insulin.
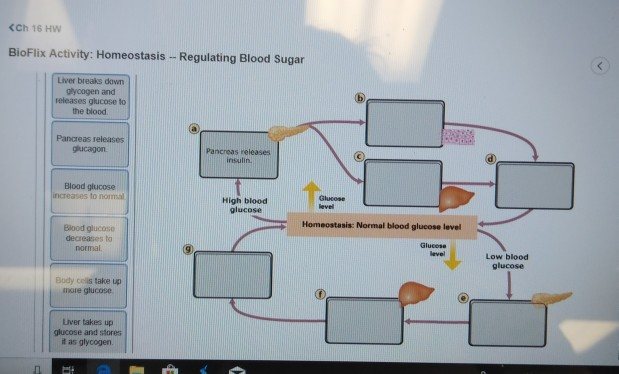
It is a complication some people with diabetes experience. This diagram shows how the body keeps blood glucose at a normal level.drag each label to the appropriate location on the diagram. <ch 16 hw bioflix activity: It mainly comes from foods rich in carbohydrates, like bread, potatoes, and fruit.
Liver (the pancreas responds to high blood glucose levels by releasing insulin.) b.a liver cell responds to insulin by taking in glucose and converting it to. Hyperglycemia means the amount of sugar (glucose) in the blood is elevated beyond normal. How your body makes glucose. 5.2 how does homeostatic help control my body temperature?
Small regular meals spread over the course of the day will also help manage your appetite and keep blood glucose levels stable. Watch how insulin and glucagon do a great job regulating glucose in. Explain how the body maintains an optimal level of blood glucose. This keeps glucose, amino and fatty acids from getting to high in the blood and helps keep blood sugar levels stable in the body.
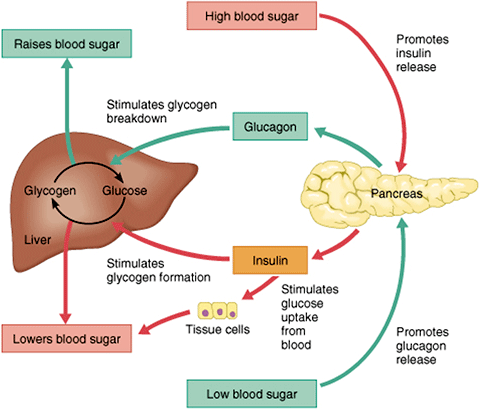
Blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, primarily glucose, are maintained by the body within a narrow range. Glucagon is released overnight and between meals and is important in maintaining the body's sugar and fuel balance. If the patient's finger is still bleeding, keep the cotton wool or gauze in place and secure with some tape. The diagram below shows how the concentration of glucose in the blood is regulated.
Glucose is a simple sugar and approximately 4 grams of glucose are present in the blood of a. Understanding how to maintain healthy blood glucose levels during exercise is particularly important for people with diabetes. The liver acts as the body's glucose 'reservoir'. How the body processes sugar.
Normally, the body maintains balanced blood sugar levels (what doctors call blood glucose homeostasis) by means of an intricate, tightly controlled system. How does the body control glucose in the blood? When the blood glucose concentration gets too high liver cells can take in glucose and store it. Your doctor may give you different targets.
Blood flow is a pulse wave that moves out from the aorta and through the arterial branches, then is the arteries deliver oxygenated blood, glucose and other nutrients to the brain and the veins carry this blood is pumped through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle, then distributed to the body. To keep the body running smoothly, a continuous concentration of 60 to 100 mg/dl of glucose in blood plasma is needed. Most people find that their blood glucose levels improve if they space their meals and snacks evenly throughout the day. Glucose helps keep blood sugar levels consistent in your body, giving it glucose plays a vital role in maintaining those levels and providing your body with the energy it everything from the food you eat to your inner mechanics can play a role in how your body produces and uses glucose every day.
It signals the liver to break down its starch or glycogen stores and helps to form new glucose units and ketone units from. Both high blood glucose levels and low blood glucose levels are stimuli that trigger specific responses by the body. Pancreas releases insulin b.body cells take up more glucose c. The concentration of glucose in the blood must be kept at a set point.
Regulation of blood glucose is largely done through the endocrine hormones of the pancreas, a beautiful balance of hormones achieved through a negative feedback loop. Helps the learner understand the different processes that insulin controls in the healthy body. For example, during vigorous exercise, fever or trauma when the body׳s utilization of glucose increases, there is normally a compensatory increase in glucose delivery. The circulatory system is made up of a vast network of organs and blood vessels that deliver nutrients to every cell in the body.
Your blood sugar level is in constant flux, depending on what you've eaten, when you ate it, and what you did afterwards. Our blood glucose level, or blood sugar level, is the amount of glucose in the blood. • the body produces enough insulin but cannot utilize it effectively. Blood sugar or blood glucose supplies energy from food to all the cells in the body.
And how does it come down?