The Orbital Diagram For A Ground State Oxygen Atom Is
The most stable electron configuration—the ground state—is that in which the electrons are in the lowest possible energy states.
The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen atom is. A representation of the atomic spectrum of oxygen. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. Oxygen atomic orbital and chemical bonding information. Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom.
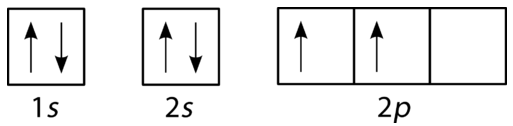
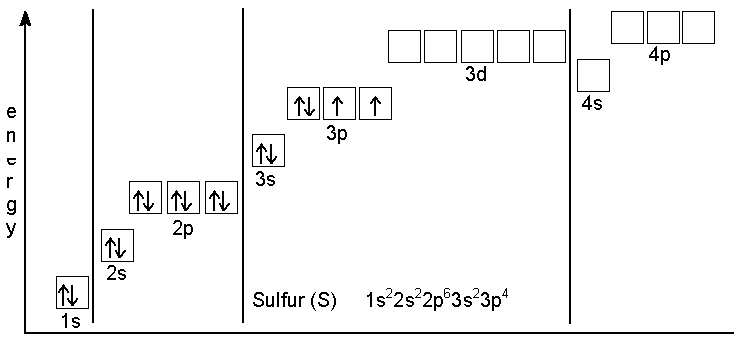
Orbital diagrams orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. In order to figure out where electrons go in an let's put all these stuff into play, how this all come together. For example, the ground state electron configuration of oxygen is 1s2 2s2 2p4. 1s box arrow up, arrow down.
This element is now called a) gallium. For the element of oxygen, you already know that the atomic number tells you the number of electrons. An atom is in its ground state when all the electrons in the atom occupy orbitals that result in the minimum chemical potential energy for the atom as a an orbital can be a wave function describing the state of a single electron in an atom (atomic orbital) or in a molecule (molecular orbital). The next atom is helium with 2 electrons.
- 73 87 Chevy Truck Air Conditioning Diagram
- Atv Key Switch Wiring Diagram
- Poulan 2150 Chainsaw Fuel Line Routing Diagram
What is the longest wavelength of light that can cause this bond to be broken? The first two electrons in oxygen (atomic number 8) has a pair of electrons in any one of the 2p orbitals (the electrons have. (a) zeff for an electron in a 2s orbital show the distribution of electrons in oxygen atom (atomic number 8) using orbital diagram. The aufbau principle is based on the idea that the order of orbital energies is fixed—both for a given element the shape of an orbital depends on the energy state of the electron.
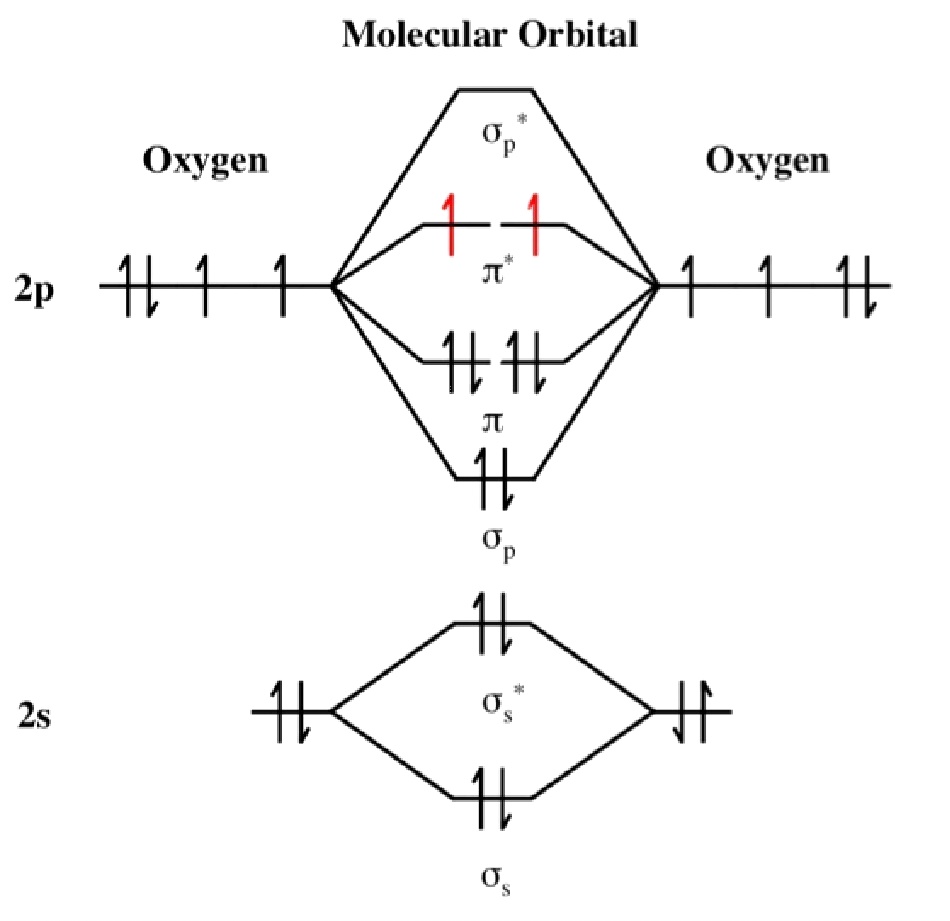
The diagram consists of only the 2s and 2p atomic orbitals (valence shell) on each oxygen atom. Ionisation energies and electron affinity. The possible orbital diagram for oxygen atom has to be given. Orbital diagram, after barrett (2002),[29] showing the participating atomic orbitals from each oxygen atom, the molecular orbitals that result from their overlap, and the aufbau filling of the orbitals with the 12 electrons, 6 from each o atom, beginning from the lowest energy orbitals, and resulting in covalent.
That means there are 8 electrons in an oxygen atom. Students (upto class 10+2) preparing for all government exams, cbse board exam, icse board exam, state board exam, jee (mains+advance) and neet can ask. How many unpaired electrons does an oxygen atom possess? In the explanation below, i show a common means of diagramming this.
The ground state electronic configuration of oxygen atom is 1s22s22p4. You should be familiar with how to determine an electron configuration for an atom and identify the valence orbital energy diagram. Each oxygen atom has 8 electrons, hence in o2 molecule there are 16 electrons. Using arrows to show the spin orientation of each electron, the orbital diagram is often shown this way:
(i) zeff for an electron in a 2s orbital is the same. A neutral hydrogen atom has one electron. An orbital diagram helps to determine the electron configuration of an element. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral oxygen is [he].2s2.2p4 and the term symbol is 3p2.
Oxygen (atomic number 8) has a pair of electrons in any one of the 2p orbitals (the electrons have opposite spins) and a single electron in. What is the ground state electron configuration of aluminum, al ? Can't really draw the orbital diagram, but use the boxes and place arrows as follows. (b) correct configuration in ground state should be 1 s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3pb3d104s1.
The molecular orbital energy level diagram of oxygen molecule is given as follows Now, you can do an electrical configuration or a orbital diagram for an excited state, but then there'd be all sorts of correct answers. We'll be doing these for ground state atoms, meaning that all the electrons are in their lowest possible energy state. Alright let's talk about orbital diagrams.
The labeling of each axis is arbitrary and is of no consequence, except to keep each p orbital overlap consistent with each other in the diagram. In the question, the only configuration for a ground state atom is d. Okay let's do the orbital diagram for iron, iron we know is on its ground state of 26. 1s (up down) 2s (up down) 2p (up down, up, up).
The ground state configuration is the lowest energy, most stable arrangement. The primary criteria, the aufbau principle, states the electrons are to be placed into the orbital of lowest energy. The ground state is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^2. For oxygen the eighth electron must pair with one of the electrons in the 2p orbitals.
The electronic configuration of oxygen (z=8) in the ground state is 1s22s22p4. The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen atom is a a b b c c d d e e which element has the following ground state electron configurati. The electrons must have opposite spins if. For the electrons of oxygen atom, which of the following statements is correct?
The bonds of oxygen molecules are broken by sunlight. Partial orbital diagrams and condensed configurations. For the electrons of oxygen atom, which of the following statements is correct? Draw the orbital diagram for the electron configuration of oxygen, atomic number 8.
A partial orbital diagram shows only the highest energy sublevels being filled. It follows an orbital can only hold 0,1, or 2 electrons.