The Orbital Diagram For A Ground State Nitrogen Atom Is
In order to figure out where electrons go in an let's put all these stuff into play, how this all come together.
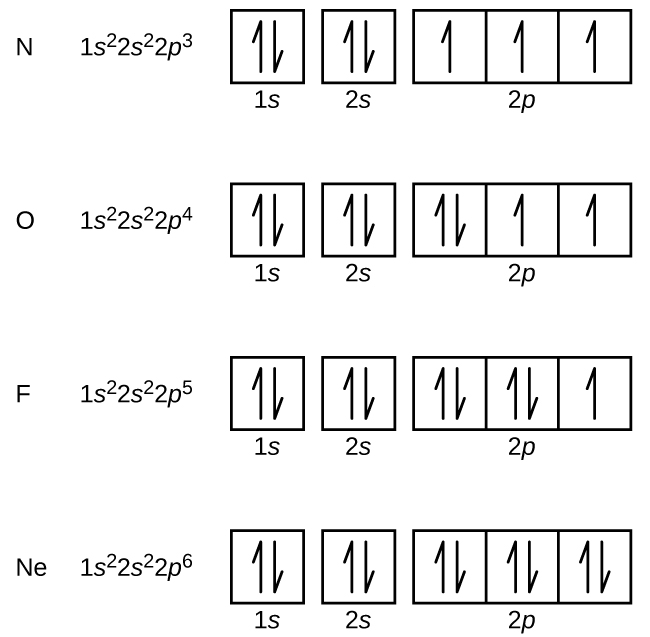
The orbital diagram for a ground state nitrogen atom is. A nitrogen atom has seven electrons. In this video we will draw the molecular orbital diagrams for diatomic nitrogen, carbon and boron. Nitrogen atoms are directly involved in various tautomeric systems and 15n chemical shifts reflect the changes in equilibria in a much better way than the nitrogen atom of methylamine and other amines has five valence electrons in four sp3 hybrid orbitals that are directed to the corners of a tetrahedron. A nitrogen atom has seven electrons.
Ionization energy tends to decrease down a group and increase across a period. Nitrogen (atomic number 7) fills the 1s and 2s subshells and has one electron in each of the three 2p orbitals, in accordance with hund's rule. If the nitrogen atom had electronic configuration 1s7, it would have energy lower than that of the normal ground state configuration 1s22s22p3, because the electrons would be closer to the. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral nitrogen is [he].2s2.2p3 and the term symbol is 4s3/2.
In the ground state, they are arranged in the electron configuration 1s 2s 2p x2p y2p z. In the explanation below, i show a common means of diagramming this. Atoms at ground states tend to have as many unpaired electrons as possible. Atoms with a high ie tend to form anions (except the noble gases).
The kossel shell structure of nitrogen. The positions of the first ten orbits of an atom on an energy diagram. The bohr model for the hydrogen atom found its best support from experimental work on the photoelectric effect. Okay let's do the orbital diagram for iron, iron we know is on its ground state of 26.
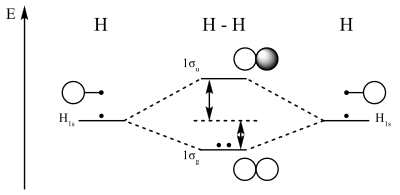
We will also calculate their bond order and determine if. An atom is defined as the smallest part of a chemical element that retains the chemical properties of the element. Now that we know about orbital diagrams and hund's rule, we can begin to explain the chemistry of the elements. Using arrows to show the spin orientation of each electron, the orbital diagram is often shown this way:
The first two electrons will pair up in the 1s orbital; The electron dot diagram for each nitrogen atom would look like this there are two shells of electrons in the nitrogen atom that actually have electrons in them, nitrogen has two electrons in the first shell, the s orbital, and five in the outer shell, the p orbital. The orbital diagram in which both pauli's exclusion principle and hund's rule violated is: Transcribed image text from this question.
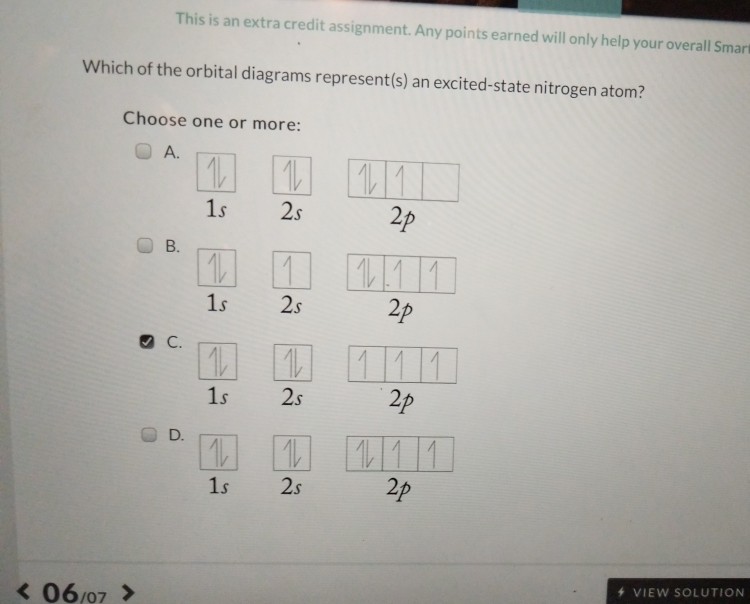
The orbital diagram for a ground state nitrogen atom is. Hence, in excited state one of the 2s electron will jump to 2p orbital,so the excited state electronic configuration should be 1s2 2s1 2px2 2py1 2pz1. When they drop back down to their ground state a photon of light is emitted. 1s (up down) 2s (up down) 2p (up down, up, up).
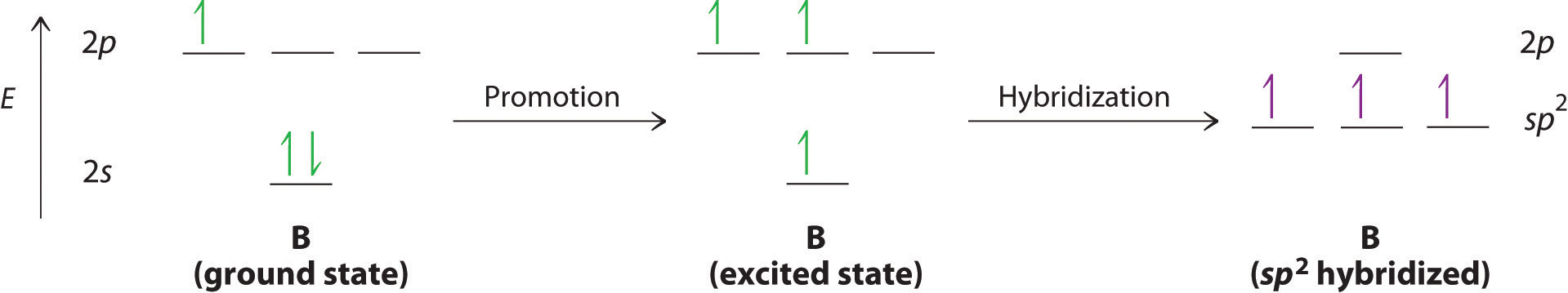
Schematic electronic configuration of nitrogen. Alright let's talk about orbital diagrams. However, the fourth sp3 orbital that is present is a nonbonding pair of hybridized orbital and is in nh3 hybridization, the three hydrogens will be based around the central atom of nitrogen. This causes nitrogen to have a.
It therefore has five what is the orbital diagram for an atom in a ground state? Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. In the ground state, they are arranged in the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p1 x2p1 y2p1 z. Although the nucleus of an atom is very dense, the electrons around it can take on a variety of positions which can be summarized as an electron.
Atoms are comprised of three subatomic particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. The positively charged protons and neutrons (which have no charge) make up the atom's nucleus, or. Orbital diagrams orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. It depends on the atom.
The electron configuration can be written as 1s22s22p4. If we look at the atomic number of nitrogen it is 7 and if we consider its ground state it is given as 1s2, 2s2,2p3. It hypervalency is almost unknown in the 2p elements for the same reason, because the high electronegativity makes it difficult for a small nitrogen atom to be a. The pauli exclusion principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital.
Can momentum be conserved for a system if there are external forces acting on the system? A partial orbital diagram shows only the highest energy sublevels being filled. To draw the orbital diagram, begin with the following observations: 9 5.1 atomic orbitals different atomic orbitals are denoted by letters.
To go back to its ground state, the electron releases energy. For example, if it was nitrogen it would be < = clockwise. Partial orbital diagrams and condensed configurations. Calculate the wavelength of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom during a transition of its electron from the n = 4 to the n = 1 principal energy level.
The ground state is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^2. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. Electronic configuration of nitrogen in ground state is 1s2 2s2 2p3 or 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz1. The orbital diagram for a ground state oxygen atom is a a b b c c d d e e which element has the following ground state electron configurati.
Ground state electronic configuration of nitrogen atom can be represented by. This is because one electron cannot.