The Diagram Below Shows A Bacterial Replication Fork
A child process uses the same pc.
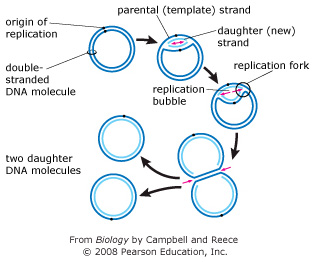
The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork. The cell is a bacterial cell, structure 1 is the cell wall and structure 2 is a mitochondrion. The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Fork system call is used for creating a new process, which is called child process, which runs concurrently with the process that makes the after a new child process is created, both processes will execute the next instruction following the fork() system call. Helicase separates the dna strands.
The rigidity of its cell wall determines the shape of a bacterium. Note that replication fork below goes right to the more forks, the faster replication is. Bacterial proliferation is the product of both replication and killing undergone by the population. The diagram below shows a cell.
The ter sequence of 23 bp are arranged on the chromosome to create trap that the replication fork can enter but cannot leave. Efficient replisome progression relies on tight coordination between the various factors of the replisome. Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the blue. Ter sequences function as binding site for tus protein.
Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the guidelines for dna recombination and repair studies cellular assays. Diagram showing dna replication in a circular chromosome. On one template strand, synthesis proceeds continuously toward the replication fork, generating the leading strand. This diagram illustrates a bacterial if the time required for two replication forks traveling in opposite directions to traverse the entire e.
The primary control of replication is exerted during initiation. The diagram below shows the position of the dna band in the centrifuge tube when the dna was labelled with the heavy isotope of nitrogen, 15n. A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication; Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand.
Multiple enzymes are used to complete this process quickly and efficiently. The bacteria diagram given below represents the structure of bacteria with its different parts. The replication machinery, the replisome complex, is composed of many specialized proteins with functions in supporting replication by dna polymerases. Many bacteria have circular chromosomes with single origins of replication.
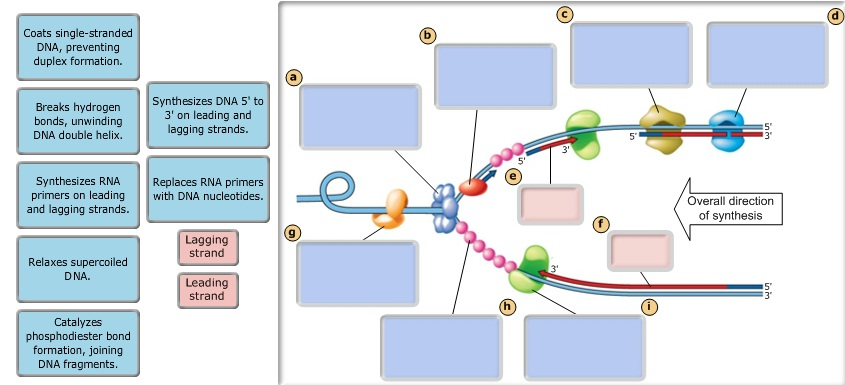
The replication fork is the site of active dna synthesis, where the dna helix unwinds and single strands of the dna replicates. The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure.
Coli chromosome meet at termination recognizing sequences (ter). Transcribed image text from this question. The diagram below shows the environmental issues raised by a product over its lifecycle. This is economical, of course, since little benefit would come from initiating replication that will never be completed.
Animal, plant, fungal and bacterial cells are different in terms of structure but also have many similarities. Multiple replication forks per chromosome allow bacteria to divide more rapidly than the replication cycle time. During dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The point at which the replication begins is known as the origin of replication (oric).
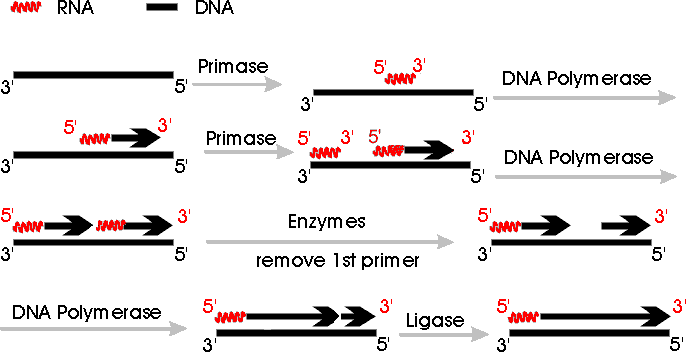
Evantually the two replication fork of circular e. (in diagram below, primer is a red squiggly line.) primase catalyzes synthesis of primer, and then the side carrying out continuous synthesis is omitted. The diagram below shows the template strands at a replication fork that is moving to the left. Explore 13 different shapes of bacteria in this page.
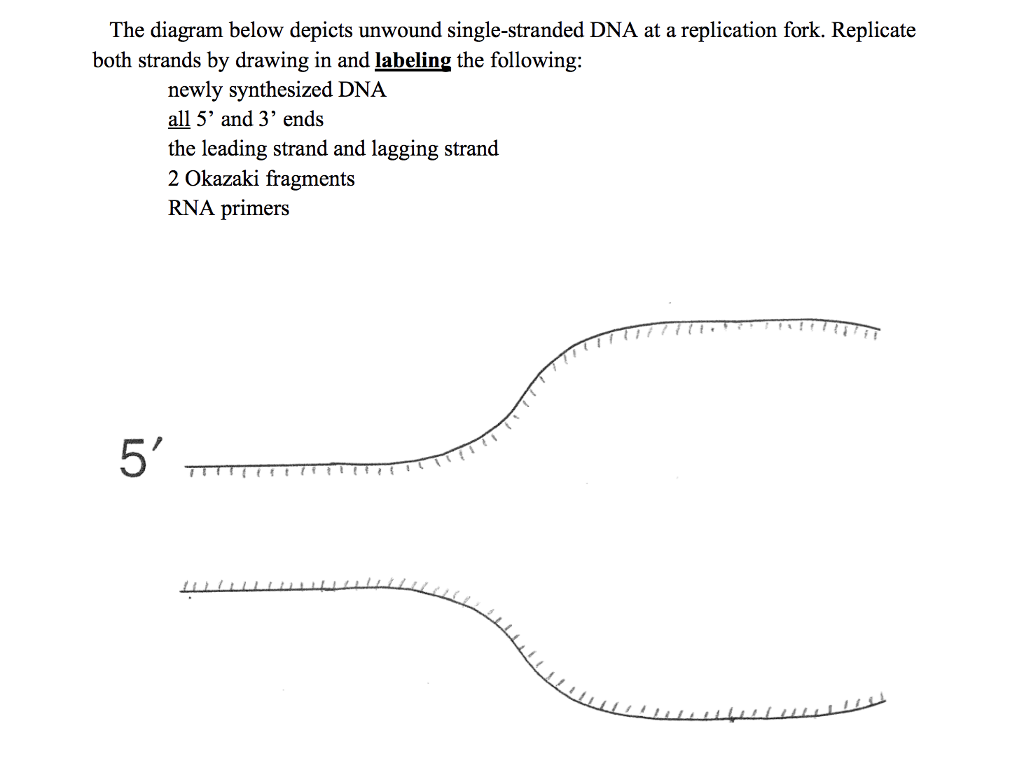
Dna replication is the process of copying the dna within our cells. The cell wall, plasmid, cytoplasm and flagella are clearly marked in the diagram. The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. The diagram below shows a replication fork with the two parental dna strands labeled at their 3' and 5' ends.
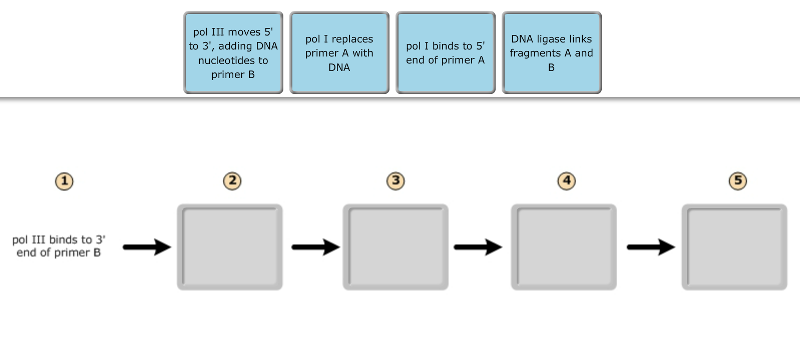
The diagram below shows a replication bubble with synthesis of the leading and lagging strands on both sides of the bubble. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to for example, let's say that part of the dna being replicated looks like this before it separates: In bacterial circular chromosomes and most plasmids, the replication is known to be terminated when either of the following occurs: Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure.
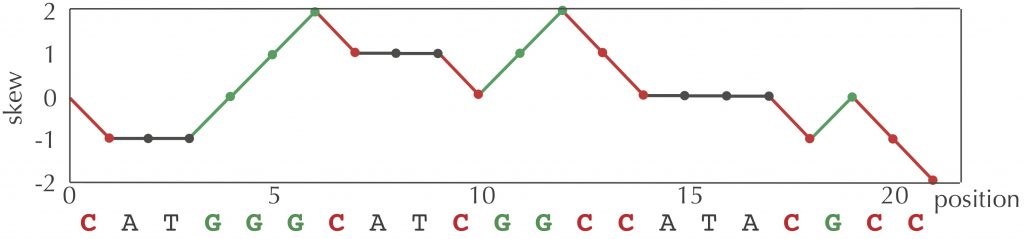
The given diagram depicts the lifecycle of a product and the consequences due to its manufacturing. Coli chromosome at 37oc is about 40 min, regardless of. The reason for this lag is that about 1500 nucleotides (the average length of a bacterial lagging strand segment) of parental dna must be exposed at the replication fork before. The forks progressing in opposite directions the results also show that the known replication mechanisms are sufficient to explain the position of the gc skew shift point.
Helicase brings about the procedure of strand separation, which. Dna has four bases called adenine (a). Recombinational repair of stalled replication fork. Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the blue targets.
Which of the following is correct? Use pink labels for the pink targets and blue labels for the blue targets. The newly synthesized dna strands the reason for this lag is that about 1500 nucleotides (the average length of a bacterial lagging strand segment) of parental dna must be exposed at the. The diagram below shows a bacterial replic clutch prep.
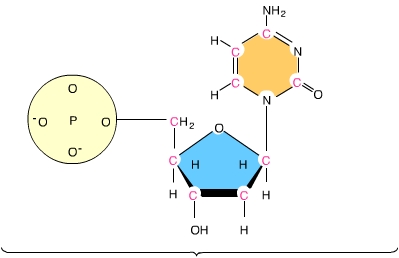
For each of the statements below, put a cross in the box that corresponds to the correct statement about dna structure or dna replication. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or old strand. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons model answer 1: Most small genomes (such as bacterial and viral dna's).








/DNA_replication_elongation2-e38fc92e8ad74586bfe0443d7490d3ce.jpg)