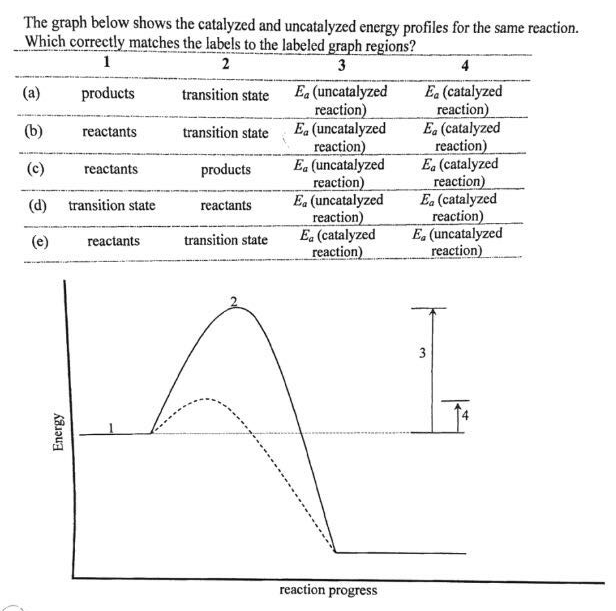
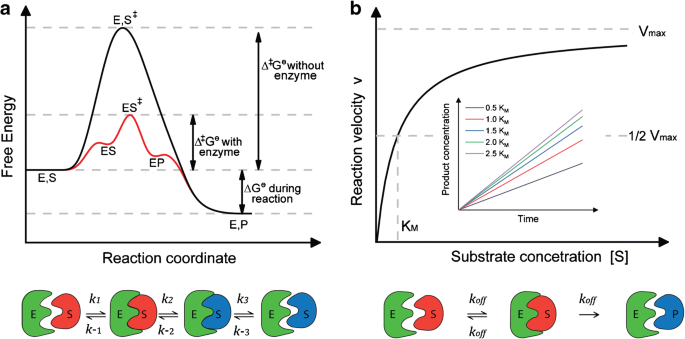
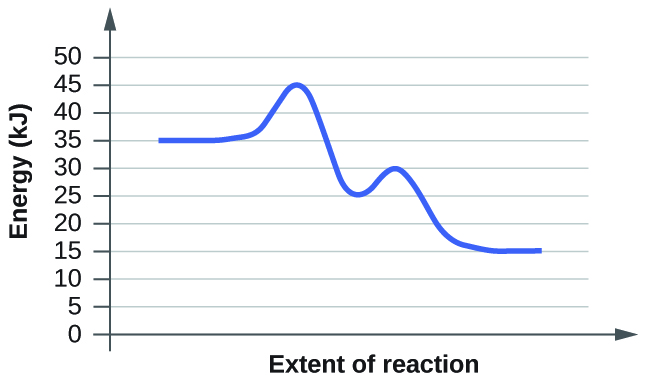
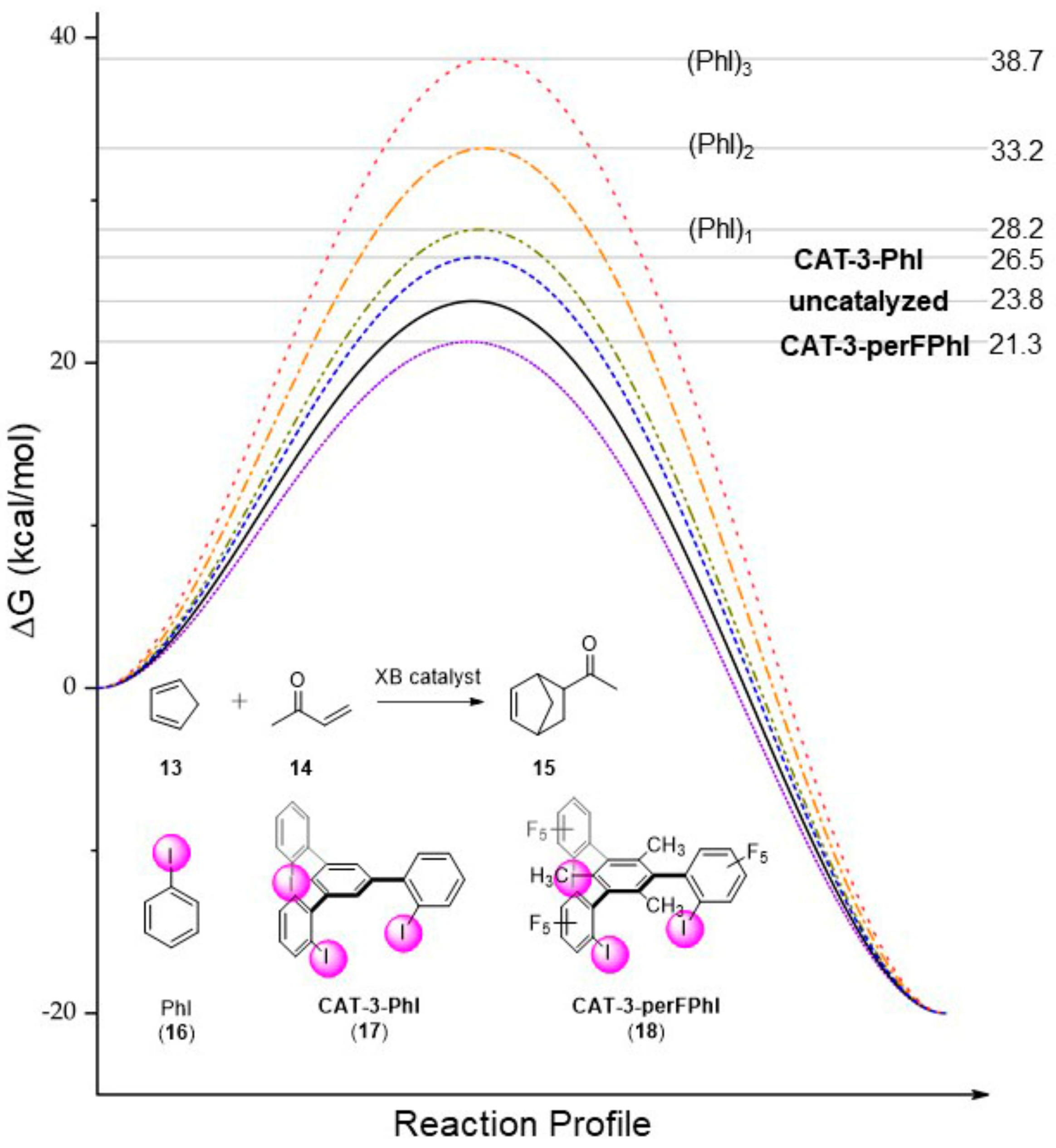
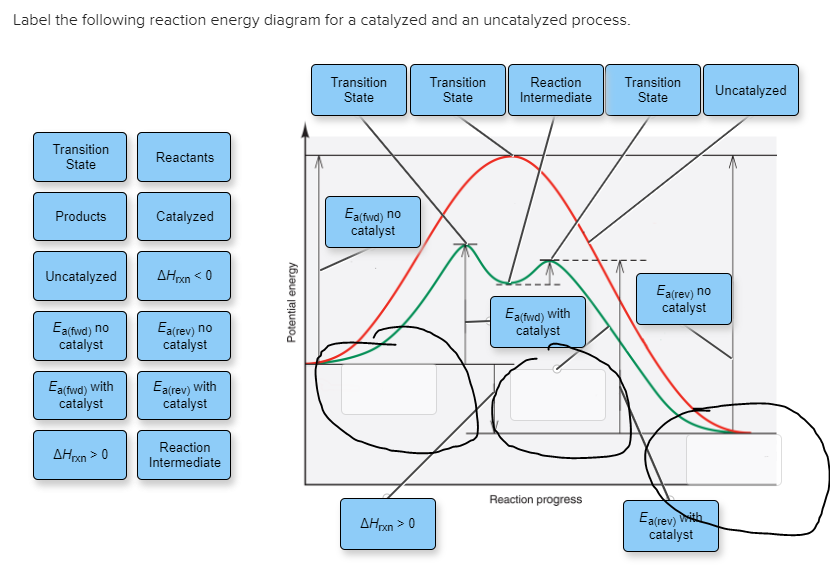
Reaction Energy Diagram For A Catalyzed And An Uncatalyzed Process
In order to achieve an optimum effect of washing process, on the woven fabric in different washing time, enzyme wash and then silicone wash were carried out for cotton fabric.
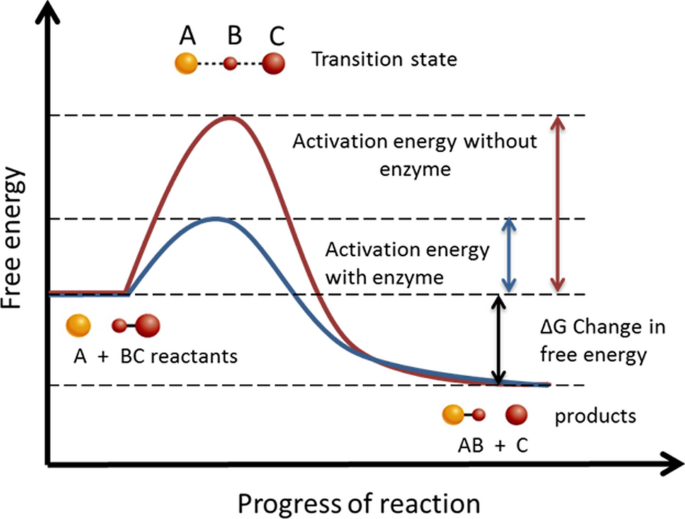
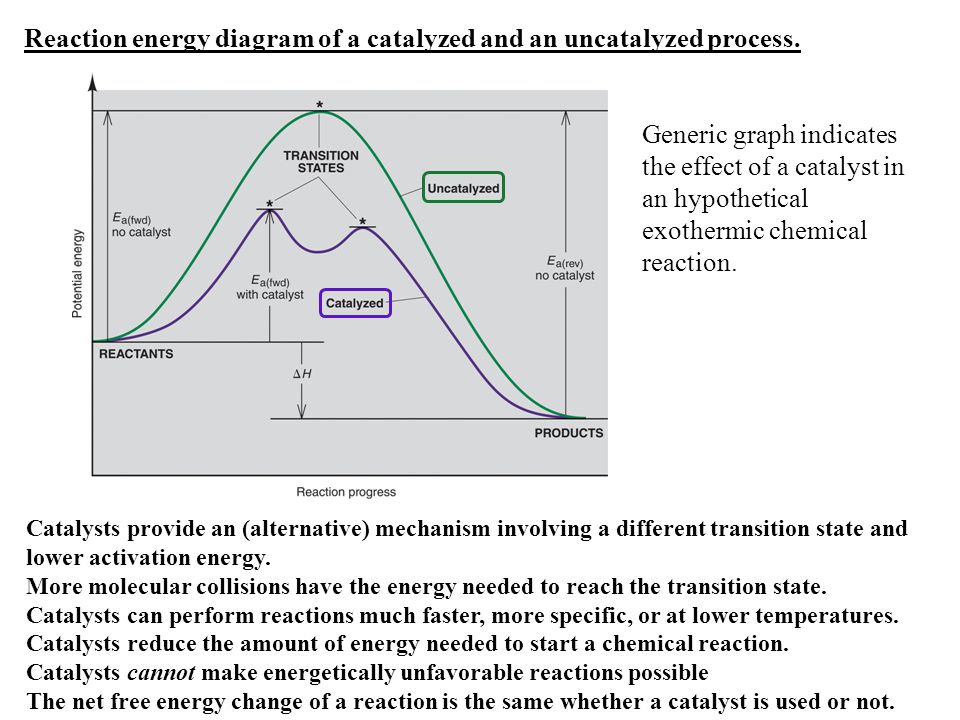
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. (ts) of the uncatalyzed and catalyzed reaction. Cellulose + catalyst æ glucose + catalyst. Remember that the 🔼h of reaction remains the. This does not change the frequency of collisions.
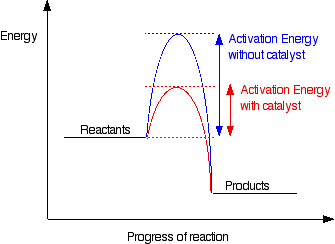
Adding a catalyst has exactly this effect of shifting the activation energy. Ea uncatalysed rxn ea catalysed rxn(lower). Usually, this will be more complicated than the original, uncatalyzed reaction. Challenges associated with analysis is discussed, as is the benefits of inline pat ✔ immediate understanding.✔ representative of reaction at process.
Notice that the energies of the reactants and products are the same for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction. (a) standard free energy change of the. In addition, the catalyst is regenerated in the process. So, of the choices given in this question, the ones that are different from the uncatalyzed reaction would be
Analyzing the potential energy diagram of a regular/uncatalyzed and a catalyzed (adding a catalyst) reaction. Catalysts lower the activation energy for reactions. The energy relationships of a reaction are explained on the basis of energy diagrams. The following diagram shows an energy diagram for the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid.
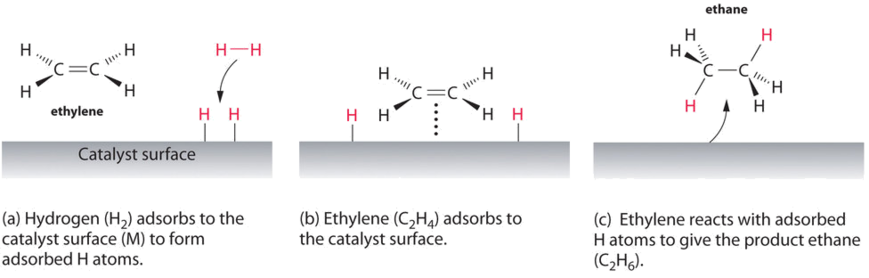
A homogeneous catalyst is in the same phase as the reaction mixture. A catalyst speeds up the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy; 2c, an annotated reaction coordinate diagram for the first chemical step is given. Positive fields are defined in the opposite direction.
Not all molecules of the same type will possess the same amount of energy 1. The peak representing activation energy is lower for the catalyzed reaction. Why does a potential energy diagram showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy not move left on the reaction pathway scale (compared to uncatalysed reaction) if a catalyst speeds up reactions? What is the ratio of the rate constant for the catalyzed reaction to that for the uncatalyzed reaction at 25c?
Is the uncatalyzed free energy cost for intermediate formation, given by. A catalyst allows an alternative reaction pathway that has a lower activation energy than the uncatalysed reaction. A catalyst provides an it is simply that the majority of particles will react via the easier catalysed route. Keq depends only on the difference in energy level between reactants and products.
Of the flow of electrons and contribute to stabilizing to rationalize the role of the cage on the reduction of the reaction energy barrier, a set of geometries representative of the reactant and transition states. D⟶ it show the change in enthalpy of reaction i.e. For a reaction that can take place with or without catalysis by an enzyme, what would be the effect of the enzyme on the: Silica supported polyphosphoric acid catalyzed synthesis of substituted indazoles.
In the diagram below, label the two reaction pathways as either catalyzed or uncatalyzed. Draw and label a reaction coordinate diagram for an uncatalyzed reaction, s → p, and the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme, e. Change the equilibrium constant for a reaction. The haber process (making ammonia).
Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Activation energy for the same reaction when catalyzed is 11.9kj. Features of enzyme catalyzed reactions. Catalyzed reactions use alternative paths to speed reactions, so it's crucial to understand reaction kinetics, mechanisms, and pathways.
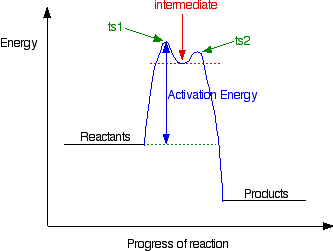
• the rate of catalysis is given by the turnover • catalyst forms a covalent intermediate that reacts faster than uncatalysed reaction • in order for catalysis to be efficient, the activation energy for formation of the intermediate and for its. The way in which this is accomplished is by providing an alternate mechanism. In other words, why is there a minimum energ. A catalyst provides an alternative pathway for a reaction.
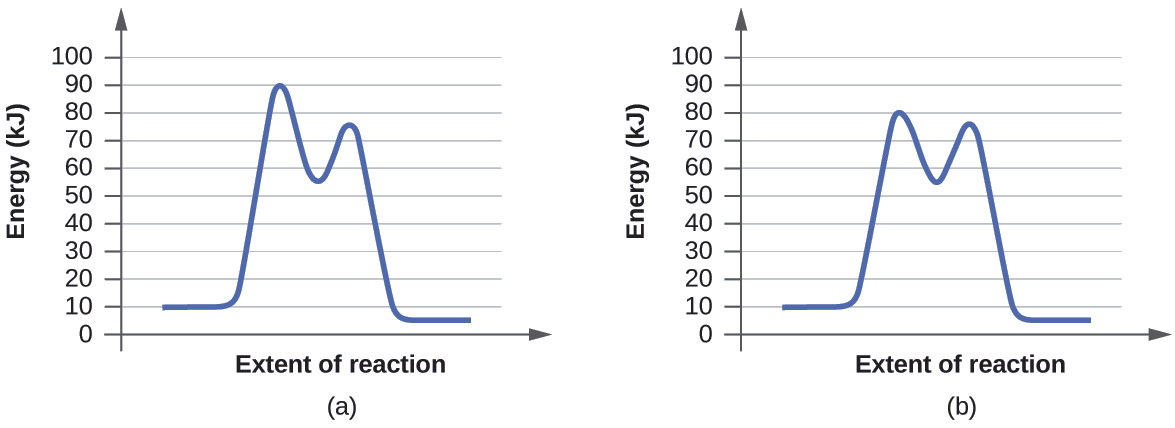
Alternative catalysts for a model decomposition reaction. A⟶ show the catalyses activation energy which is due to addition of catalyst. The comparison of catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions using energy diagrams is to be shown. Compare the activation energies you have determined with the values for other catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions.
The activation energy is higher for a noncatalyzed reaction (a) than for the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme (b). The table describes three common catalysts. The way that a catalyst works is by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction. From the diagram above, we can see that the hypothetical reaction proceeds in a single step without the catalyst, but takes four steps when catalyzed.
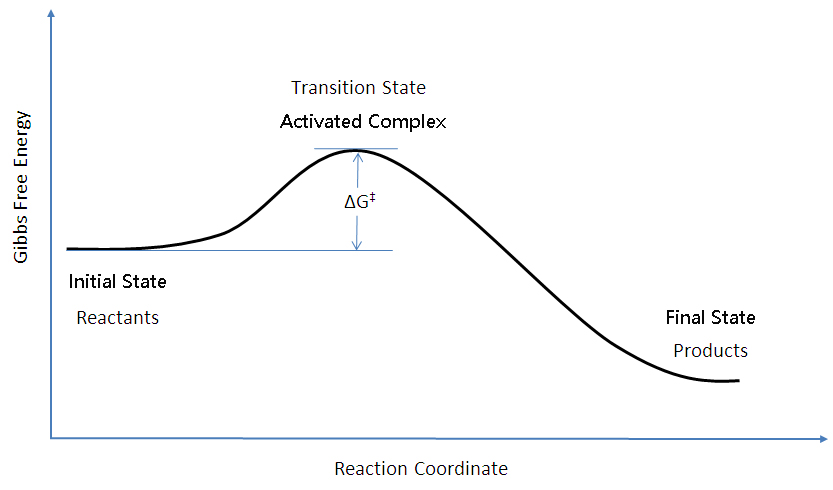
Also label the activation energy ea, and enthalpy δh. (twice the absorbance of the fully reacted sample is used in the final calculations 2. Reaction proceeds slowly at first at uncatalysed rate. One of the product is a catalyst for the reaction.
Reaction profile or energy / enthalpy diagram for uncatalysed reactions. Nevertheless, because of its lower ea, the reaction rate of a catalyzed reaction is faster than the reaction rate of the uncatalyzed reaction at the same temperature. • a catalyst accelerates a reaction without being consumed. In an exothermic reaction, the energy of products is lower than that of the reactants.
Transcribed image text from this question. Figure 12.19 shows reaction diagrams for a chemical process in the absence and presence of a catalyst. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions.