Orbital Diagram For Neutral Magnesium Atom
Timberlake lectureplus 4 learning check o1.
Orbital diagram for neutral magnesium atom. This problem has been solved! Magnesium orbital diagram awesome electron arrangements recall. 650.0 °c (923.15 k, 1202.0 °f) boiling point: Kbr, lif, and nacl 2 electrons:
Be able to construct molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear diatomic interrelate bond order, bond length, and bond strength for diatomic and triatomic molecules, including neutral and ionized rationalize molecular structure for several specific systems in terms of orbital overlap and bonding. A pair of electrons with. This just shows energy levels so let's take this a step further. This webelements periodic table page contains properties of free atoms for the element the ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral magnesium is [ne].3s2 and the term symbol schematic electronic configuration of magnesium.
Orbital diagrams orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Magnesium is element 12, so it has 12 protons and 12 electrons. (i) an atomic orbital has n = 3. Alright let's talk about orbital diagrams.
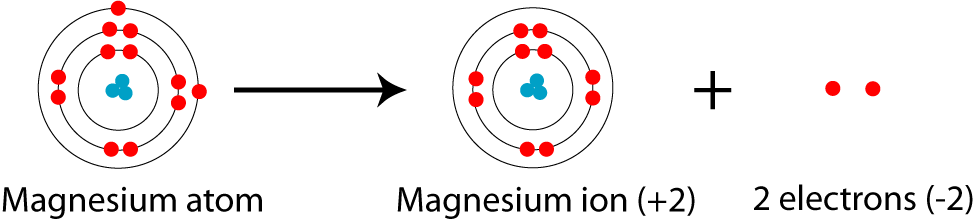
Thus, a magnesium ion has the same electron configuration as the sodium ion but a different charge. (ii) list the quantum numbers ml and l of electron in 3rd orbital. It is written out, as opposed to orbital diagrams which are depicted pictorially. Deduce (i) the number of protons and (ii) the electronic configuration of the element.
Use the aufbau principle to write complete electron configurations and complete orbital diagrams for atoms of the following elements sodium. The shape of an orbital depends on the energy state of the electron. Therefore, as we learn more about the electron's position. Bohr model establishes the concept of definite electron energy levels within atoms.
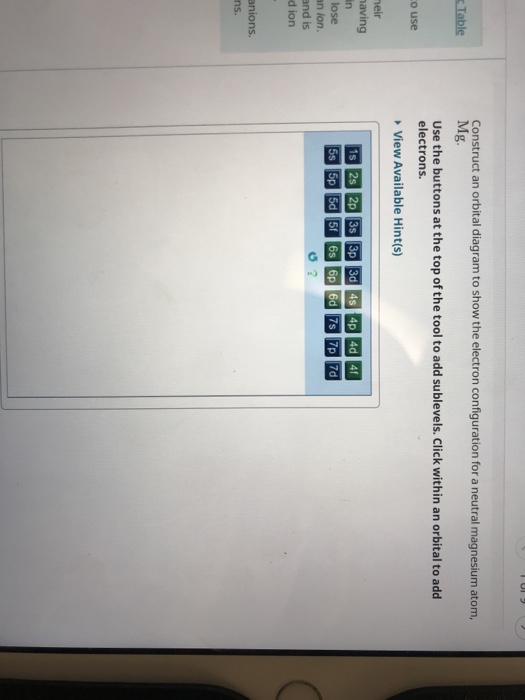
1107.0 °c (1380.15 k note: Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. An atom of an element contains 29 electrons and 35 neutrons. Construct an orbital diagram to show the electron configuration for a neutral magnesium atom, mg.
Yields of atomic iodine iq+ (q≥2) fragments resulting from photoexcitation and photoionization of the target ions ih+ and i+ have been measured in the figure 4 shows the molecular orbital diagram for the neutral ih molecule. The alkaline earth metal magnesium (atomic number 12), with its 12 electrons in a. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. A neutral hydrogen atom has one electron.
The external links below are not a part of this site and their content is not the responsibility of this site. The orbital notation of an element shows us visually where electrons in an atom of this element are most likely located. The kossel shell structure of magnesium. Atomic orbitals and electron configurations.
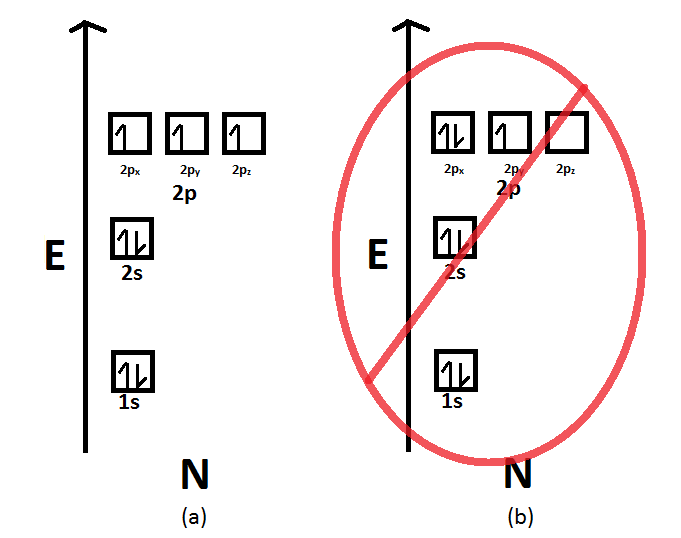
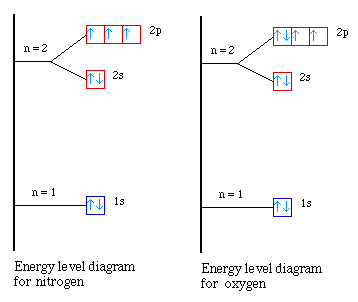
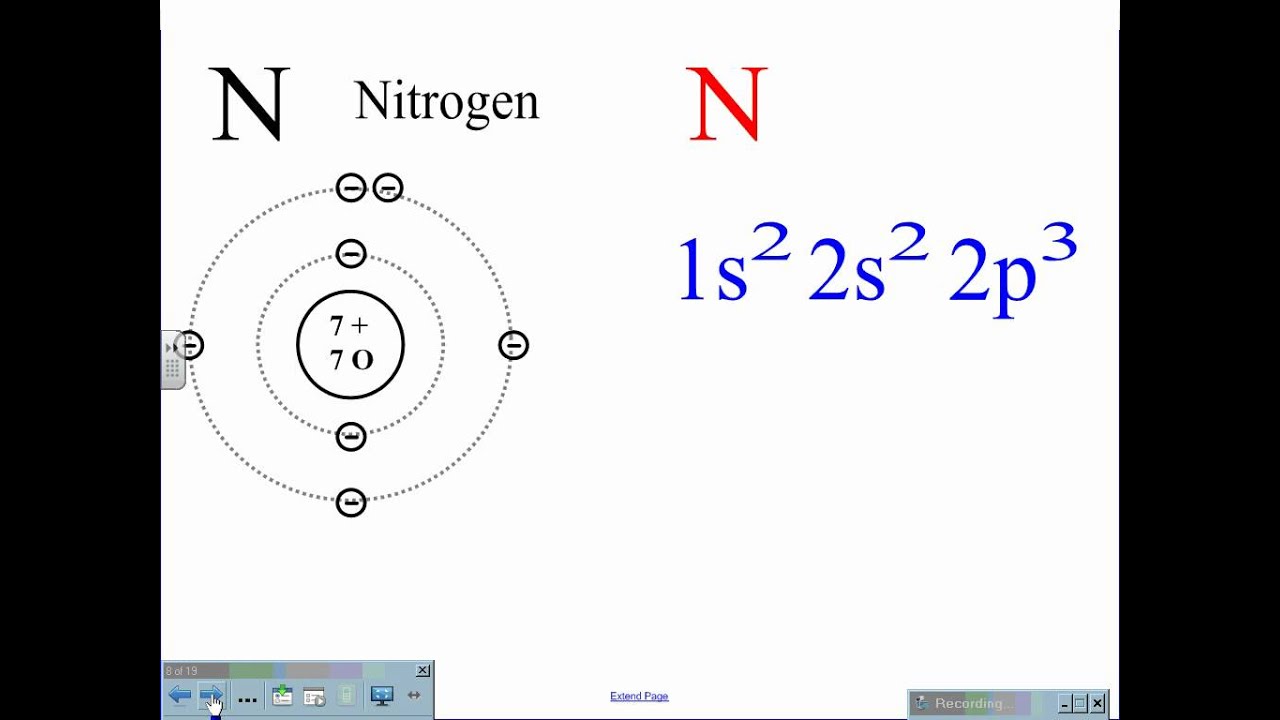
Orbital diagram for carbon, showing the correct application of hund's rule. In the diagram below, the black circle represents the nucleus of the atom, and each circle represents the electrons are shown as arrows (↑ and ↓) in the diagrams below. Electrons in an oxygen atom. Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom.
.shapes & orbital diagrams (s, p, d, & f). The heisenberg uncertainty principle states that we can't know both the energy and position of an electron. Video explanation on orbital diagrams and how to depict the electronic configuration of atoms using orbital diagrams. Construct an orbital diagram to show the electron configuration for a neutral magnesium atom, mg.
In order to figure out where electrons go in an atom we have to. The first electron goes into the 1 st energy level (k shell) An orbital diagram helps to determine the electron configuration of an element. The element in question is magnesium (mg) with atomic number 12.
Electron configuration electron configuration is shorthand for the arrangement of electrons in atomic orbitals. The atomic number (or proton number) is 8. Protons = atomic number (z). Atoms are made up of extremely small subatomic particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons.
In the neutral atom it has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 and the orbital diagram is ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓↑↓↑↓ ↑↓. But bohr's model was rather simplistic and as scientists made more discoveries about more complex atoms, bohr's model was modified and eventually was replaced by more sophisticated models. Which nonmetals could form an ionic compound with magnesium with the formula mgx2 (where x represents the nonmetal)? Chemistry bohr model of the atom excited states and ground states.
What are the possible values of l and ml ? The other part of the atomic nucleus is made up of neutrons, electrically neutral particles with a figure 2.11 orbital shape diagrams for the s, p, d, and f subshells. The electrons fill the orbitals, reaching 12 when the 3s orbital is filled. Write the orbital diagram for the.
The above diagram simplifies how to fill in the electron configuration from lowest to highest. This page explains what atomic orbitals are in a way that makes them understandable for introductory courses such as uk a level and its equivalents. Atomic electron configurations and i'm not having any luck but if you go to this site, you should be about to see what the 1s, 2s, 2px, 2py, 2pz, and 3s orbitals look like together. Because it is a neutral atom, the number of.
An atomic orbital is defined as the region within an atom that encloses where the electron is likely to be 90% of the time. Posted on january 27, 2011 by admin. Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun. Click within an orbital to add electrons.
Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals we start with a single hydrogen atom (atomic number 1), which consists of one proton and one electron. Iodine is a halogen atom so it attracts the electron from the hydrogen when. Timberlake lectureplus 3 orbital diagram for a magnesium atom. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add sublevels.