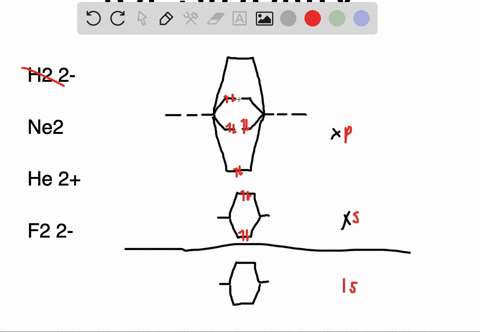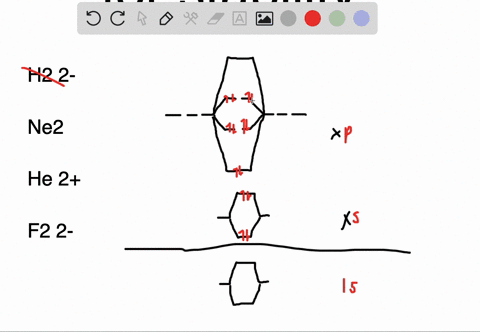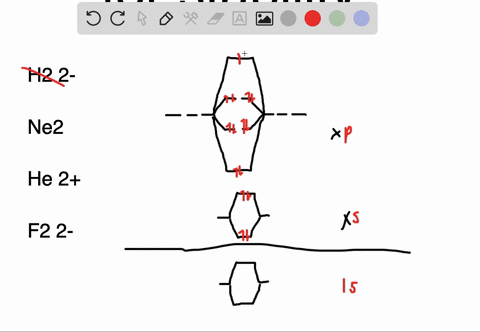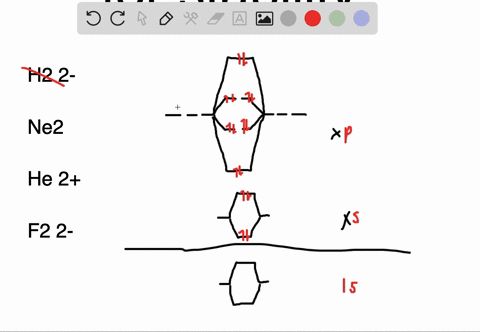
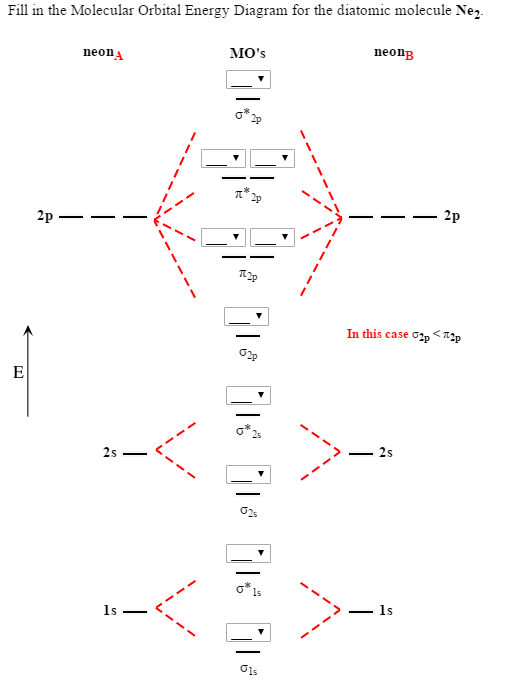
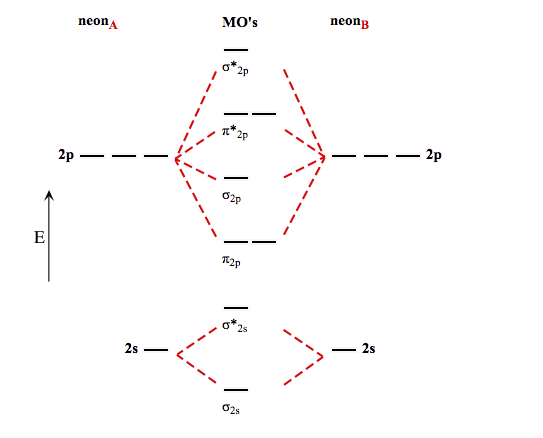
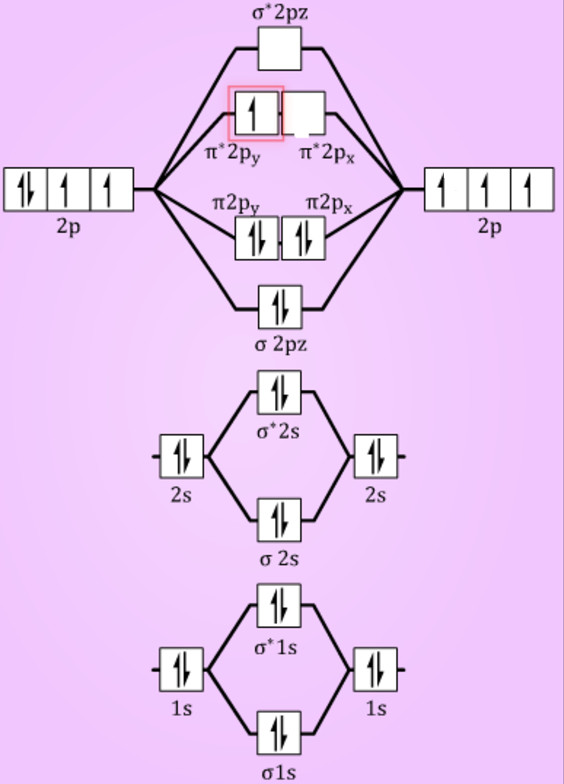
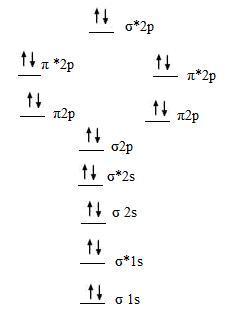Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Ne2
We use the following procedure when drawing molecular orbital diagrams.
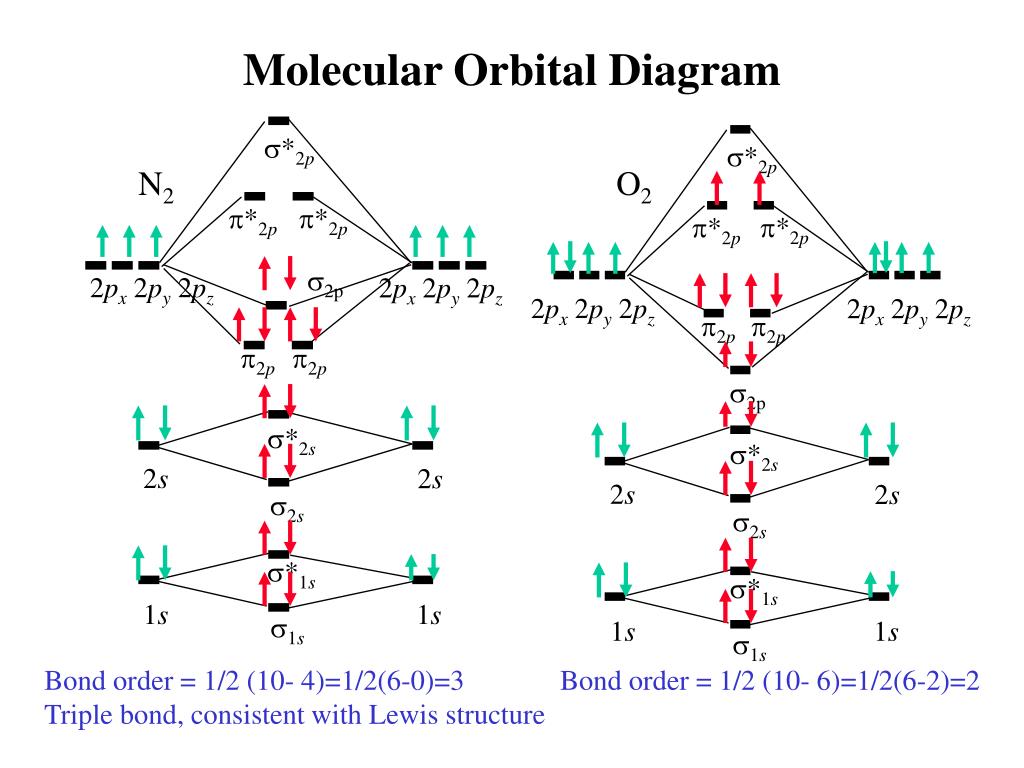
Molecular orbital diagram of ne2. The molecular orbital volume encompasses the whole molecule. The orbital correlation diagram for diboron, however, is not generally applicable for all homonuclear diatomic molecules. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2). Will the mo diagram be the same as that of $\ce{n2}$ or not?
Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of n2 using its diagram. The molecular orbital diagram of hypothetical molecule is given in the attachment. We assume that the electrons would fill the molecular orbitals of molecules like electrons fill atomic we will use this diagram to describe o2, f2, ne2, co, and no. Molecular orbital diagram for no?
Chemistry · 1 decade ago. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the #1s# orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. The other is for after nitrogen.
- 2006 Suzuki Gsxr 600 Wiring Diagram
- 98 Toyota Avalon Radio Wiring Diagram
- John Deere Lx172 Mower Deck Belt Diagram
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas ( 1 ion) (n2( )). Seeing a molecular orbital diagram for n2 will clarify what i mean. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. One is for the elements up to nitrogen.
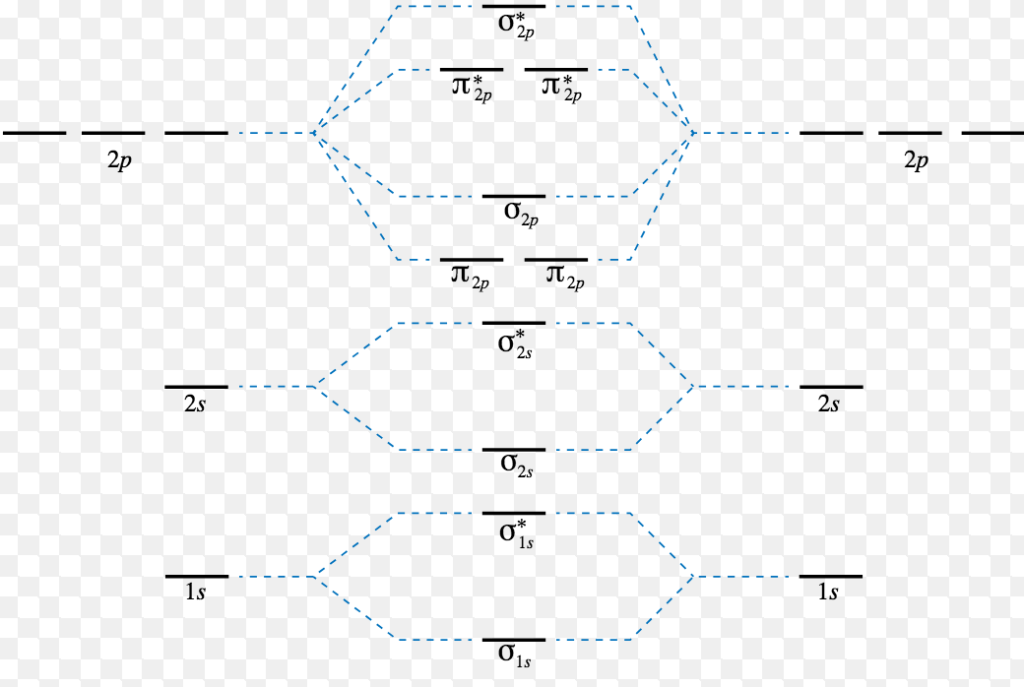
Within the diagram, orbitals are represented by horizontal lines. The orbital correlation diagram in predicts the sa. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in latex by means of the package modiagram. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s(2).
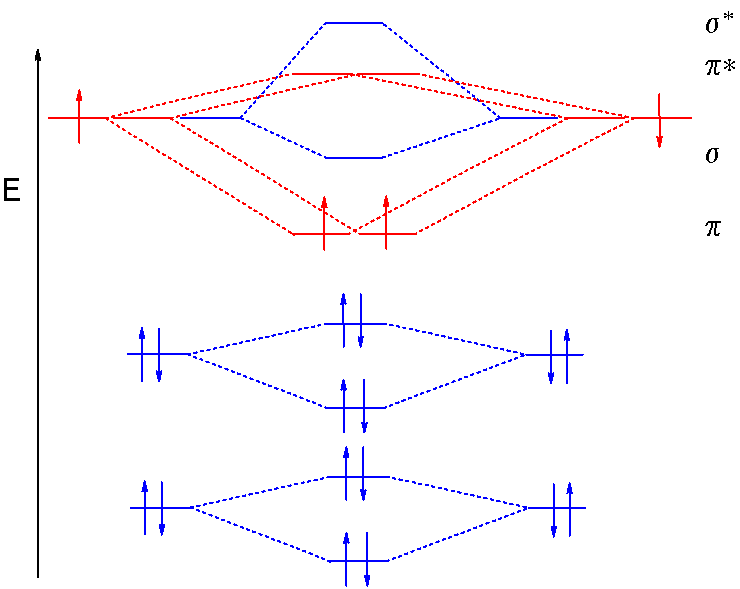
Neon atom has 10 electrons and its electronic configuration is. Fill from the bottom up, with 9 valence electrons total. However, we can predict that the be2 molecule and the ne2 molecule would not be stable. The molecular orbital theory explains how there are no unpaired electrons in the bonds between the two n atoms.
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves this is smaller than the 945 kj bond energy of n2— not surprising, considering that oxygen has two electrons in an antibonding orbital, compared. What is the orbital diagram for nitric oxide?? | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry source : According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be, as there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen.
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The bond order of is, 3. The molecular orbital diagram of are shown below. When two nitrogen atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.
This would also have two molecular orbitals formed from the overlap of 1s orbitals on the atoms, giving a molecular orbital diagram of the same appearance it is now possible to obtain the ground state electronic configurations of the diatomic molecules of the second period from o2 to ne2 by inserting. B, c, n, o, f, ne. There are two mo diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (n2, o2, ne2, etc). One of the molecular orbitals in this molecule is constructed by adding the mathematical functions for the two 1s atomic orbitals that come together.
One atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a n2 molecule will have 14 electrons so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond next 2 in 1s sigma anti bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma bon. Bellywelly asked in science & mathematics. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Individual atomic orbitals ao are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram.
Now note that even in this advanced molecular orbital theory a bunch of approximations is introduced, and the answer in general depends on at which level of theory calculations are done. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12. Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. As the bond order value for molecule is zero, it is unstable and cannot exist.
We can see this by a consideration of the molecular electron. The molecular orbital diagram shows the creation and filling of mos in a bond. A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. As it can be seen from the mot of o2 , the electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
The first major step is understanding the difference on the other hand, molecular orbital theory visions the electrons of a covalent bond to be delocalized over the entire molecule. The net contribution of the however, we can predict that the be2 molecule and the ne2 molecule would not be stable. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. Molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule :