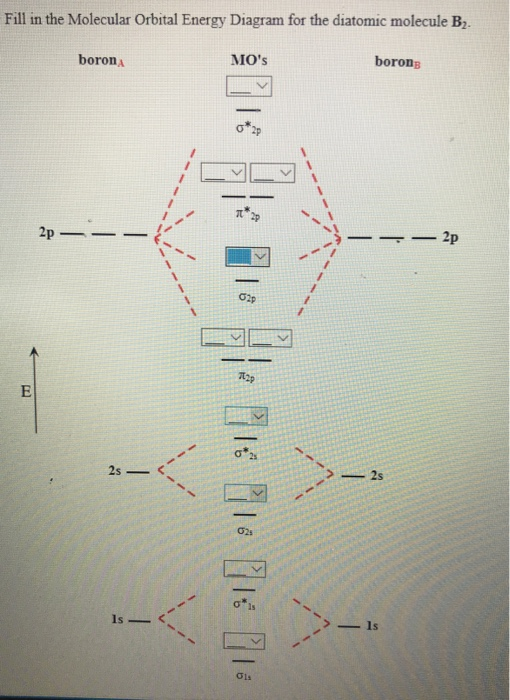
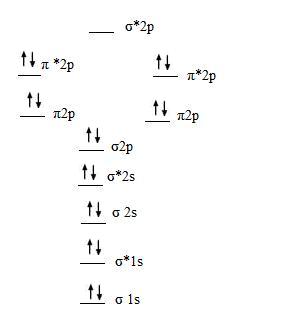Molecular Orbital Diagram Of B2
The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f.
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. A study in 1993 demonstrated that the prevalence was much higher than anyone thought. Draw a cartoon energy level. Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. In molecules, atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals which surround the molecule.
I also calculated the bond order of this molecule to be 3/2. We use the pauli exclusion principle and hund's rule to fill the orbitals in an aufbau process. The subscripts g and u refer to the parity of the orbitals g (german gerade, even) indicates that the orbital (or orbital combination) is symmetric with. This was on a quiz and i somehow got the bond order and the lumo indicated wrong.
Men were 24% and women. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. For example, to give you a glimpse at where we are headed. A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic.
- Trailer Wiring Diagram For 2006 Chevy Silverado
- 2017 Ford Super Duty Wiring Diagram
- Cobra 3190 Alarm Wiring Diagram
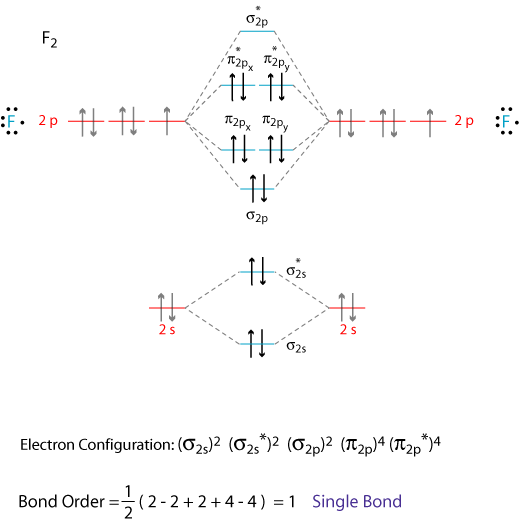
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for:(i) be2(ii) b2 and. The molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions experiments have shown that o2 and f2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but b2, c2, and n2 are best described by a model that. The orbital correlation diagram for diboron, however, is not generally applicable for all homonuclear diatomic molecules. Part a by drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2, c2, n2, o2, and f2, predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic.
Figure b a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for ferrocene. Molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms, that is, in terms of orbitals, orbital diagrams, and electron configurations. | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule : Mo occupancy and molecular properties for b2 through ne2.
He2 ∗ σ1s σ1s ∗ σ1s c. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. They combine to form the. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry.
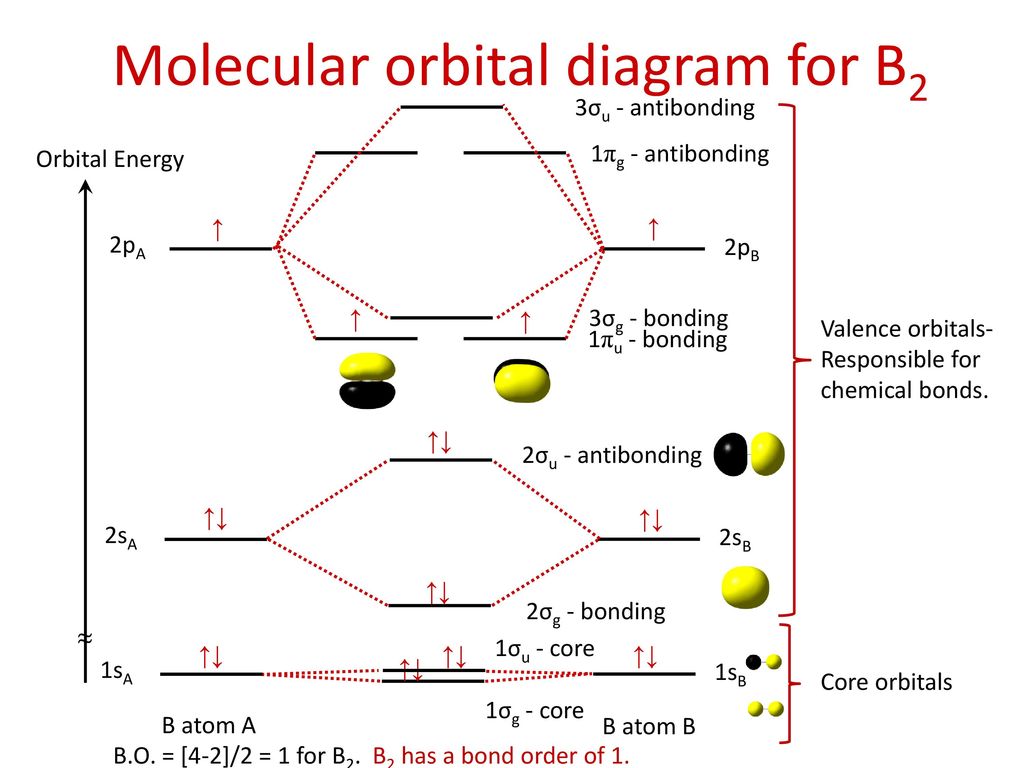
Determine whether each is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. • because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. For example consider b2 (each atom has an electron configuration of [he]2s22p), which has a total of 6 valence electrons.
The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories if you can understand the foundation and skeleton of the diagram specific to that molecule, then it will be easier and faster for you to draw it. 502 x 496 png 50 кб. Mo energy diagram for o 2. Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations.
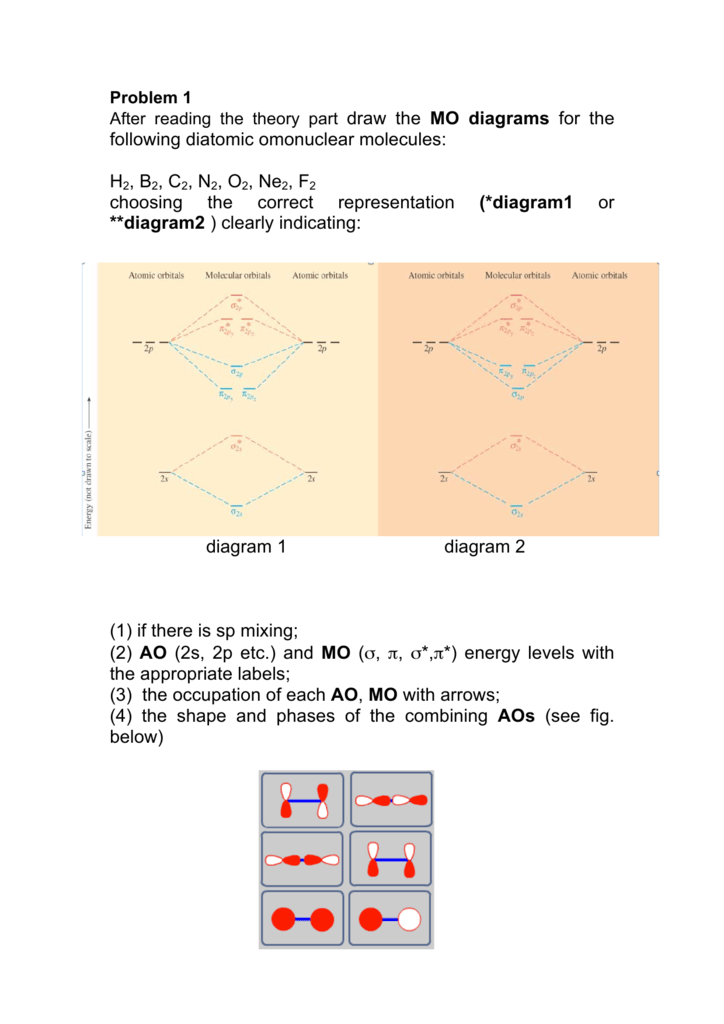
Molecular orbital theory provides an alternative model to valence bond theory that better describes the electron behaviour and physical/chemical properties of. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. Principles of molecular orbital theory. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in latex by means of the package modiagram.
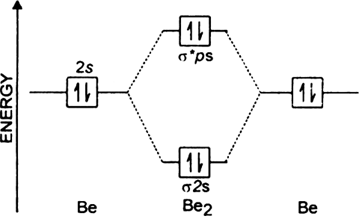
From the periodic table as we have already discussed the molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules of 1st two periods starting from hydrogen to neon. Similarly, the molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear diatomic compounds of the alkaline earth metals (such as be2), in which each metal atom has an ns2 valence electron configuration, resemble the diagram for the he2 molecule in part (c) in figure 9.20 molecular orbital. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
Start studying molecular orbital theory. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. We can ignore the #1s# orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Li2, be2, b2, c2, n2, o2, f2, and ne2.
• the following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. The finished valence molecular orbital diagram is pictured below. For information about the more traditional molecular structure. For example, homonuclear diatomic molecules of second row elements like li2, be2, b2 , c2, n2 , the σ 2pz mos is higher in energy than π 2px and π 2py mos.
Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. We have three valence electrons from each b atom, so b₂ will have six valence electrons. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that he2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Natural history, diagnosis, and emerging treatment options.
365 molecular orbital diagram key draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12. As well, i filled in the sigma 2px and pi 2py orbits. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, ψ, analogous to the.
Eight electrons from each oxygen atom add up to 16 electrons in the o 2 molecule. And (b) he 2 in which two of the electrons figure 4. = 1 stable diamagnetic b. This one pretty much applies to all main group elements heavier than nitrogen.
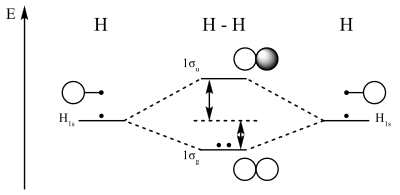
Molecular orbital energy diagrams for (a) h 2 showing both electrons in the bonding sigma mo; An mo diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each mo. Sleep apnea was known a few decades before the prevalence was understood.