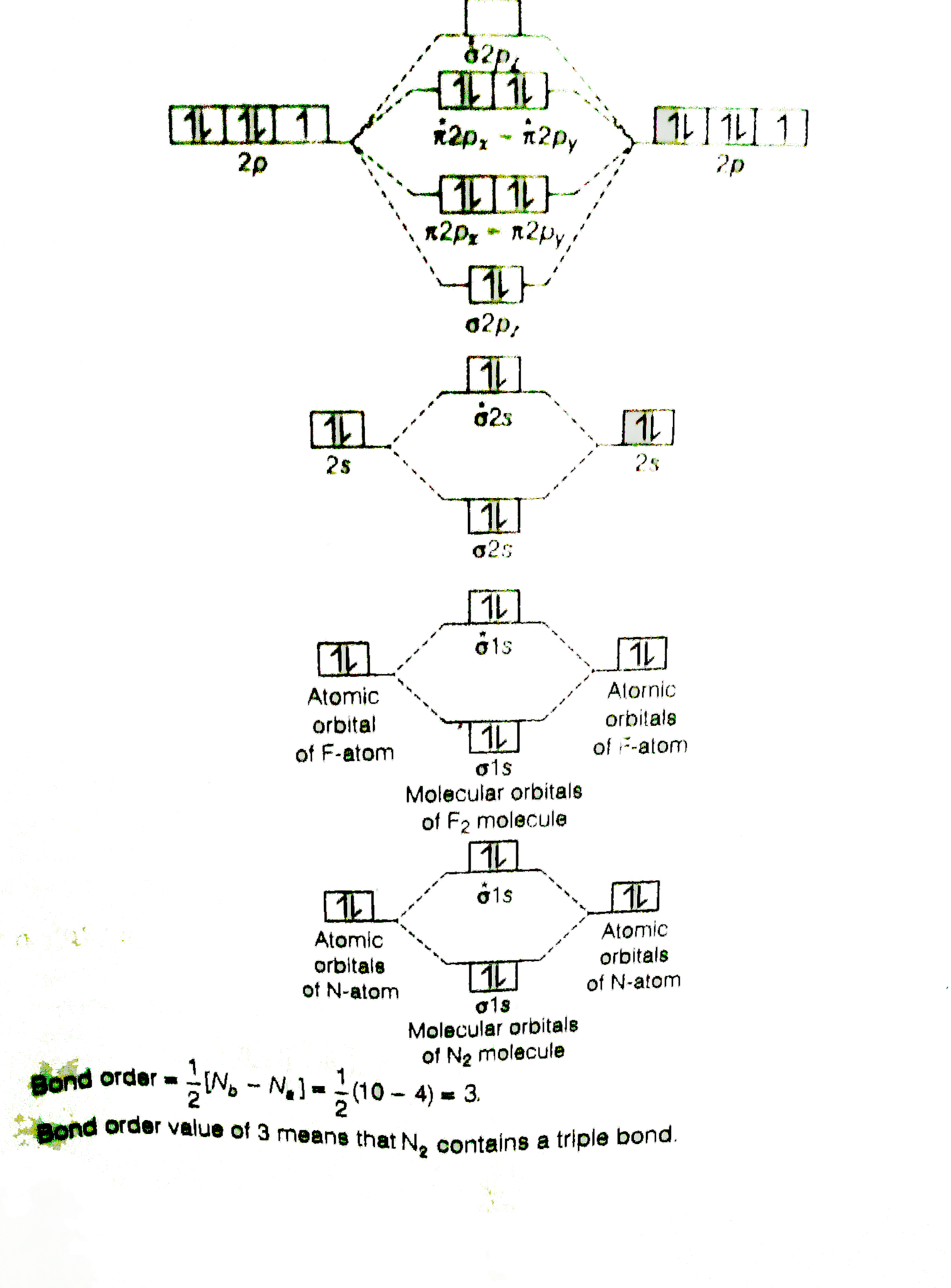Molecular Orbital Diagram For C2
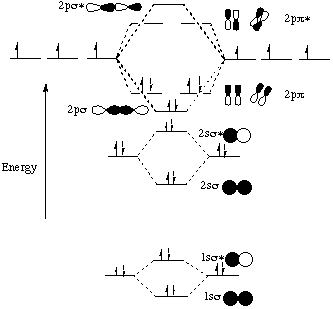
Sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4) so this is only according to molecular orbital theory right.
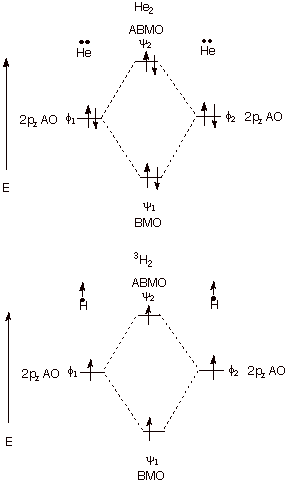
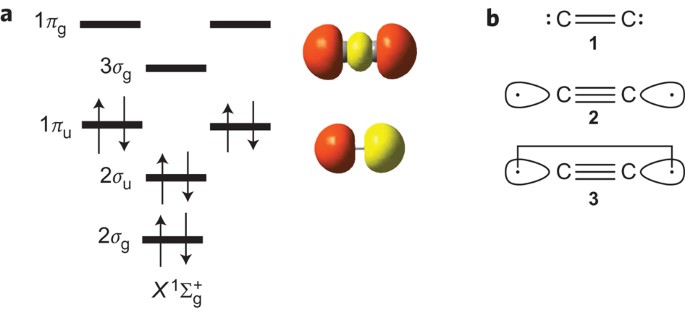
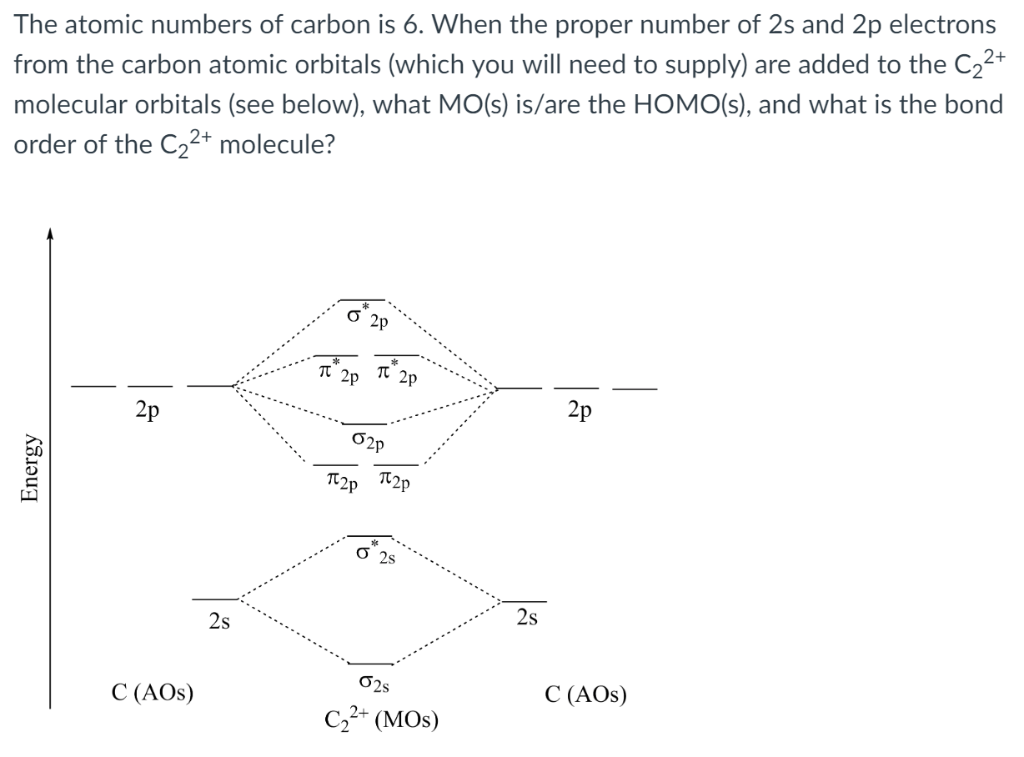
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer (c2). • because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Bonding order is 2, and it is diamagnetic. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the molecular ion, n2+.
X2, y2, z2 xy xz yz. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f.
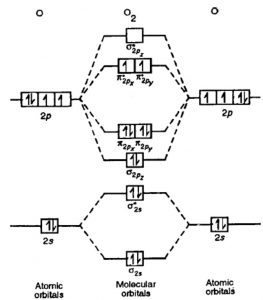
The molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions experiments have shown that o2 and f2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but b2, c2, and n2 are best described by a model that. In the h 2 molecule the two hydrogen electrons go into. The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a way of looking at the structure of a molecule by using molecular orbitals that belong to the molecule as a the energy diagrams are shown in figure 2. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories if you can understand the foundation and skeleton of the diagram specific to that molecule, then it will be easier and faster for you to draw it.
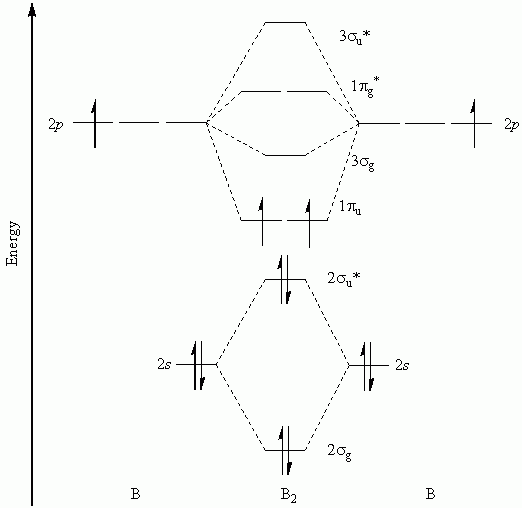
• all molecular orbital nodes must be symmetrically. .diagram for o2 is not the same as the mo energy level diagram for the c2 gas phase fragment. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. Draw a molecular orbital diagram and determine the bond order expected for the molecule b2.
Lumo = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital homo = highest occupied molecular orbital. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. This ion has a total of three valence electrons. A bonded carbon atom would need orbital overlap for each orbital present, sp2a, sp2b, sp2c and 2pz.
N2+ has a weaker longer bond than n2, but o2+ has a stronger, shorter bond than o2. Fill from the bottom up, with 8 electrons total. Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory. • when bonds are formed, atomic orbitals combine according to their symmetry.
For full credit on mo diagrams, • label increasing energy with an arrow next to the diagram. Molecular orbital theory (mo theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic.
Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer (c2). Calculate the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in simple molecules. Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations. • for any bonding orbital.
Molecular orbital theory provides an alternative model to valence bond theory that better describes the electron behaviour and physical/chemical properties of. It turns out that only when the bond lengths are relatively short (as in b2, c2, and n2) can the. Because the first two electrons completely fill. So again, it's drawn in the familiar pattern.
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the co molecule. This one is a lot easier and faster to draw. How do we create an mo energy level diagram for a heteronuclear diatomic species in which both atoms this is also true for molecular orbitals.
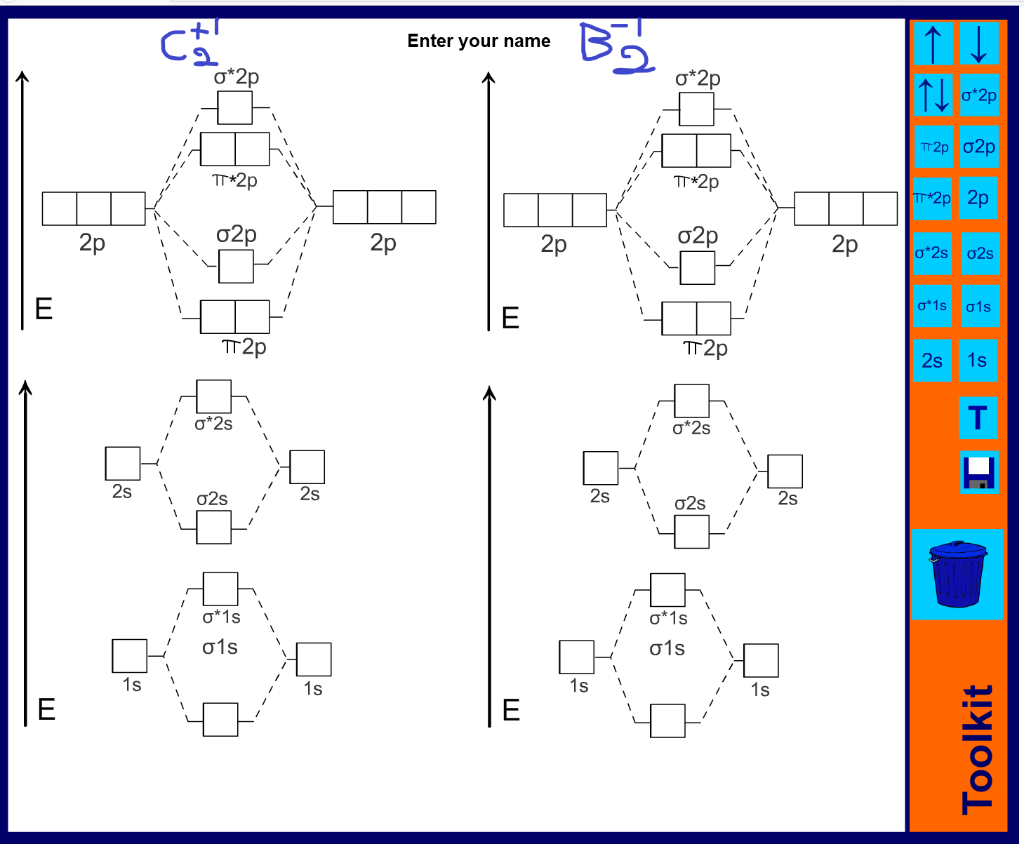
Li2, be2, b2, c2, n2, o2, f2, and ne2. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2p_(sigma), so that is where the extra electron will be added. C2v a1 z a2 rz b1 x, ry b2 y, rx.
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that construct a molecular orbital diagram of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate. Bonding order is 2, and it is diamagnetic. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in latex by means of the package modiagram. They consist of the symbol for the element in the.
The problem provides you with the mo diagram for the #c_2# molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule : For information about the more traditional molecular structure. Orbital diagrams give you all of the information you need about the electron configuration and occupied spin states for chemistry or physics, and are easy dot diagrams are very different to orbital diagrams, but they're still very easy to understand.
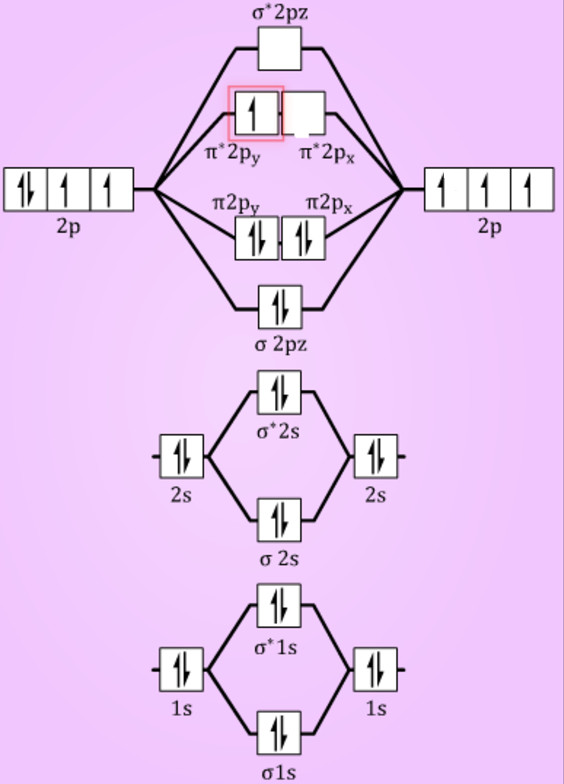
Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12. An mo diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each mo. • the following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals.
(c) their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules. You have the, here on this side you would have the so when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon. A1g t1u t1u t1u eg eg t2g t2g t2g. This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic be2+, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only.
• pay attention to whether the question asks for valence electrons or all electrons. Each hydrogen atom has one 1 s electron. Fill from the bottom up, with 8 electrons total.