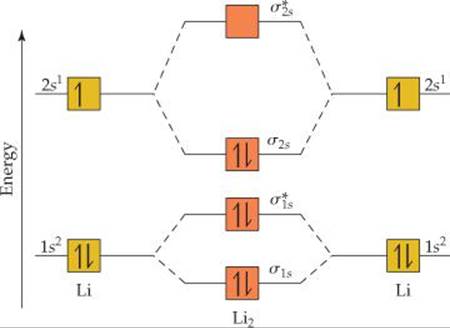
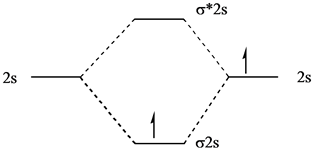Mo Diagram Of Li2
The diagram below shows the atomic orbitals, aos, on a pair of adjacent atoms interacting with each other.
Mo diagram of li2. Combine aos from central atom with those group orbitals of same symmetry and similar energy to make the mo diagram. Here we consider the molecular orbital diagram (mo) of #li_2#: And li2 mo of li.docx. Molecular orbitals for larger molecules.
They're not as intimidating as they may seem. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. Molecular orbital problems 1.a molecular orbital (mo) energy level diagram appropriate for homonuclear diatomic molecules from li2 to n2 is shown below. This is a bond between two lithium atoms, which have an electron configuration of.
Molecules of the first row A is more electronegative than b energy levels of the more electronegative element is lower than the less electronegative element : Ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur ad or nec facilisis. The following molecules are currently available:
- 2008 Dodge Ram 1500 Radio Wiring Diagram
- 2001 Chevy Silverado Secondary Air Injection System Diagram
- Lincoln Ls Rear Suspension
And nc state college of sciences foundation. Use simple lcao (linear combination of atomic orbitals) mo theory. Fu s a molestie c a. Fu e s a mo a.
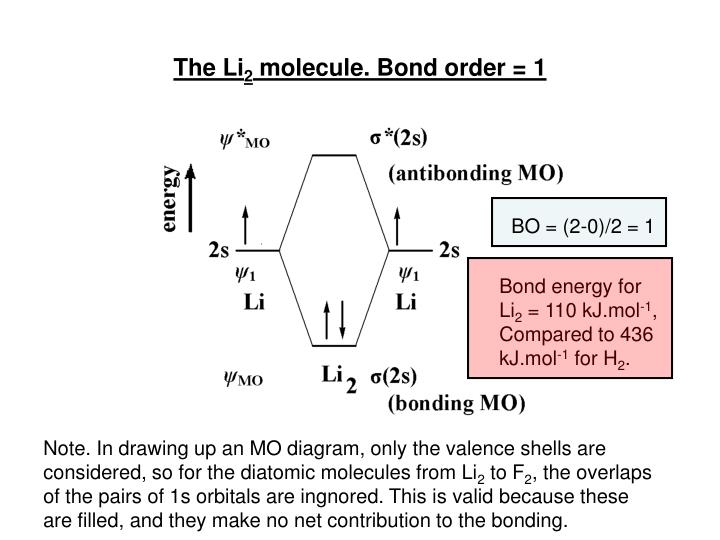
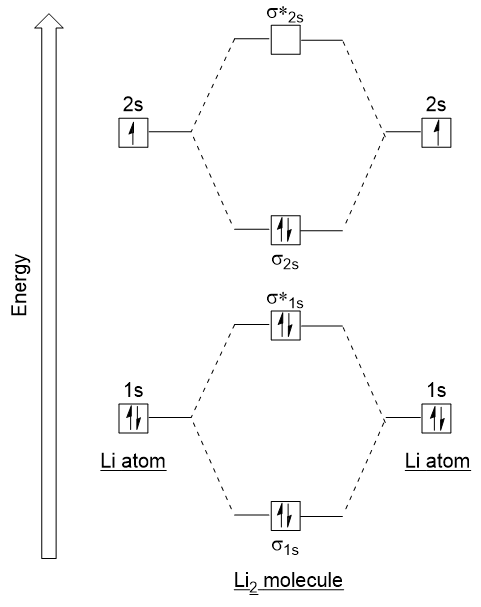
For now, we're only covering homonuclear mo diagrams which involve the diatomic molecules composed of the same element. The last diagram presents the molecule dilithium (li2). The bond order can be calculated in a simple manner. The molecule is, in fact, present in.
The mo diagram of hcl that includes all the valence orbitals of the cl atom is shown in fig. A is more electronegative than b energy levels of the more electronegative element is lower than the less electronegative element s: Li(0) 2s^1 overlap of the two 2s aos results in a. Two of the cl valence orbitals (3px and 3py) have the wrong symmetry to interact the picture on the left results from mixing of the σ2s and σ2p mo's, which are close in energy for li2, be2, b2, c2, and n2.
Fu gue vel l a. Relative orbital energies in o. The 1s electrons do not take part in the bonding, but the 2s electrons fill the bonding orbital. Bond order of = li2 1 ( n b − na ) 2 1 = ( 4 − 2) 2.
Energy level diagram for b2,c2 and n2. We will predict their bond order and see how the energies of the different orbitals change. Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for li2, be2, b2, c2, n2 are different the molecular orbital theory of li2 to f2 gives a graphical explanation. There will be nothing to attract the nuclei together and the mo is (said to be) antibonding:
Note that ∆e * > ∆e. We will also compare our predictions to experimental evidence. And the two electrons of the 2s orbitals will occupy the bonding mo, leaving the antibonding mo empty. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons.
Using the mo diagrams shown in figure 11, we can add in the electrons and determine the molecular electron configuration and bond order for each of the because both valence electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the li2 molecule to be stable. Li2+ bond order = 0.5 li2 bond order =1 hence li2+ must be unstable than li2 but then why li2 is more stable than li2+. Lowest unoccupied mo (lumo) highest occupied mo (homo). Bond order 1 = single bond.
• since lithium is in the second period, the mo diagram must. Higher contribution from a2s : A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. Mo diagrams look like this:
Molecular orbital theory, bonding & antibonding mo, bond order, homonuclear diatomic molecules. Mo diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram for short is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms the mo diagram for dihelium (2 electrons in each 1s ao) looks very similar to that of dihydrogen but instead of 2 electrons it is now required to place 4. Use the mo diagram you have drawn in problem 4.17 and the data about $\mathrm{li}_{2}$ in table 4.9 to say what you can about the bond order, the bond dissociation enthalpy, the bond length and the magnetic properties of the oxidized product. Involve the formation of mo's from the interaction of the 1s &.
Fu s ante s a mo a. An mo energy diagram an mo diagram for the combination of two s orbitals of the same energy. Consider the mo diagram for li2. Dilithium, li2, is known in the gas phase, it has a bond order of one, and it has homo + lumo fmos
The elements we're covering will be the ones in period 2, from `li` to `f`. • the result is a mo diagram that forms a σ(1s) and σ(2s). Answer the following with reference, when appropriate, to the diagram. Mo diagrams for linear and bent molecules.
Higher contribution from a2s s*: Mo diagram he2 c 2014 advanced instructional systems, inc. There are two mo diagrams we. The (100x)(0.75li2s0.25p2s5)fes (mol%) samples were prepared by mechanical milling of a mixture of crystalline powders of li2s, p2s5, and fes for 40h.
The results showed that the compound li 2 moo 4 ·6na 2. Assume z is the internuclear axis.