Magnesium Chloride Bonding Diagram
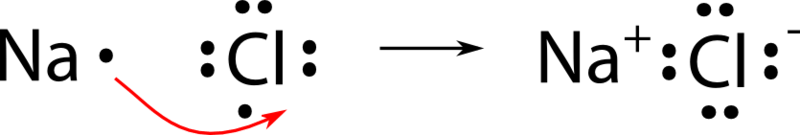
Ionic bonds are formed when positively and negatively charged ions are held together by electrostatic the number of charges on the ions:
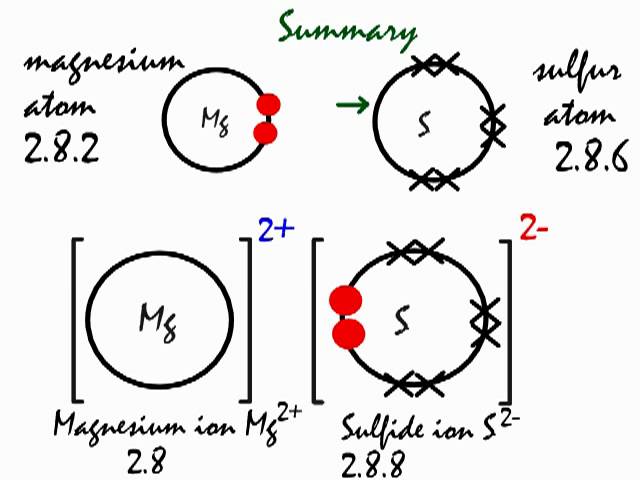
Magnesium chloride bonding diagram. The hydrated magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea water. Magnesium chloride must be heated until it is molten before it will conduct electricity. Magnesium bonds with fluorine to make magnesium 4. It can achieve an octet by gaining one valence electron to form cl⁻.
Magnesium chloride,mgci2,also known as chloromagnesite, is a colorless crystalline solid. Carbon tetrachloride does not conduct electricity. The ionic charge is shown on the centre of only one of the ions. Anhydrous mgcl2 contains 25.5% elemental magnesium by mass.
A (magnesium and oxygen undergo ionic bonding). There are many compounds which have ionic bonds. Sodium chloride and magnesium chloride are ionic and consist of giant ionic lattices at room temperature. So two chlorine anions form an ionic bond with one magnesium cation for form mgcl2, a neutral chemical compound.
- Fuse Box Diagram For 2005 Ford Focus Zx4
- 2012 Jeep Wrangler Speaker Wiring Diagram
- 2010 Vw Eos Fuse Box Diagram
Magnesium chloride is the name for the chemical compound with the formula mgcl2 and its various hydrates mgcl2(h2o)x. Metallic bonding is the electromagnetic interaction between delocalized electrons and. For example, sodium chloride, nacl, is an ionic compound. The final formula for magnesium chloride is mgcl 2.
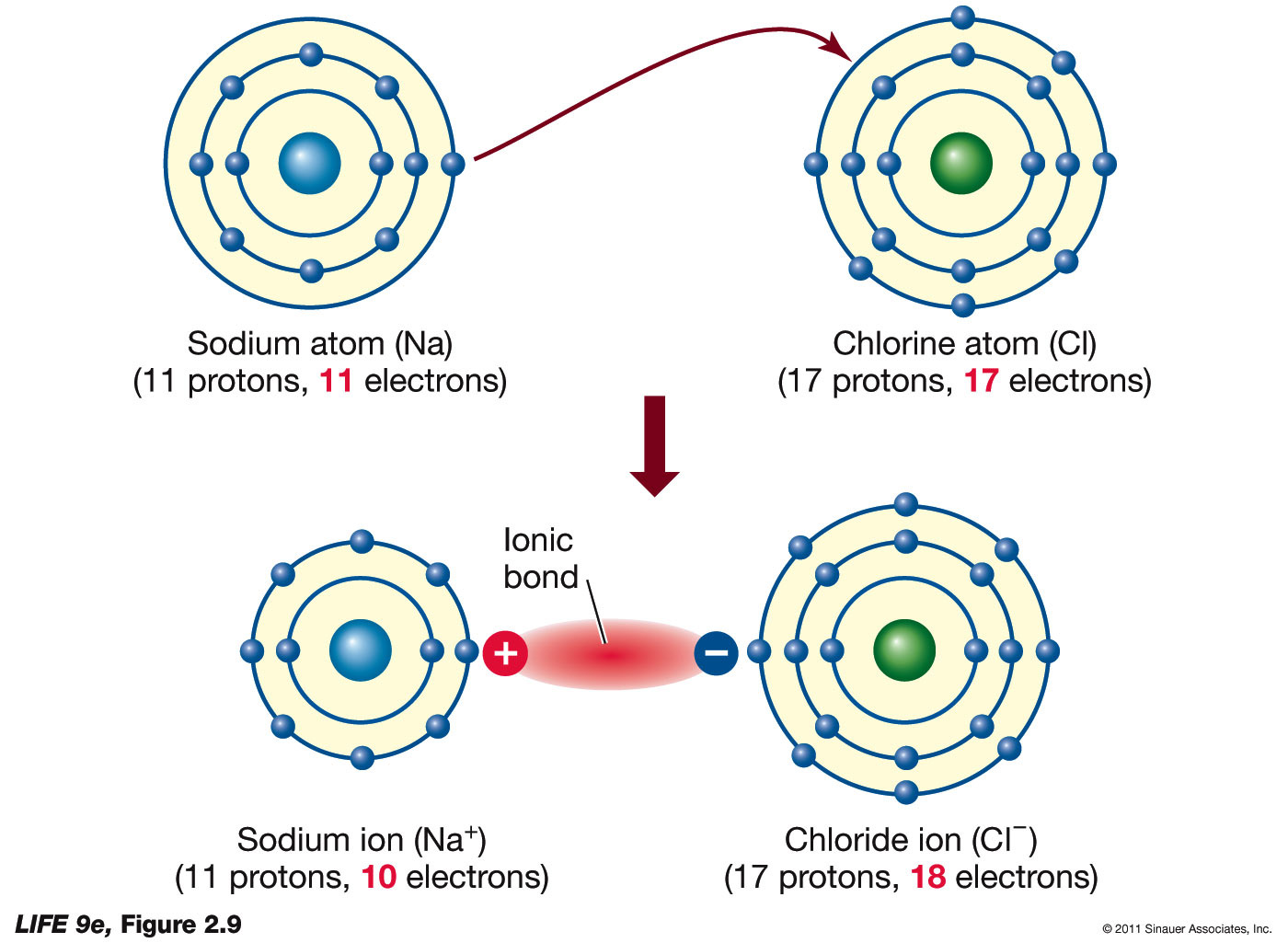
(b) use data from table above and your knowledge of the bonding in these metals to explain why the melting point of magnesium is higher than that of sodium. (a) the diagram below represents a part of the structure of sodium chloride. Magnesium chloride is a widely used reagent in chemistry and molecular biology as a source of magnesium ion. Ionic bonds are when atoms gain or lose electrons to become charged species (ions) that share an electrostatic interaction called an ionic bond.
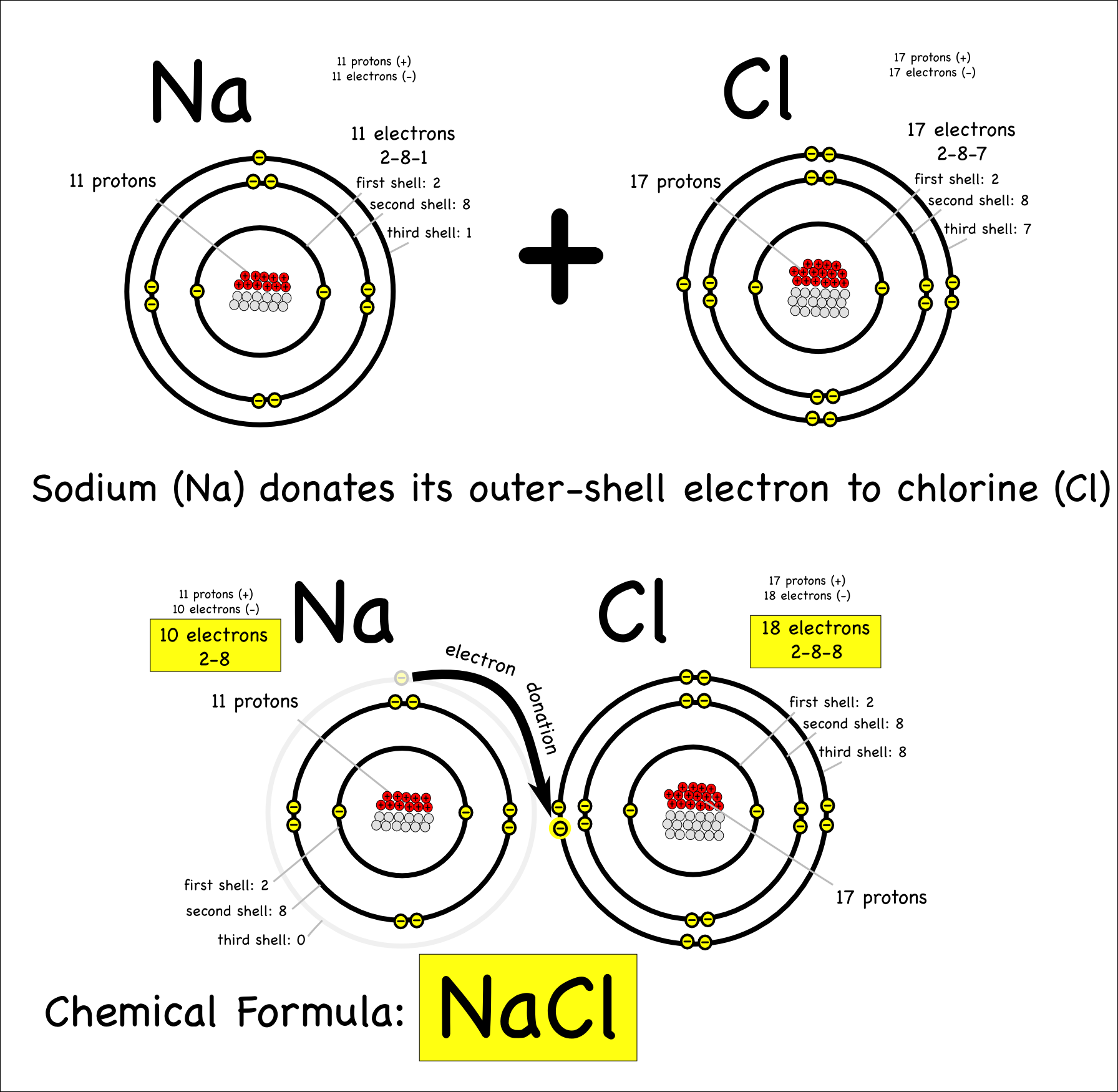
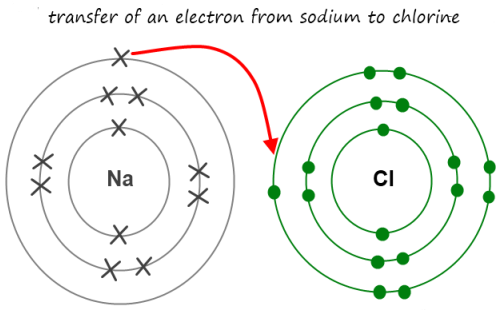
Magnesium dichloride is commonly known as magnesium chloride. The oppositely charges of the magnesium and chloride ions attract each other and form ionic bonds. Mg forms ionic bond to cl by donating its valence electrons to two cl atoms. They are called ionic compounds, and they are formed when metals react with nonmetals.
Sodium chloride crystals are brittle. Magnesium chloride is the name for the chemical compound with the formula mgcl2 and its various hydrates mgcl2(h2o)x. These salts are typical ionic halides, being highly soluble in water. Electrolysis separates the molten ionic compound into its elements.
Write down the electronic structure of a magnesium atom and use it to explain what this phrase means. These salts are typical ionic halides, being highly soluble in water. Magnesium atomic orbital and chemical bonding information. It causes less damage to concrete and is less corrosive to metals than other.
Magnesium has a variety of biological roles in enzymology, cell membrane and wall structural integrity, muscle cell physiology, and nucleic acid structure.1,2 magnesium is an essential. We will use sodium chloride as an example to demonstrate the nature of the ionic bond and how it forms. Sodium chloride has a high melting and boiling point. Magnesium is a group 2 metal so will lose two outer electrons to another atom to have a full outer shell of electrons.
In the formation of magnesium chloride (by direct combination between magnesium and chlorine), name the bond formed between the nitrogen atom in ammonia and the chloride ion is a coordinate bond. This diagram would be equally acceptable at a level. (draw it out if you need to!) Magnesium chloride is an excellent water soluble crystalline magnesium source for uses compatible with chlorides.
Magnesium oxide has exactly the same structure as sodium chloride. This site doesn't let you draw diagrams , so see. D (sodium chloride has a giant ionic structure made up of a lattice of positive and negative 2. Detailed revision notes on the topic ionic bonds:
A) a solid metal is often described as having an array of positive ions in a sea of electrons. You can use either name when talking about the compound. Sodium and magnesium chlorides are solids with high melting and boiling points because of the large amount of heat which is needed to break the strong ionic attractions. It is soluble in water and alcohol and is used in the ceramic and textile industries.
Fluorine can form either covalent or ionic bonds. Table salt is sodium chloride (nacl), which is a simple compound of two elements that are chemical bonds are formed when electrons in different atoms interact with each other to make an starting with magnesium and oxygen atoms, use lewis diagrams to show the formation of the ionic compound. Magnesium chloride cannot be formed by covalent bonding because there is a metal element. The slideshow shows dot and cross diagrams for the ions in sodium chloride, magnesium oxide and calcium chloride.
Mgcl2·6 h2o in distilled water and make up to 100 ml. An ionic compound contains positive and negative ions. Which statement correctly explains how magnesium and chlorine combine to form magnesium chloride? Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools.
Details of the ionic bonding of magnesium chloride and calcium chloride. Covalent bonding occurs only when two or more the bonding in magnesium metal is known as metallic bond. Magnesium chloride is highly soluble, reduces water activity, and is chaotropic (i.e., disrupts hydrogen bonds in water), imposing a potential limit to life on earth (hallsworth et al., 2007). Magnesium has atomic number 12 (so has electronic configuration 2.8.2).
The electrons from one atom are shown as dots, and the modelling ionic bonding.