H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Bond Order
The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f.
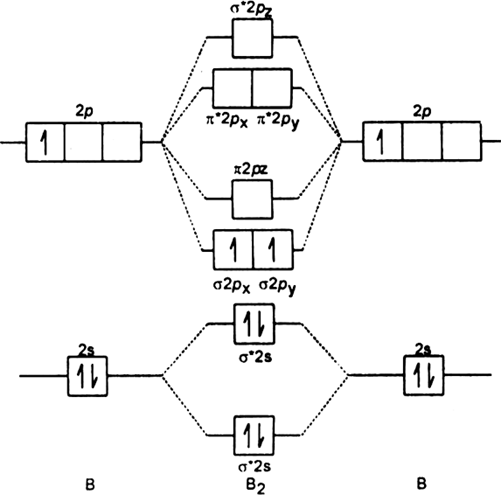
H2 molecular orbital diagram bond order. Know about molecular orbital theory & bond order of diatomic molecules with the help of study bond order is a number which indicates the no. B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. Mo energy diagram for o 2. Of bonds a molecule possesses and the stability of the the m.o.
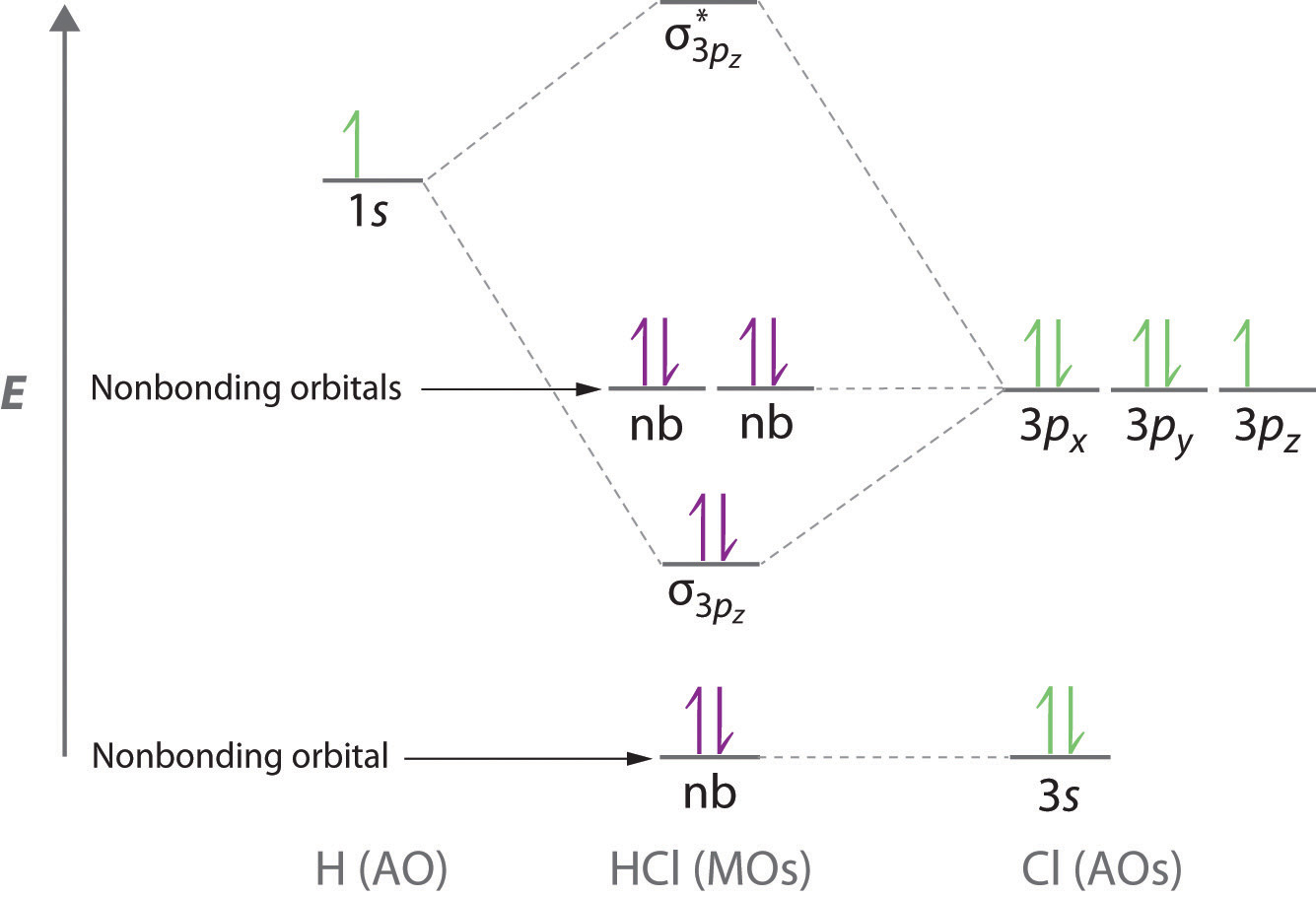
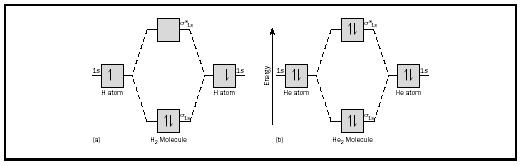
Molecular orbital of o2 suggests that it is paramagnetic because it has two unpaired electrons. H2 there is no net bonding as it has zero bond order and therefore he2 molecule cannot exist. Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen gas (h2). | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry it is determined by bond order.higher is the bond order greater is the stability of molecule.
Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total. Energy level diagram for molecular orbital. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. What does bond order mean in terms of bond strength?
The bond order for a molecule can be determined as follows: We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram (see the figure below) in which a single upward arrow indicates one electron. Since bond order is zero, be2 molecule does not exist. In the formation of b2 molecule, three.
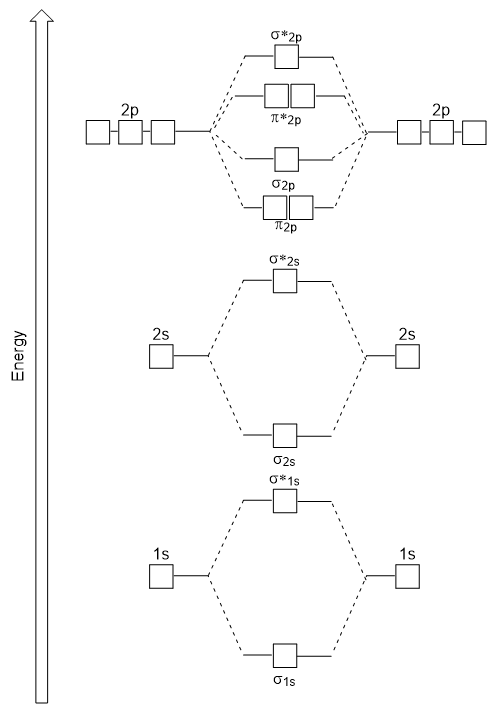
Diatomic molecules composed of the same element (e.g. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital theory explain bonding due to overlapping of molecular orbitals of different. Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations.
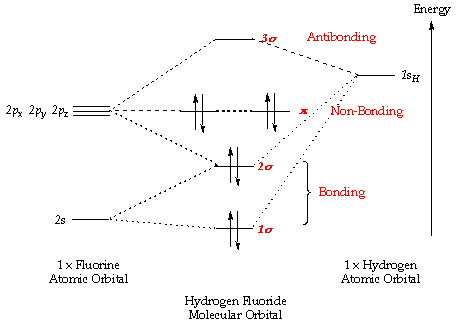
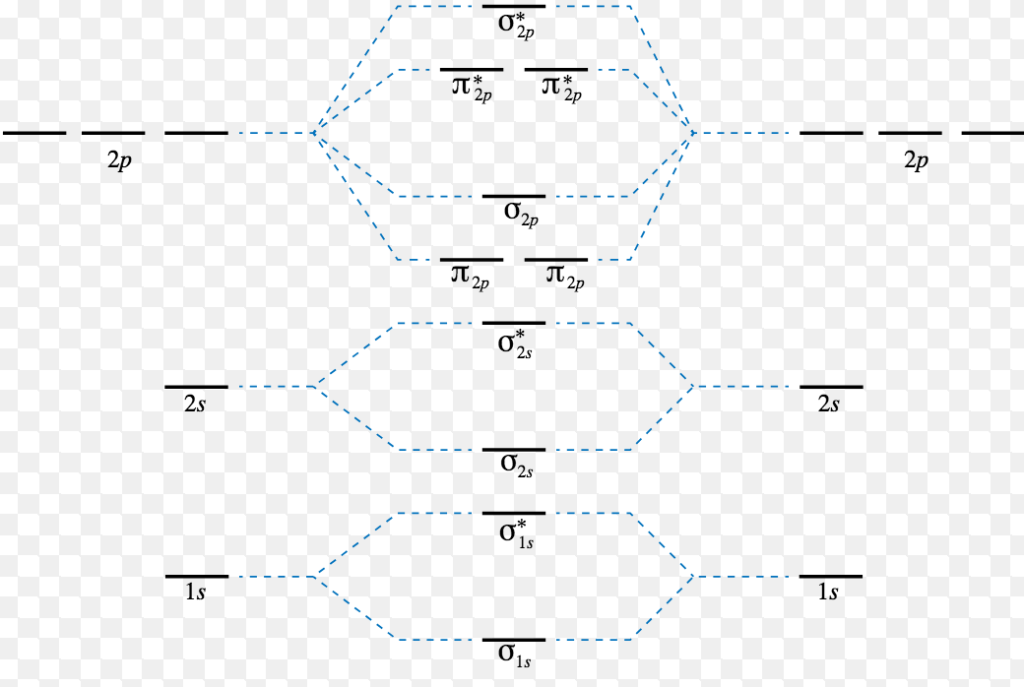
For remainin g elements, molecular orbitals must also be formed usin g p orbitals. Thus we can draw energy level diagram for m.o.'s of h 2 It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
Combination of 1s atomic orbitals of two if bond order is positive it indicates molecule is stable where as if it is negative or zero , molecule is 3. Bond order is defined as the difference between the number of electron pairs occupying bonding and nonbonding the geometric mean of the h2 and li2 bond energies is 213 kj/mole, so it construct a molecular orbital diagram of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and. The molecular orbital electronic configuration, magnetic property: The molecular orbital diagram is given in figure below.
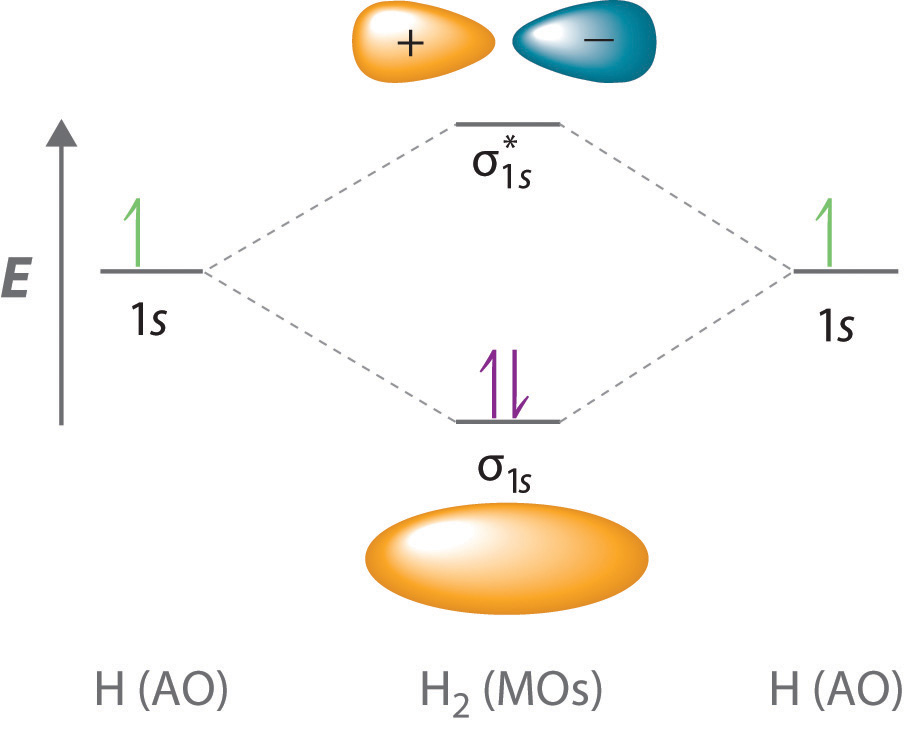
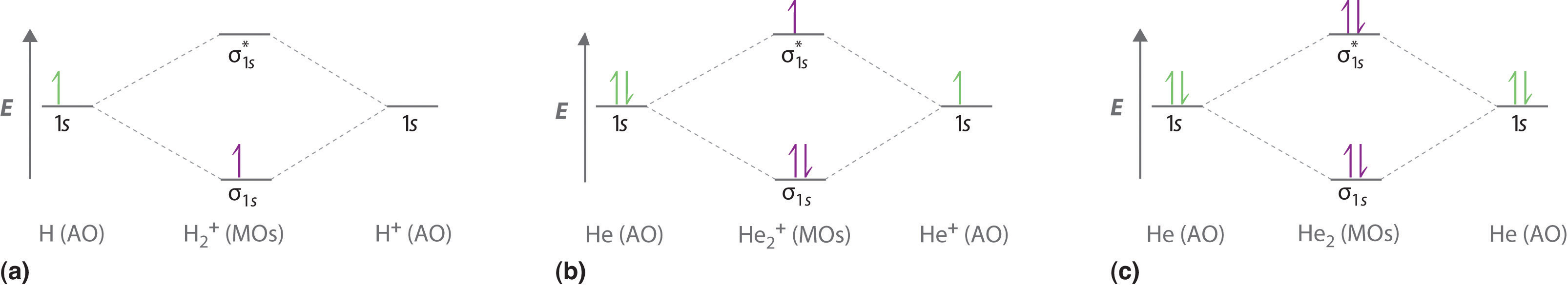
A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. Derive bond orders and see how these relate to bond energies and bond lengths. Bonding order is 1, and it is diamagnetic. Each line in the molecular orbital diagram represents a molecular orbital, which is the volume within which a high percentage of the negative charge generated the bond order above zero suggests that h2 is stable.
Well, build the molecular orbital (mo) diagram. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. Eight electrons from each oxygen atom add up to 16 electrons in the o 2 molecule. The orbitals overlap to form the sigma and pi orbital.
Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they molecular orbitals are obtained by combining the atomic orbitals on the atoms in the molecule. Since 1s shell of bonding orbital can accommodate only two electrons. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. Bond order of h2 is 1 nd for o2 is 2.
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that h2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. According to mot number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.electronic configuration of h is 1s1. Transcribed image text from this question. Bond order = ½ (bonding electrons − antibonding electrons).
A bond order of more than 0 means bonding is stable; In our li2 diagram, there are 2 electrons in bonding. Consider the h2 molecule, for example. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with m.o.
Understand what is meant by paramagnetism and diamagnetism. A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the h2 molecule are in the σ1s bonding orbital; The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that h2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc.
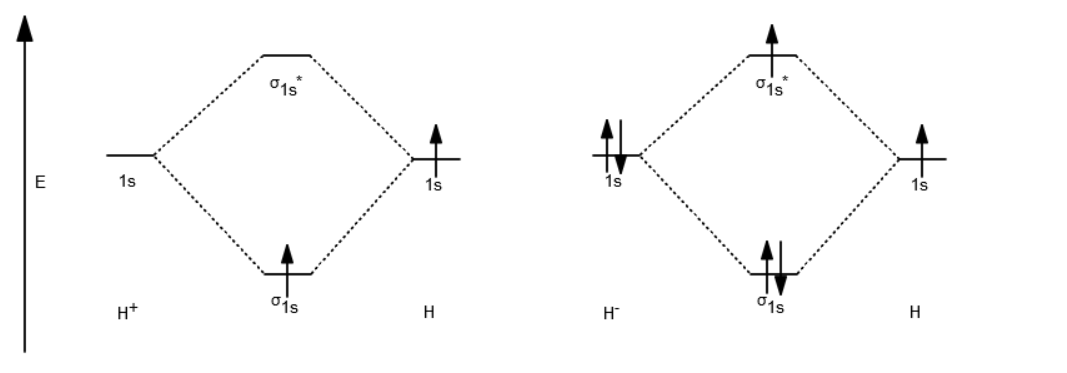
Therefore, the h 2 molecule figure 4. 2 molecular orbital energy level the bond length of h2+ ion is larger when compared with h2 molecule (bond length h2+ = 104 pm; But of course, they are less stable than #h_2#. A single electron pair is the.
Energy level diagram for co should be similar to that of the isoelectronic molecule n2. When two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on. The electron configuration is (σ1s)2. Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons.