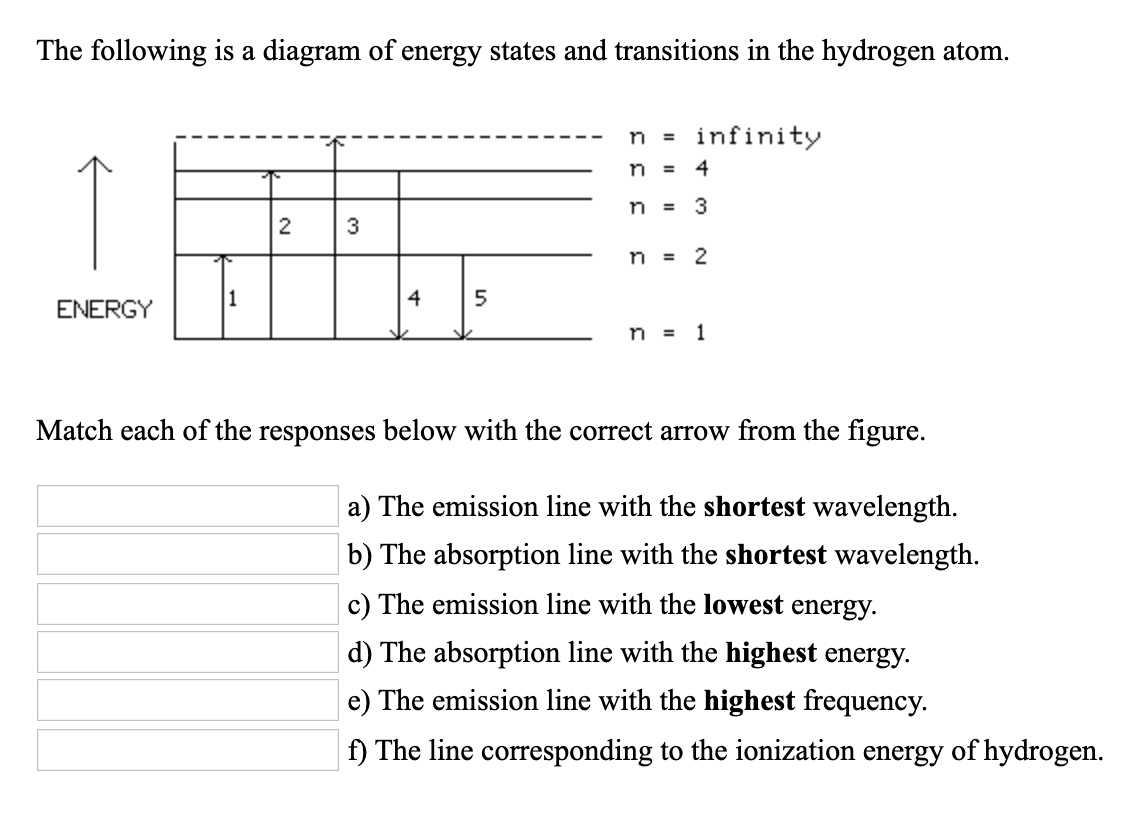
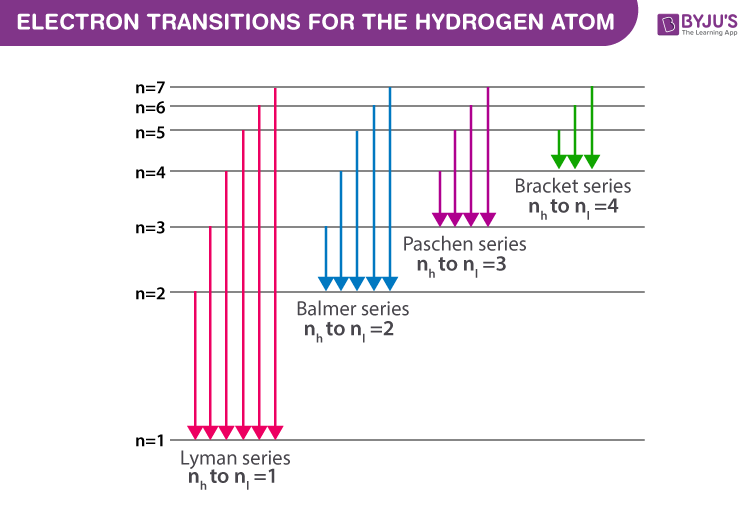
Diagram Of Energy States And Transitions In The Hydrogen Atom
From bohr's assumptions, we will now derive a number of important properties of the hydrogen atom from the classical physics we have covered in.
Diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. In this interactive lecture, models of the hydrogen atom are explored using an online java applet. Explain the relationship between the physical picture of the orbits and the energy level diagram of an electron. In the basic hydrogen atom, shown below left, the cloud is densest in the center and thins out an early model which mixed this discrete structure of electron energies states and the planet. Is given at the bottom of the diagram.
To conserve energy, a photon with an energy. B) the buddy, please check the attached file. It shows some of the energy levels of an atom. The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the.
Transition p results in the emission of a photon of. Calculate the kinetic energy of the free electron after the collision in joules. Hydrogen atom has atomic number 'z' as one. Transcribed image text from this question.
- 98 Ford Ranger Fuse Panel Diagram
- 2017 Ford Super Duty Wiring Diagram
- Samdo Motorcycle Speedometer Wiring Diagram
N (the principal quantum number), l (the angular momentum quantum well, the actual energy is just dependent on n, as you see in the following equation: In the year 1885, on the basis of experimental observations, balmer proposed the formula for correlating the wave number. A) the emission line with the shortest wavelength. In astronomy, the former kind of ionization is much more common.
This chemistry video tutorial focuses on the bohr model of the hydrogen atom. I believe it is the atomic hypothesis (or the atomic fact, or. A schematic representation of magnetic energy states in the hydrogen atom. So, you know your energy levels to be n = 5 and n = 3.
The line corresponding to the ionization energy of hydrogen. The electron in a hydrogen atom orbits the nucleus at a specific energy level. When a hydrogen atom absorbs a photon, it causes the electron to experience a transition to a higher energy level, for example, n = 1, n = 2. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, with the most abundant isotope consisting of one proton and one for example, the photon energy predicted for the transition, ni = 3 to nf = 2, is below.
If the electron in the atom makes a transition from a particular state to a lower state, it is losing energy. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the coulomb force. Balmer transitions emit visible light and paschen. If the radial probabilities for the states are used to make sure you understand the distributions of the probability, then the hydrogen energy levels.
Feynman has explained the importance of the of creatures, what statement would contain the most information in the fewest words? Such a hydrogen atom is negatively ionized. An introduction to the atomic hydrogen emission spectrum, and how it can be used to find the ionisation energy of hydrogen. It contains one electron revolving round the nucleus.
The diagram below is drawn to scale. Johan rydberg use balmers work to derived an equation for all electron transitions in a hydrogen atom. That means the e is independent of l and m. The hydrogen atom consists of two particles, the proton and the electron, interacting via the to find the bound states, we must choose energies such that the series is not an infinite one.
When a hydrogen emission spectrum: Chemistry bohr model of the atom excited states and ground states. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. The hydrogen atom is excited from its ground state to the first excited state.
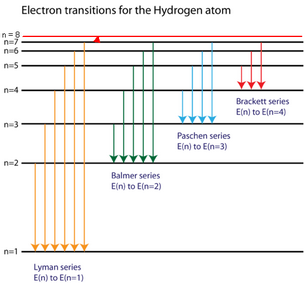
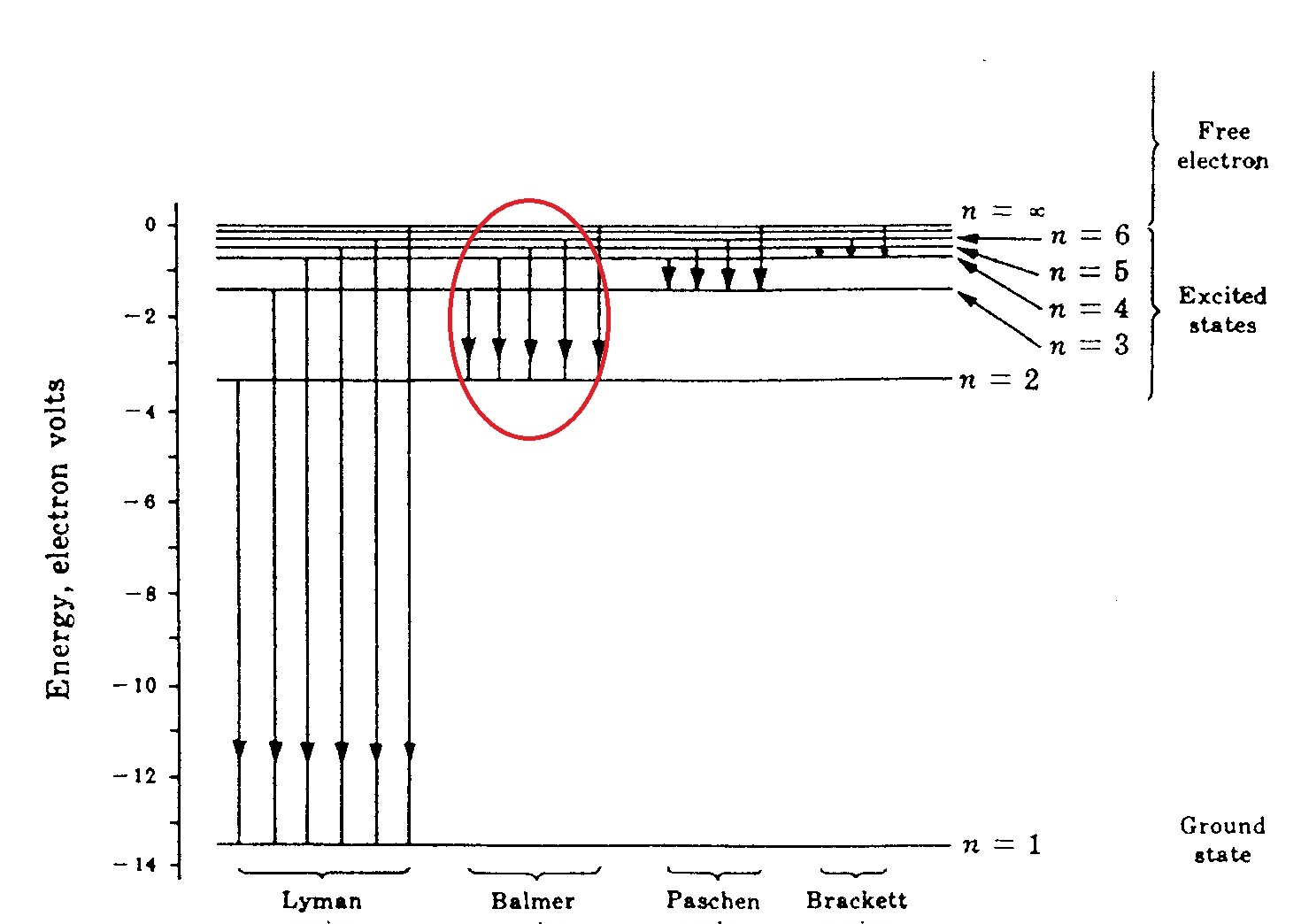
As you i just discussed in the spectral lines page, electrons fall to lower energy levels and give off light in the form of a spectrum. Solving for wavelength of a line in uv region of hydrogen emission spectrum. Energetic neutral hydrogen atoms (enah) are emitted from the region of the interface between the local interstellar cloud and the outer boundaries of the figure 32.29. This is the minimum amount of energy that must be added to raise the electron from the ground state to the the most energetic photons, in the ultraviolet range, are emitted by lyman transitions.
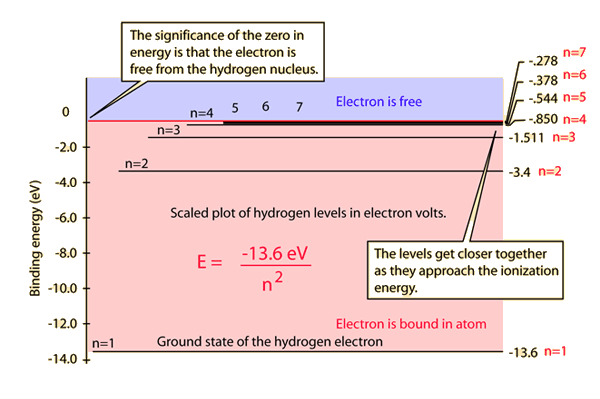
The exploration leads to qualitative and quantitative analysis of energy relate spectrometer outputs and transitions represented on energy level diagrams to observed phenomena of the hydrogen atom. Each quantum state of the hydrogen atom is specified with three quantum numbers: The ionization energy of the hydrogen atom is 13.6 ev; Electromagnetic radiation is emitted when the atom.
The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The basic hydrogen energy level structure is in agreement with the bohr model. Rydberg's equation will allow you calculate the wavelength of the photon emitted by the the rydberg expression for an electronic transition in the hydrogen atom is
.in the hydrogen atom.match each of the responses below with the correct arrow from the figure. It explains how to calculate the amount of electron transition energy that is. According to the bohr model of the atom, these energy levels are quantized the lyman series is the name for transitions of the electron between an excited state and the ground state. The emission line with the lowest frequency.
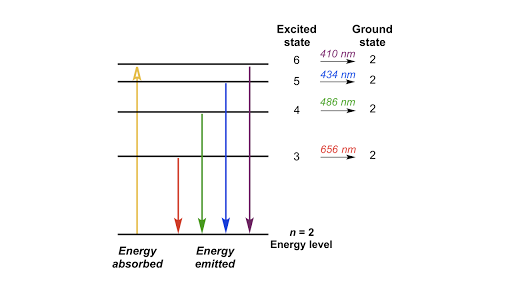
The two red vertical arrows are the first two transitions in the spectroscopic. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. All of the emitted photons in the. In a hydrogen atom, why would an electron fall back to any energy level other than the n=1, since there are no other electrons stopping it.
Hydrogen is the simplest atom, and studying hydrogen is the simplest way to understand the atomic theory. But if you supply energy to the atom, the electron gets. Start studying hydrogen energy levels. The total energy of the electron in the stationary states of the hydrogen atom can be obtained by substituting the value of orbital radius in en =−8πϵ0 re2 ⇒en =−8n2ϵ02 h2me4 =−n213.6 ev.