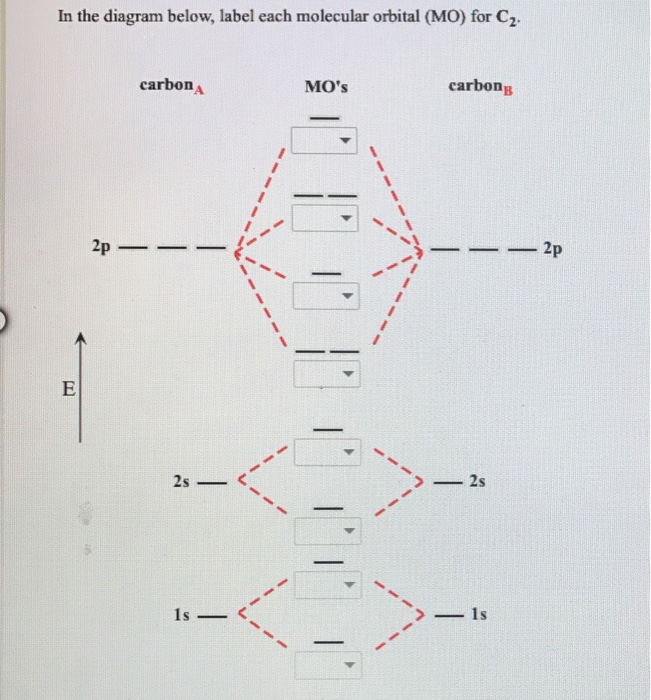
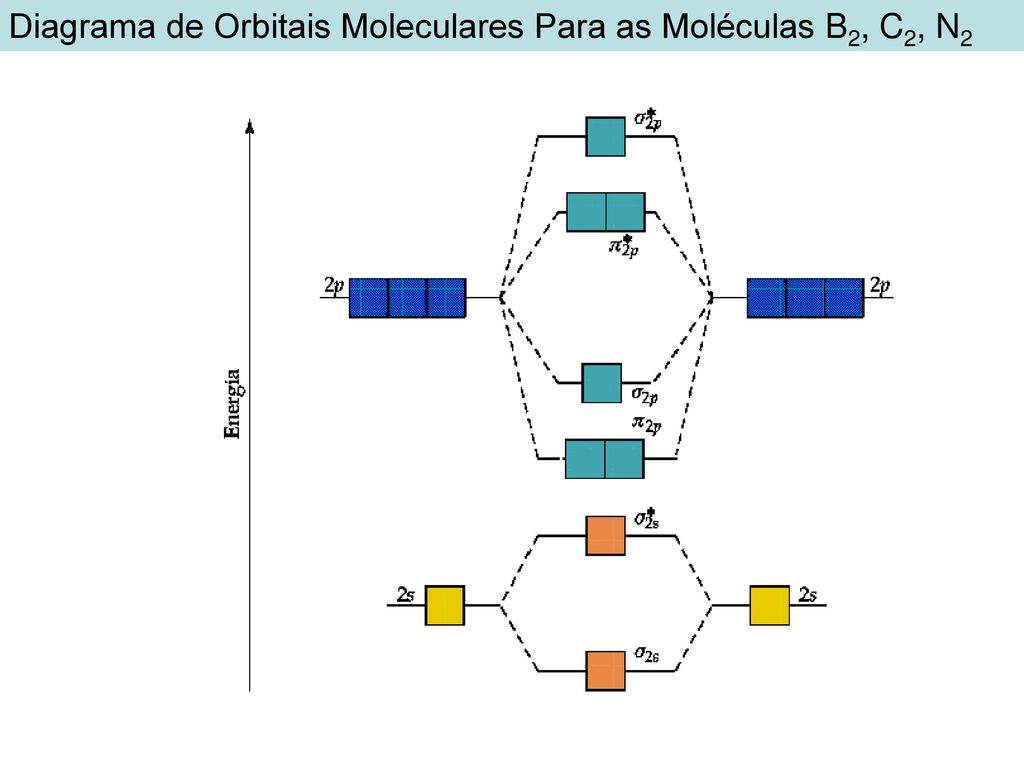
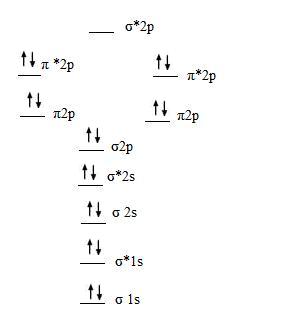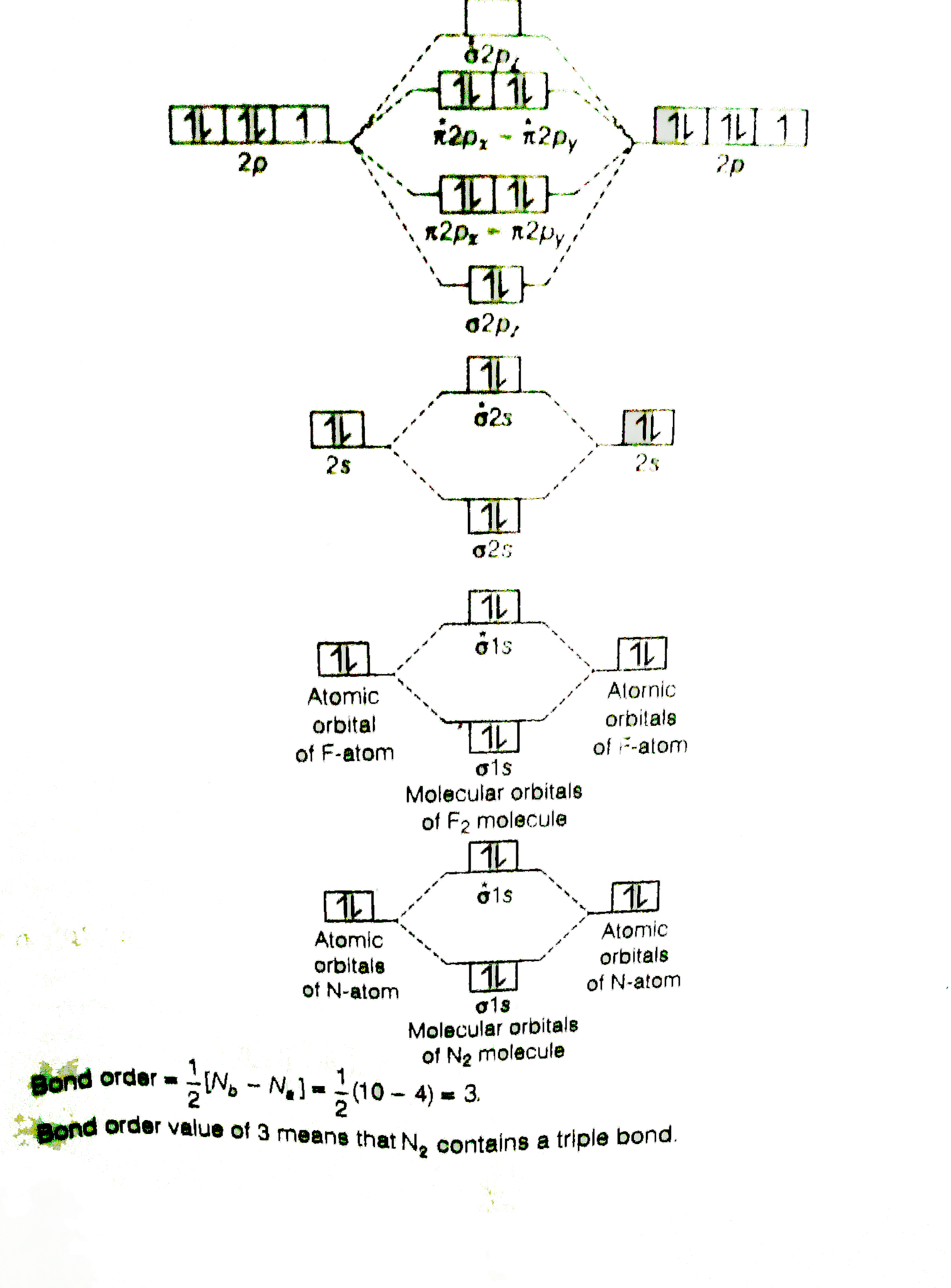C2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2p_(sigma), so that is where the extra electron will be added.
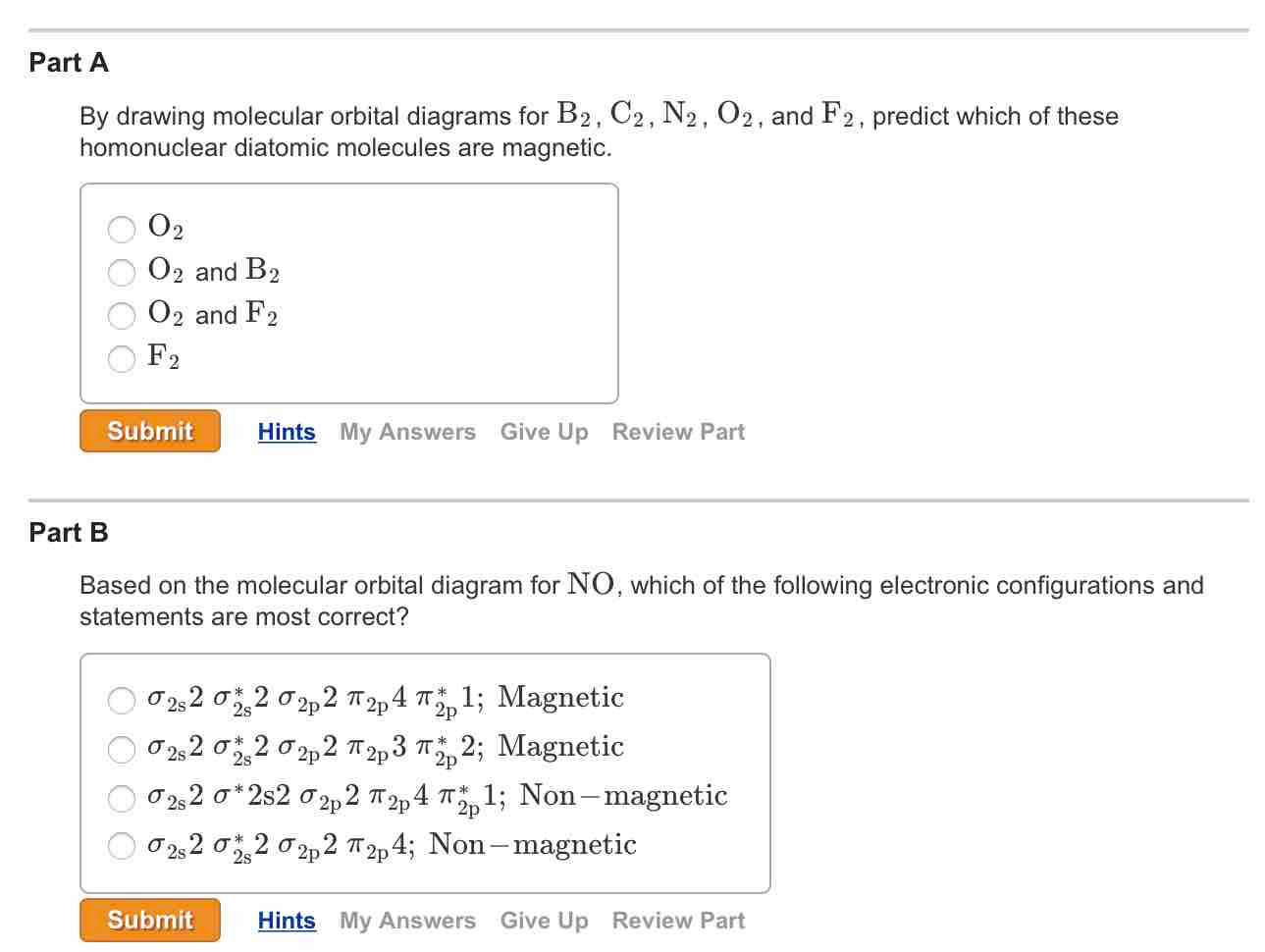
C2 molecular orbital diagram. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. The molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p experiments have shown that o2 and f2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but b2, c2, and n2 are best. | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry source : Draw the mo diagram for the sih 3 + cation.
Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory. Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the co molecule. Figure 8.35 the molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that h2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that he2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table:
A) write out the complete mo. Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for o2. Fill from the bottom up, with 8 electrons total.
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations in c2 there are two paris of electrons in the π bonding orbitals, so we have what amounts to a double bond here; Arrange the following ion terms in order of increasing energy: Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. In other words, the bond order in.
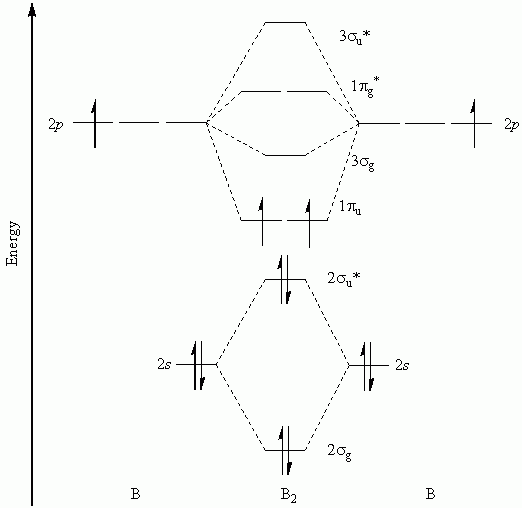
Now note that even in this advanced molecular orbital theory a bunch of approximations is introduced, and the answer in general depends on at. Once you have the molecular orbitals and their energy ordering the ground state configuration is found by applying the pauli principle, the. I have been taught that the mo diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. It turns out that only when the bond lengths are relatively short (as in b2, c2, and n2) can the.
Note, however, that these lcao diagrams are schematic, drawn to emphasize lcao construction rather than attempting to represent the orbital. Sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4) so this is only according to molecular orbital theory right. N2+ has a weaker longer bond than n2, but o2+ has a stronger, shorter bond than o2. An mo diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each mo.
Valence bond theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. How does the directional nature of orbitals affect the bond strength? Bond orders and stability of molecules. Polyatomic species like methane, ch4, can be described in terms of molecular orbital theory, however, the diagrams can be very difficult to visualise.
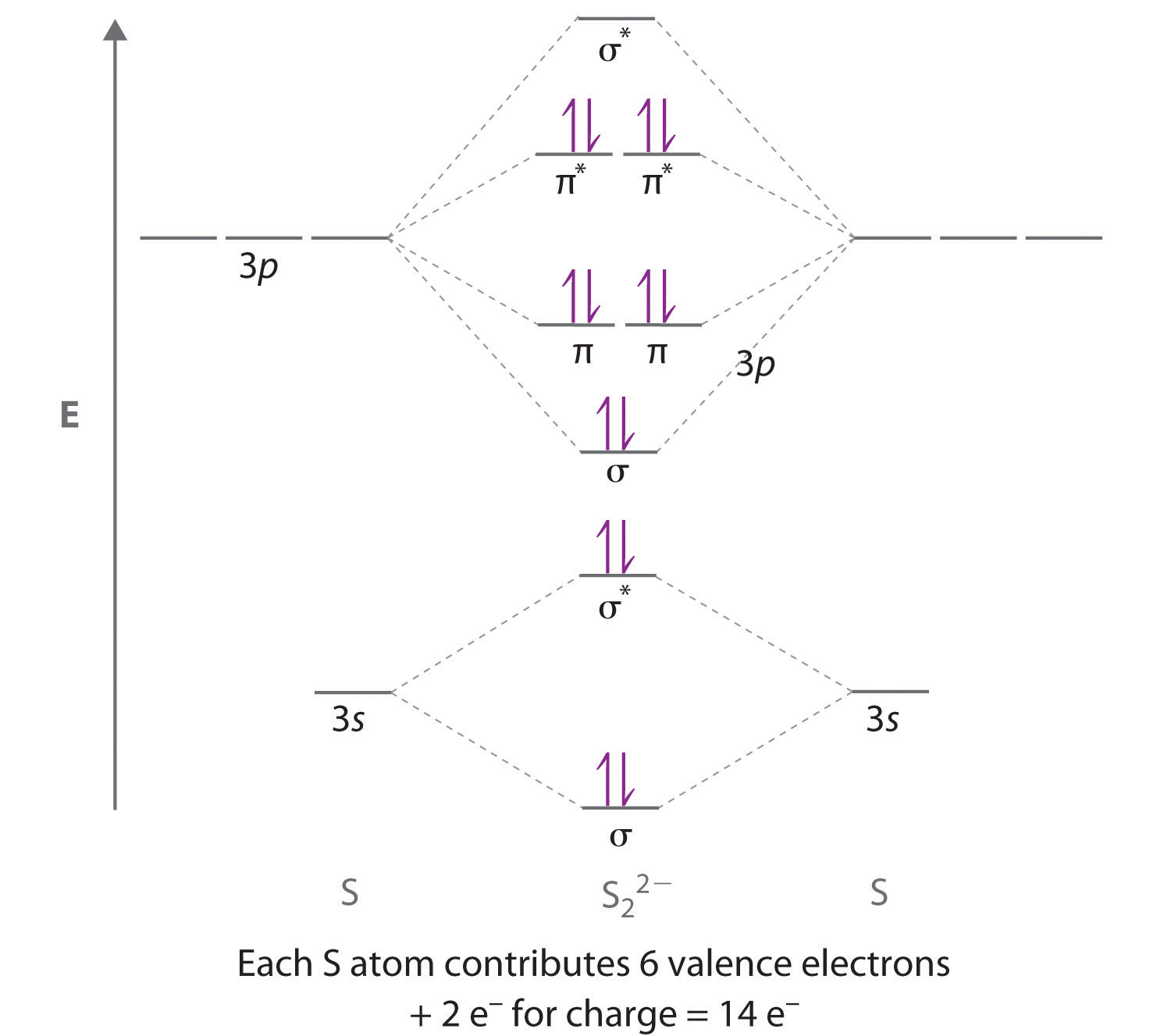
Eight electrons from each oxygen atom add up to 16 electrons in the o 2 molecule. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. Bh3 has a c3 principal axis of symmetry, 3 c2 axes (┴ c3), 3 σv. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f.
Mo energy diagram for o 2. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. Valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory.
Using your molecular models from part 3: Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. Why is it that the number of atomic orbitals used to generate molecular orbitals is equal to the number of molecular. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond.
What will be the molecular orbital diagram for nitrite ion? Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12. Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations. That no degenerate molecular orbitals arose in the above examples is a result of the fact that the c2v point group to which h2o and the allyl system.
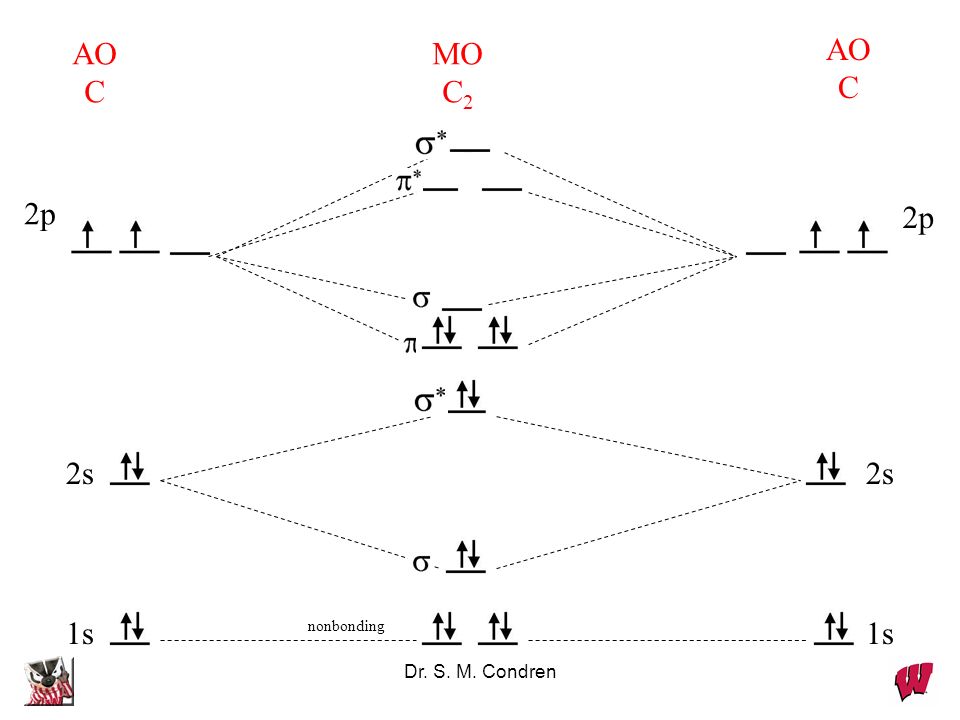
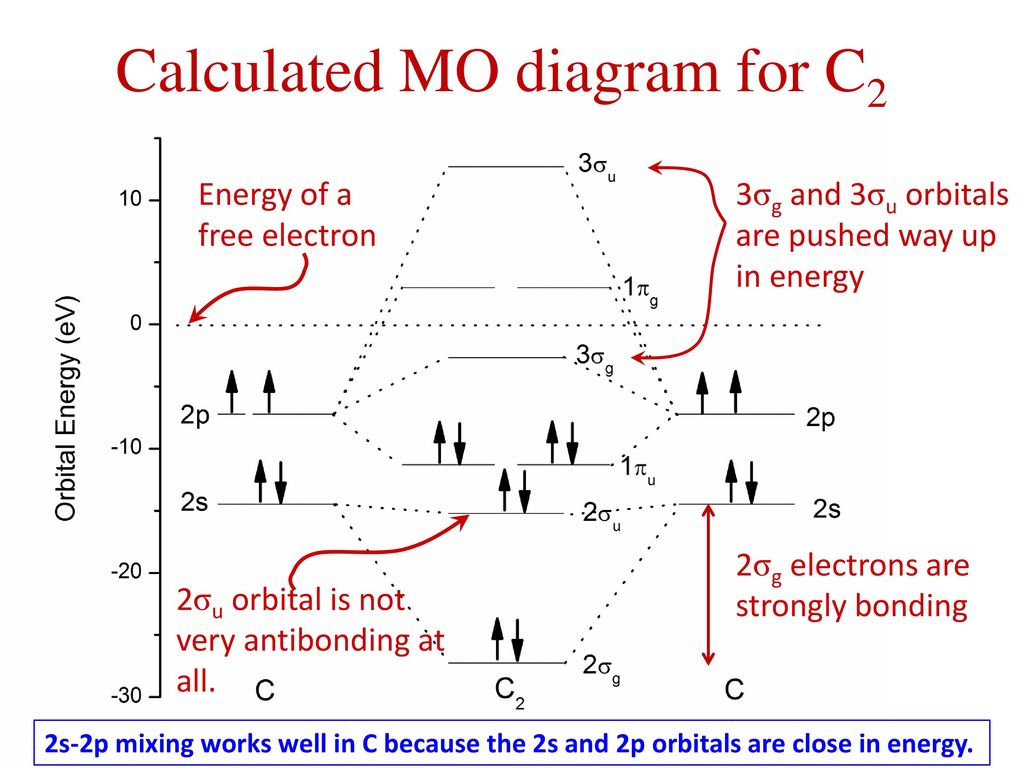
Unlike most texts on molecular orbital theory and quantum mechanics, this text treats polyatomic molecules before linear molecules before atoms. Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer (c2). Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, o2. Can you explain how atomic orbitals interact and give rise to molecular orb.
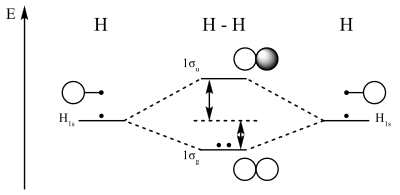
Bonding order is 2, and it is diamagnetic. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Bonding order is 2, and it is diamagnetic. Is h2 a viable molecule for the molecular orbital theory?
Fill from the bottom up, with 8 electrons total. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. The problem provides you with the mo diagram for the #c_2# molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram.
For information about the more traditional molecular structure. Calculate the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in simple molecules. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Last time you learned how to construct molecule orbital diagrams for simple molecules based on the symmetry of the atomic orbitals.
Each molecular orbital can only have 2 electrons, each with an opposite spin. Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer (c2). The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a way of looking at the structure of a molecule by using molecular orbitals that belong to the molecule as a figure 4. A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic.
Molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule : A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of.