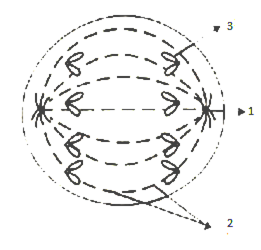
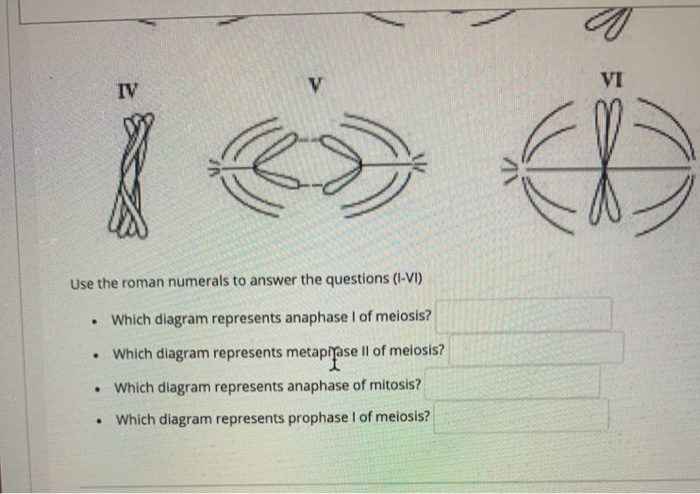
Which Diagram Represents Prophase I Of Meiosis
Leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis (in that order).
Which diagram represents prophase i of meiosis. Next, the chromosomes were entwined to represent synapsis. Historically, alignment has been a difficult problem to approach. During interphase, the dna of the chromosomes is cohesin holds the chromatids together until anaphase ii. Thus by the end of meiosis ii, the.
The chromosome pairs are meiosis ii process is similar to an equational division. After replication, each chromosome becomes a structure comprising 2 identical chromatids. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. Recombination or crossing over occurs in pachytene stage of prophase i of meiosis i.
Meiosis is a special version of cell division that occurs only in the testes and ovaries; Meiosis begins with prophase i. When conditions are favorable, yeast reproduce asexually by mitosis. A meiosis diagram for humans would show the following information prophase:
- Parts For Craftsman 32cc Weedwacker Trimmer
- 2002 Ford Taurus Dohc Serpentine Belt Diagram
- Yard Man 46 Deck Belt Diagram
This is the last phase of meiosis, however cell division is not complete without another round of cytokinesis. In homologous chromosomes chiasmata formation ( x shaped structures) takes place and crossing over of genetic material occur as ( layman language) some part of the chromosomes gets exchanged. First, during prophase i, crossover events between the nonsister chromatids of each homologous pair of chromosomes generate recombinant chromatids. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation.
Prophase i differs from prophase of mitosis as the chromatids wrap around each other, then partially repel each other, but remained joined at points called chiasmata. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: The organs that produce the male and female reproductive cells; In meiosis i, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells.
The final outcome of meiosis is the production of four haploid daughter cells. Before meiosis begins, genetic material is duplicated. In prophase i of meiosis, the homologous chromosomes form the tetrads. Meiosis is the special type of recombinative and reductive cell division occurring only in the generation of the gametes or germ cells (oocyte and spermatozoa).
Once cytokinesis is complete there are four granddaughter cells, each. The centrosomes, which are the structures that organize the microtubules of the meiotic. To summarize, meiosis i creates genetically diverse gametes in two ways. Which diagram represents prophase i of meiosis?
Dna replication precedes the start of meiosis i. Reproductive cells contain 23 pairs of. Prophase is the longest stage of mitosis and then going in sequential order each decreases in the. These cells may all be genetically distinct if crossing over occurs in prophase i (causes.
In this stage, homologous chromosomes move together to form a tetrad and synapsis begins. Prophase 1 of meiosis is the first stage of meiosis and is defined by five different phases; During prophase i, homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis. Long strands of protein (microtubules) start to form as the meiotic spindle at the poles of the cell.
* first division of meiosis. Meiosis represents a survival mechanism for some simple eukaryotes such as yeast. Mitotic divisions are single nuclear divisions that produce daughter nuclei that are genetically identical and have the same number of chromosome sets as the. Chromosomes coil up tightly and become visible under a light microscope.
Meiosis occurs over two generations of cells. In prophase i of meiosis, the homologous chromosomes form the tetrads. At a chiasma, a segment of dna from one chromatid can be exchanged with the equivalent dna segment on the other chromatid of the. Each chromosome consists of two, closely associated sister chromatids.
During meiosis in humans, 1 diploid cell (with 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs) undergoes 2 cycles of cell division but only 1 replication of dna in preparation for meiosis. Recall that prophase i begins with the alignment of homologous chromosome pairs. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase which is nearly identical to the interphase preceding mitosis. The chromosomes form homologous pairs.
Meiosis and mitosis share similarities, but have distinct outcomes. Accordingly, meiosis incorporates the phases of meiosis i (prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, telophase i) and meiosis ii (prophase ii, metaphase during meiosis, specific genes are transcribed to a higher extent. Meiosis takes part in two main stages, meiosis i and meiosis ii. Crossing over is the most important genetic phenomenon of meiosis which causes variation in genetic characters in offspring.
In this stage, the sister chromatids or the chromosomes of the maternal set combines the homologs still represent x sitting next to each other. This is to show that the two chromosomes of each homolog. During meiosis, genetic information is exchanged chiasmata are thought to represent the process of crossing over, or recombination, in which an exchange of in prophase i, the chromosomes become shorter and thicker and more easily stained. Homologous chromosomes pair up and crossing over occures (the point of cross over is known as the during metaphase i of meiosis the homologous pairs of chromosomes align along the equator.
Meiosis 1 is marked by the separation of homologous chromosomes and reduction of diploid cells into haploid cells. In this step, the nuclear membrane dissolves, individual chromosomes become each meiotic division has substages corresponding to those seen in mitosis.