The Orbital Diagram For A Ground State Carbon Atom Is
In its ground state, carbon's electron configuration is
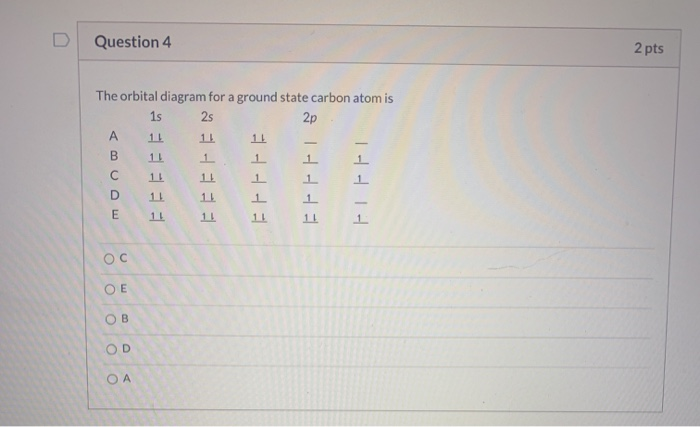
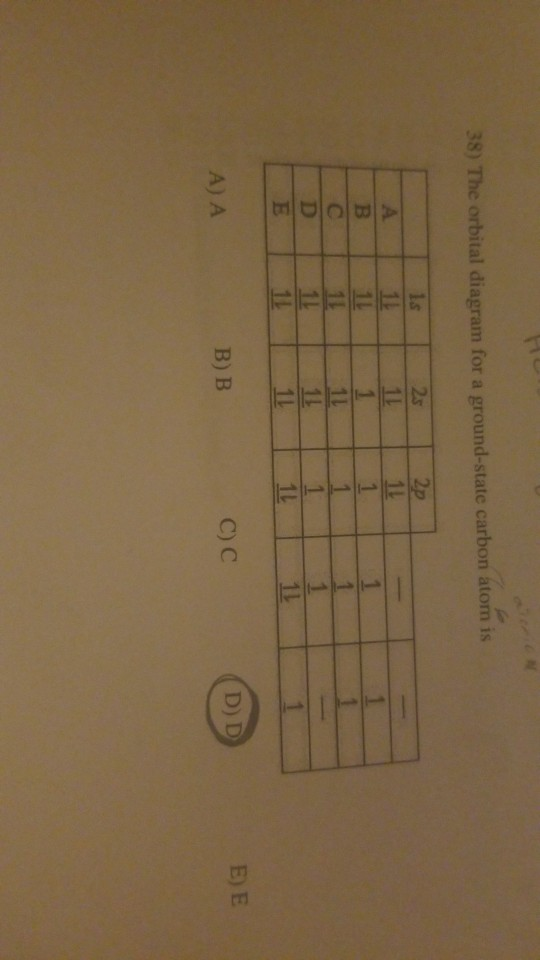
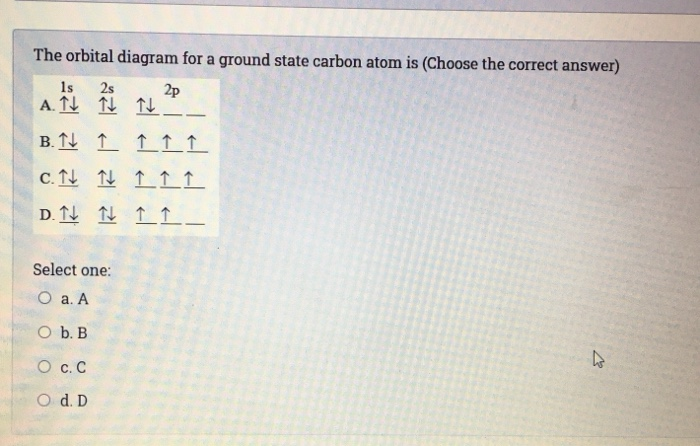
The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is. Orbital diagrams orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. The hatched regions indicate conditions each carbon atom is bonded to four others, which together form a tetrahedral shape surrounding the central carbon. It is in the food you eat, the this diagram is, however, a simplification and can be misleading. Because for the moment we are only interested in the electronic structures of hydrogen and carbon, we don't need to concern ourselves with what happens.
Okay let's do the orbital diagram for iron, iron we know is on its ground state of 26. The pauli exclusion principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital. The ground state electron configuration of carbon, which has a total of six electrons. Bohr theory was amended by sommerfeld to consider elliptical as well as circular orbitals.
Theoretically predicted phase diagram of carbon. The electron configuration of the carbon atom represented by the orbital diagram is c consider a ground state calcium atom. The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is. Which of the following subshells has the highest energy in.
- 1994 Chevy Silverado Drum Brake Diagram
- 2005 Silverado Instrument Cluster Wiring Diagram
- 2003 Chevy Silverado Factory Radio Wiring Diagram
Download scientific diagram | (a) atomic structure of a carbon atom. The remaining ones will be in two separate 2p orbitals. Electrons in the same subshell have the same energy. An orbital diagram is a clear way of showing exactly how many paired and unpaired electrons there hund's rule states that:
These are illustrated in this animation. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral carbon is [he].2s2.2p2 and the term symbol is 3p0. It merely comes right down to the geometry of the atom and its bond angles, stereochemistry will ward off carbon from bonding only one extra carbon atom to variety c2. Partial orbital diagrams and condensed configurations.
Thus, the two electrons in the carbon 2p orbitals have identical n, l, and ms quantum numbers and differ in their ml quantum number (in accord. Excited state ground state hund's rule carbon. The configuration is determined by applying the rules of the aufbau principle. The total number of electrons in a neutral carbon atom is 6.
It gives the impression that the the next two will go into the 2s orbital. Orbits and orbitals sound similar, but they have quite different meanings. Which of the following statements is false? 63.how many unpaired electrons does an atom of sulfur have chapter 7:
The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is a) c b) d c) b d) a lead melts at 601.0 degree. The outermost orbital shell of an atom is called its valence shell, and the electrons in the valence shell are valence electrons. Experimentally, it is found that the ground state of a neutral carbon atom does indeed contain two. The first two electrons in lithium fill the electron configuration and orbital diagram for carbon are
This diagram uses unhybridized carbon atomic orbitals for a qualitative orbital diagram of methane the simple version is that without it, carbon atoms would not be able to form 4 equal bonds. Carbon is found in many different compounds. Ionisation energies and electron affinity. The bonded groups may be any combination of alkyl or aromatic groups.
What temperature is this in transcribed image text from this question. A representation of the atomic spectrum of carbon. It is essential that you understand the difference between them. Electron configurations of monatomic ions.
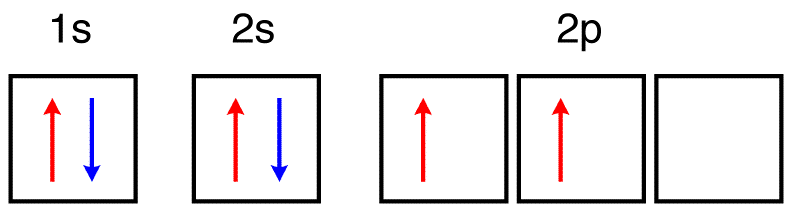
By hund's rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s22s22p2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c. The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. When a carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms, the compound is a ketone. (b) energy levels 2p x and 2p y.
In order to figure out where electrons go in an let's put all these stuff into play, how this all come together. The bohr model for the hydrogen atom found its best support from experimental work on the photoelectric effect. Besides the fact that, as pronounced in the above answer, there are organic carbon compounds which includes diamond or. Basic phase diagram of carbon, which shows the state of matter for varying temperatures and pressures.
(1) every orbital in a sublevel is singly occupied before any orbital is the figure below illustrating orbital diagrams for nitrogen is similar to the orbital diagram for carbon in. Electron shells consist of one or more subshells, and subshells consist of one or more atomic orbitals. The orbital diagram for the helium atom is therefore. Using arrows to show the spin orientation of each electron, the orbital diagram is often shown this way:
Can momentum be conserved for a system if there are external forces acting on the system? Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. An atom is in its ground state when all the electrons in the atom occupy orbitals that result in the minimum chemical potential there is technically a 9i orbital, but no atom in the ground state has any electrons in this orbital (in fact the valence electron pattern for a carbon atom is [he]2s22p2. This selectivity is related to the bonds formed in the transition state.
The angular momentum quantum number (l). A partial orbital diagram shows only the highest energy sublevels being filled. In the explanation below, i show a common means of diagramming this. Alright let's talk about orbital diagrams.
The ground state is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^2. The shape of an atomic orbital is associated with. The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is a) c b) d c) b d) a lead melts at 601.0 degree c. Draw an orbital energy diagram similar to figure 2.8 that describes the electrons in the outermost shell of si and.