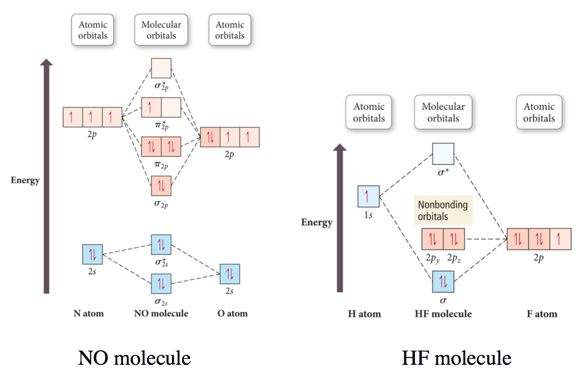
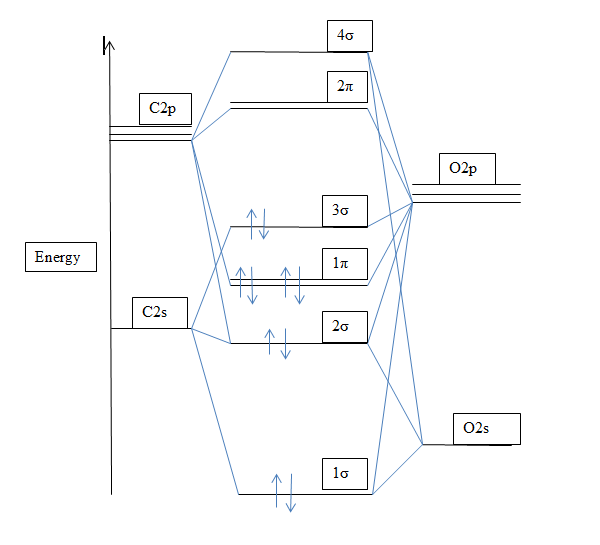
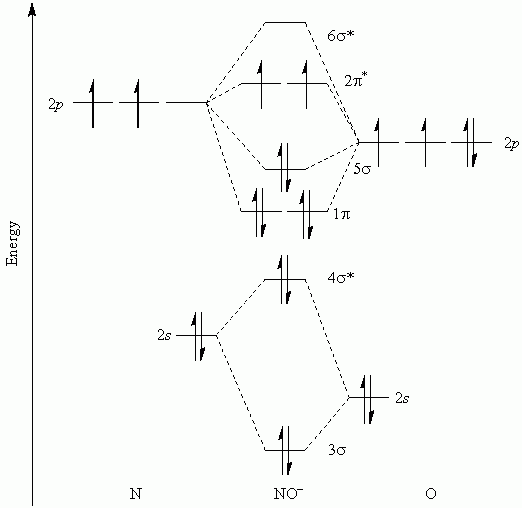
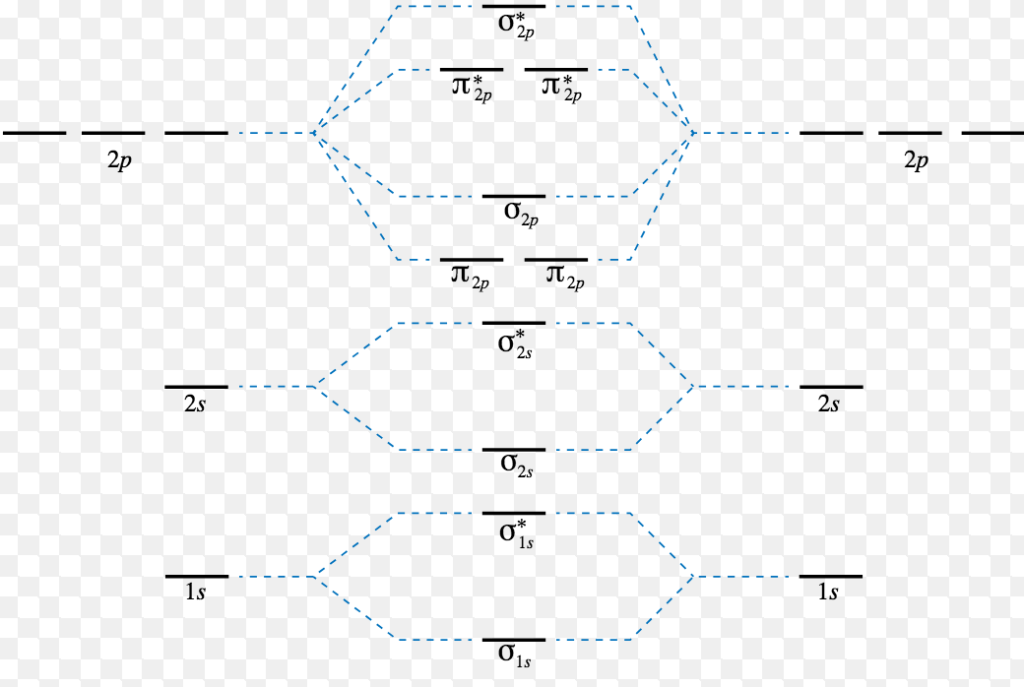
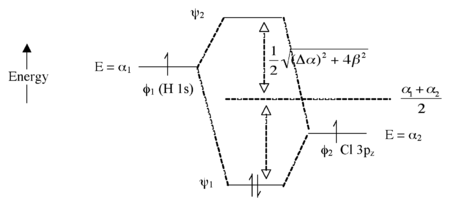
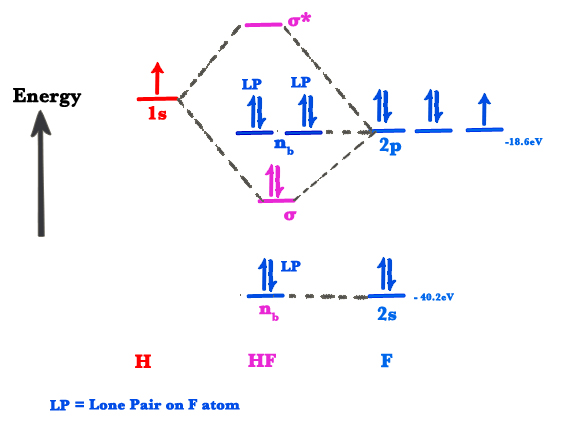
Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice
Molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms, that is, in terms of orbitals, orbital diagrams, and electron configurations.
Molecular orbital diagram practice. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f. Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the co molecule. Determine how many valence electrons you have on each atom (you can ignore the core electrons as core orbitals contribute little to molecular orbitals).
Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. University of sydney has created a practice website for reviewing different parts of molecular orbital diagrams. This gives you the total number of electrons you will have to distribute among the molecular orbitals you form. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12.
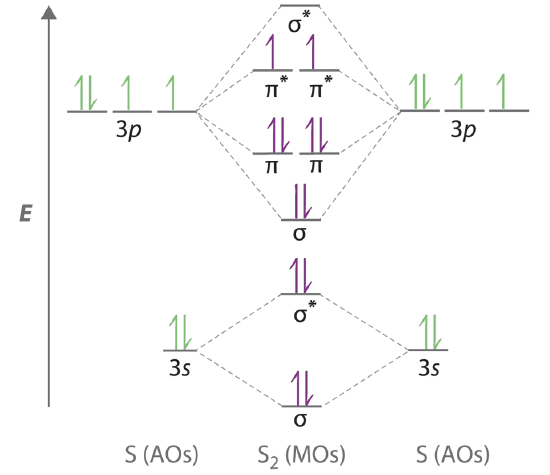
21 254 просмотра 21 тыс. Combination of 1s atomic orbitals of two atoms form two molecular orbitals called as sigma 1s and when in same manner, the 2s and 2p atomic orbitals, eight atomic orbitals on two atoms can give rise to eight molecular orbitals. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory. The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram.
A molecular orbital diagram , or mo diagram , is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in latex by means of the package modiagram. 9 molecular orbital diagram for co. For information about the more traditional molecular structure.
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. 365 molecular orbital diagram key draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Molecular orbital theory provides an alternative model to valence bond theory that better describes the electron behaviour and physical/chemical properties of. Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc.
(lcao) molecular orbital method in particular. Molecular orbital energy diagrams for (a) h 2 showing both electrons in the bonding sigma mo; So again, it's drawn in the familiar pattern. Mo energy diagram for o 2.
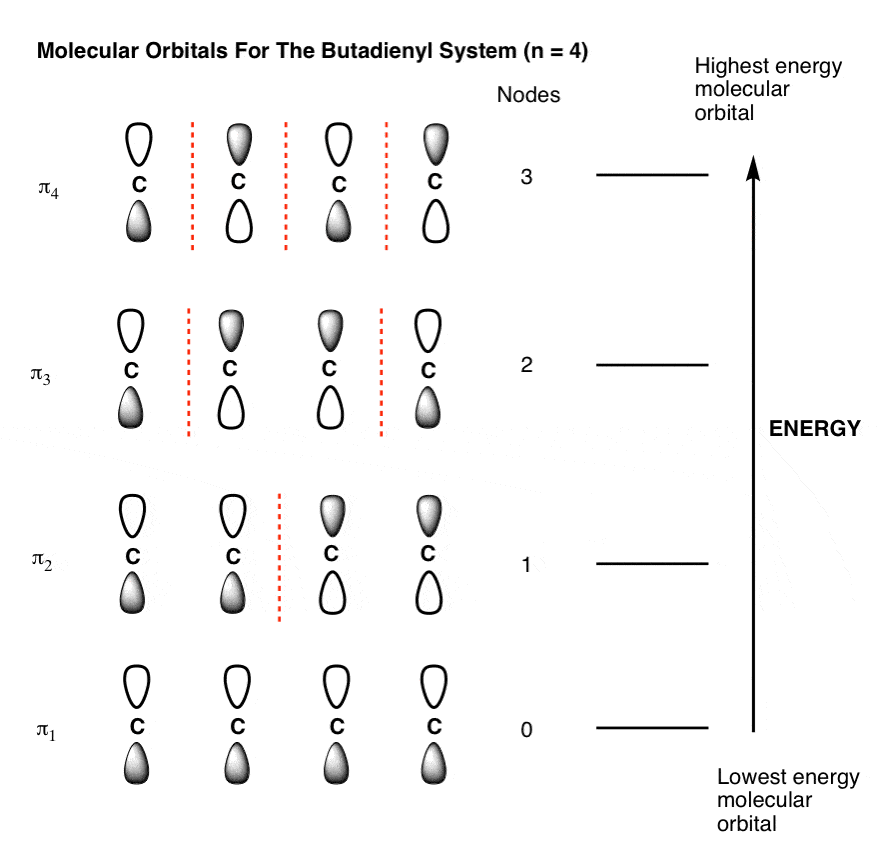
Eight electrons from each oxygen atom add up to 16 electrons in the o 2 molecule. For example, to give you a glimpse at where we are headed. Previously, we've seen what the molecular orbitals of benzene look like, and that the fact that they are partially duplexed (or to use the proper nomenclature, degenerate) helps to explain benzene's unusual stability. The following molecules are currently available:
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that construct a molecular orbital diagram of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate. Western connecticut state university molecular orbital theory. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable. The following questions pertain to the f2 molecule
Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. Calculate the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in simple molecules. Now carbon monoxide's mo diagram is And (b) he 2 figure 4.
| online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule : In chemistry molecular orbital (mo) theory is a method for determining molecular. The molecular orbital electronic configuration, magnetic property: Analysis done by bond order.
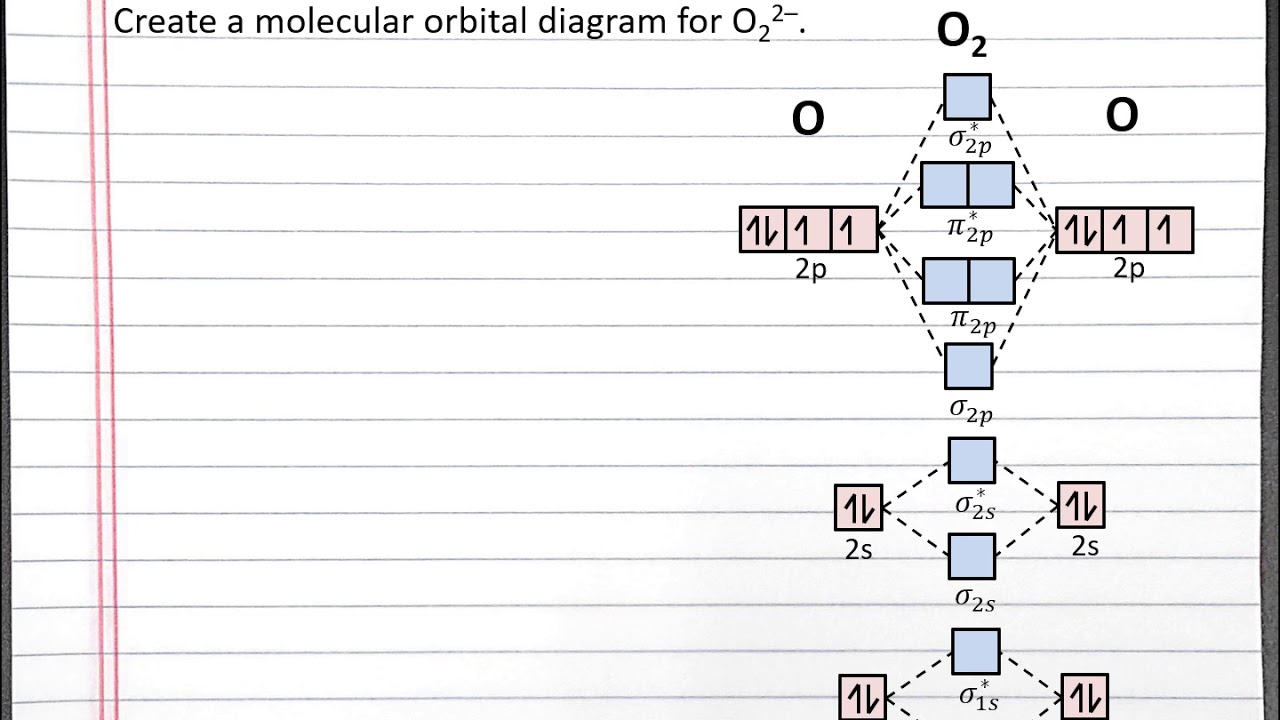
The molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and the result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below. They combine to form the molecular orbitals indicated above. General chemistry i che 110. You can practice labeling and filling molecular orbitals with this interactive tutorial from the university of sydney.
The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories if you can understand the foundation and skeleton of the diagram specific to that molecule, then it will be easier and faster for you to draw it. Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations. Molecules of the first row Energy level diagram for molecular orbital.
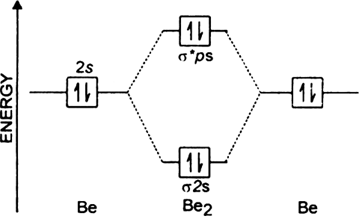
A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. These problems are for practice in drawing your molecular orbital diagrams, molecular electron configurations and determining bond order. Molecular orbital diagram, antiaromaticity, and structure. Since bond order is zero, be2 molecule does not exist.
The molecular orbital theory is a technique for modeling the chemical bonding and geometry of the molecular orbital theory builds off of valence bond theory and valence shell electron pair repulsion this diagram can be used to calculate the bond order of the diatomic molecule. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons.