Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice Problems
Lumo = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital homo = highest occupied molecular orbital.
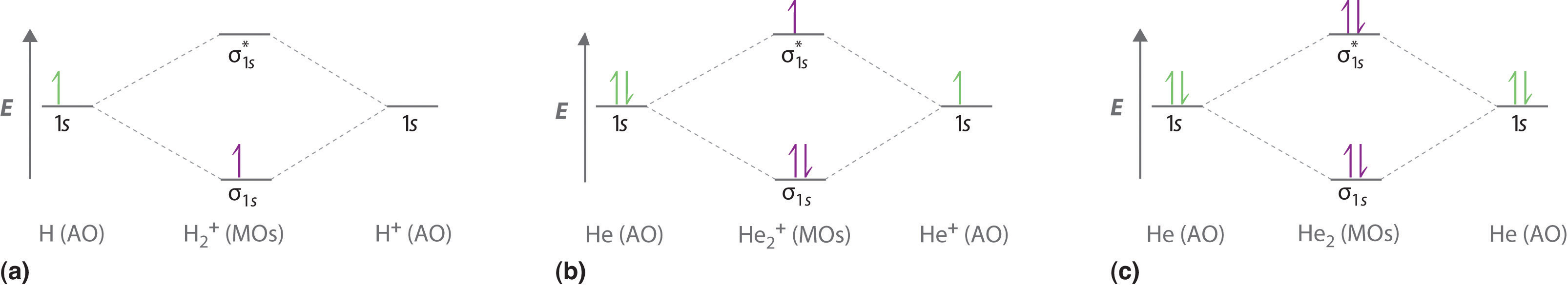
Molecular orbital diagram practice problems. Molecular orbital diagrams, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons draw the. Distinctive aspects of the representational. Molecular orbital diagram for co5:09. Whether h2+ and h2− exist.
A molecular orbital diagram , or mo diagram , is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding. The following four statements about circular orbits are equivalent. Draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for this molecule. The following questions pertain to the f2 molecule:
A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. For example, to give you a glimpse at where we are headed. A) draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for this molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in latex by means of the package modiagram.
- 2004 Honda Rancher 350 Wiring Diagram
- Mercury Outboard Control Box Wiring Diagram
- 2008 Dodge Ram Ac Relay Location
A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. If either exists, write its electron configuration. Mullikan, incorporates the wave like characteristics of electrons in describing bonding behavior. Now carbon monoxide's mo diagram is
These problems are for practice in drawing your molecular orbital diagrams, molecular electron configurations and determining bond order. Valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory. These problems are for practice in drawing your molecular orbital diagrams, molecular electron. Derive any one of them from first principles.
Molecular orbital theory describes molecules in a similar way to atoms, using orbitals, orbital diagrams and electron configurations. An mo diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each mo. This is very easy to draw: Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the co molecule.
Molecular orbital theory provides an alternative model to valence bond theory that better describes the electron behaviour and physical/chemical properties of. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and you can practice labeling and filling molecular orbitals with this interactive tutorial from the university of sydney. Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule.
If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule. Molecular orbital energy diagram for oxygen diatomic. You've reached the end of your free preview. Prepare an orbital interaction picture and a molecular orbital diagram for each of the following:
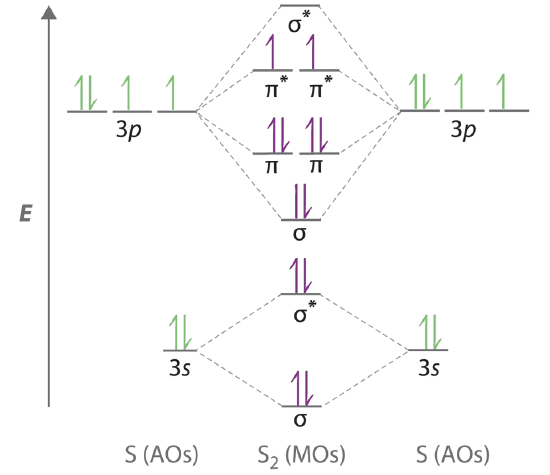
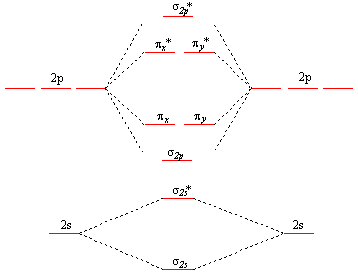
| online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule : The molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and the result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below. Analysis done by bond order. In mo theory, there is no hybridization and all orbitals on the molecule (now called molecular orbitals) can be made by combining any and all of the atomic.
(a) may result from overlap of p atomic carbon monoxide has ten bonding electrons and four antibonding electrons. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. Molecular orbitals are the energy states of a molecule in which the electrons of the molecule are filled just as atomic orbitals are the energy states of an atom in which no. Want to read the whole page?
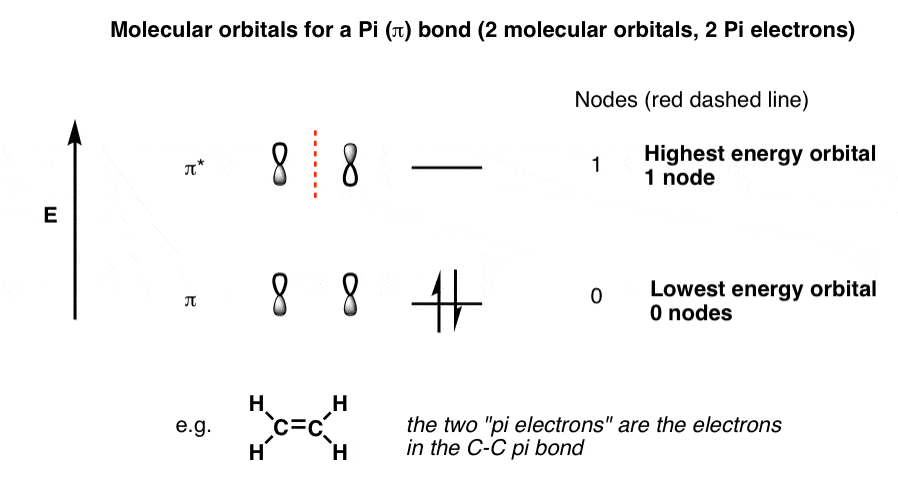
Tags molecule, molecular orbital diagram, molecular physics, orbital picture. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Molecular orbital (mo) theory is a more accurate way to use calculations to predict molecular geometries and energies than vb theory. Bond order (h2 molecule) =.
Bond orders and stability of molecules. (lcao) molecular orbital method in particular. Give the molecular electron configuration for the. Orbital diagrams orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom.
Valence bond (vb) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. Therefore it which of the following is the correct electron configuration for c2. Valence bond theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. Molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms, that is, in terms of orbitals, orbital diagrams, and electron configurations.
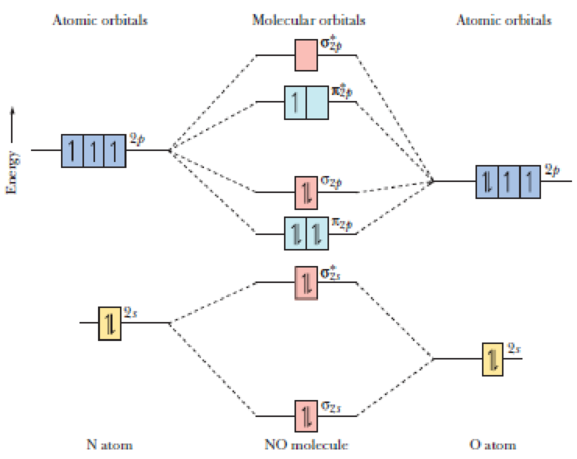
Configurations and determining bond order. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Molecular orbital theory, bonding & antibonding mo, bond order, homonuclear diatomic molecules. The molecular orbital theory, initially developed by robert s.
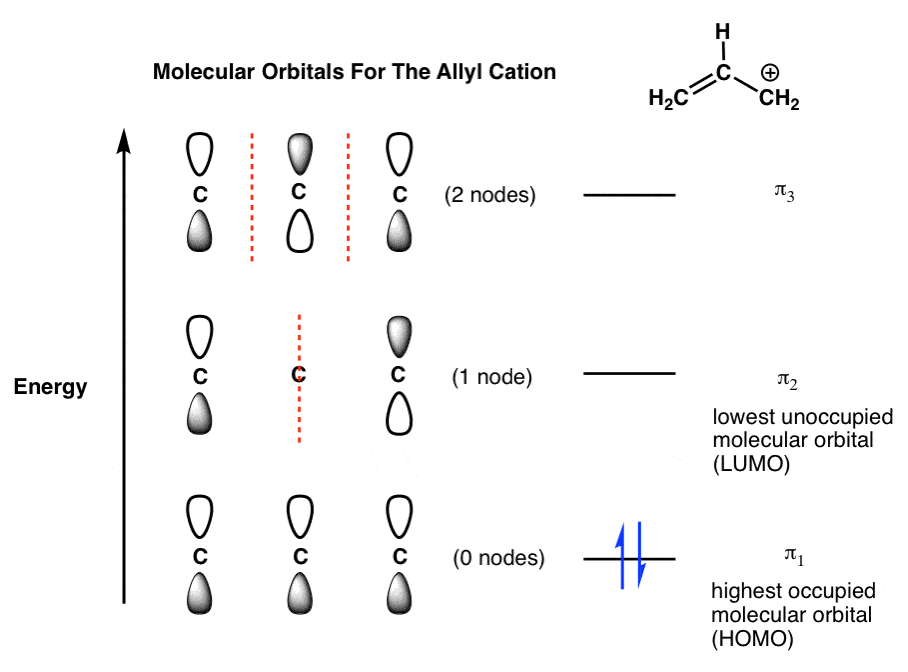
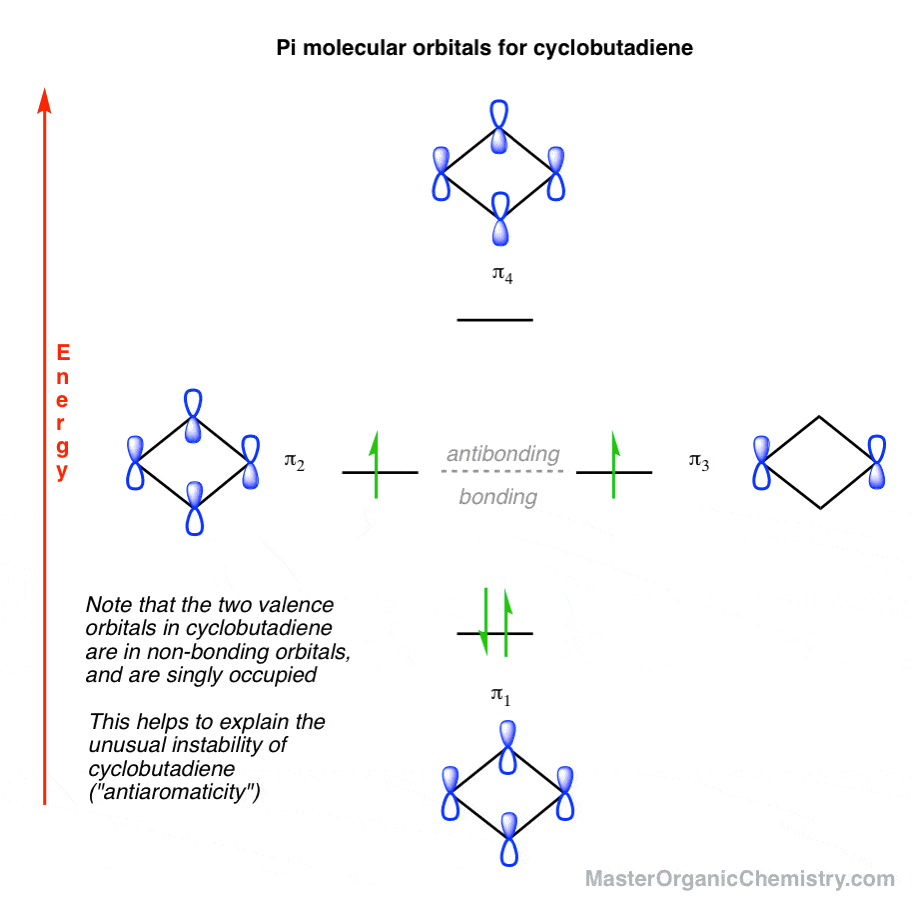
Label all of the orbitals specifically. The molecular orbital diagram of butadiene, and a system for drawing all of its pi molecular orbitals, and determining the homo and lumo. Electron orbital diagrams showing energy levels (n), subshells or sublevels(s, p, d, f), and orbitals. I don't really know what that is.but it's interacting with both hydrogen's 1s orbital and.
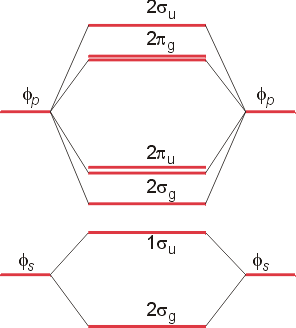
Molecular orbital theory posits the notion that electrons in molecules likewise exist in different orbitals that give the probability of finding the electron at notice that the orbitals of the separated atoms are written on either side of the diagram as horizontal lines at heights denoting their relative energies. Use mo diagrams to find bond orders and predict. For information about the more traditional molecular structure. The molecular orbital theory (often abbreviated to mot) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by f.
Methods for solving problems in orbital mechanics using conservation of energy and momentum are discussed. We will practice drawing many 3d structures to train our minds to imagine in three dimensions, and to help us understand a topic under discussion, such as parallel p orbitals in. 9 molecular orbital diagram for co. So again, it's drawn in the familiar pattern.