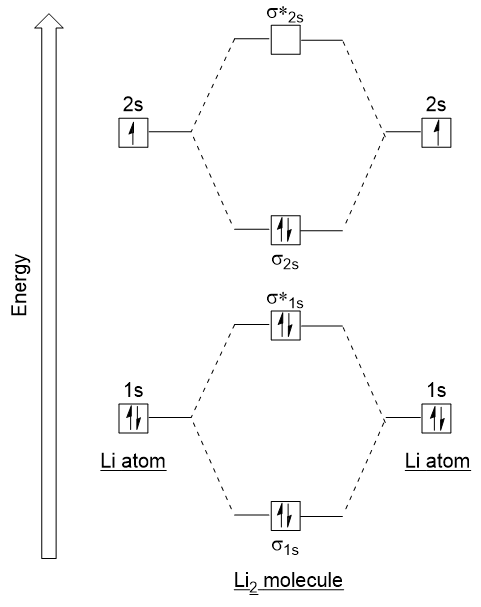
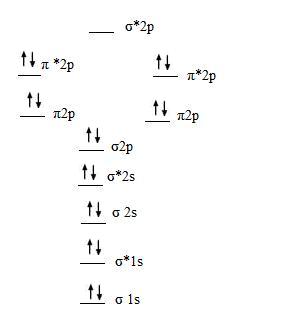Li2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
From this diagram, calculate the bond order for o2.
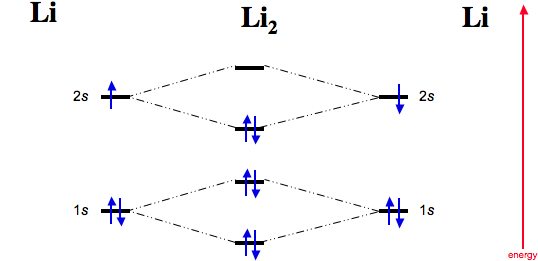
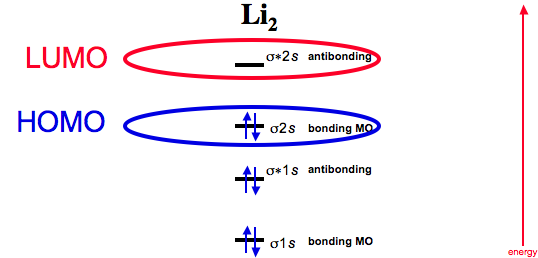
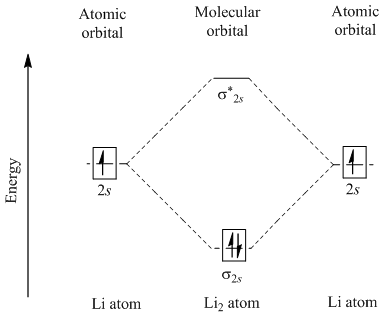
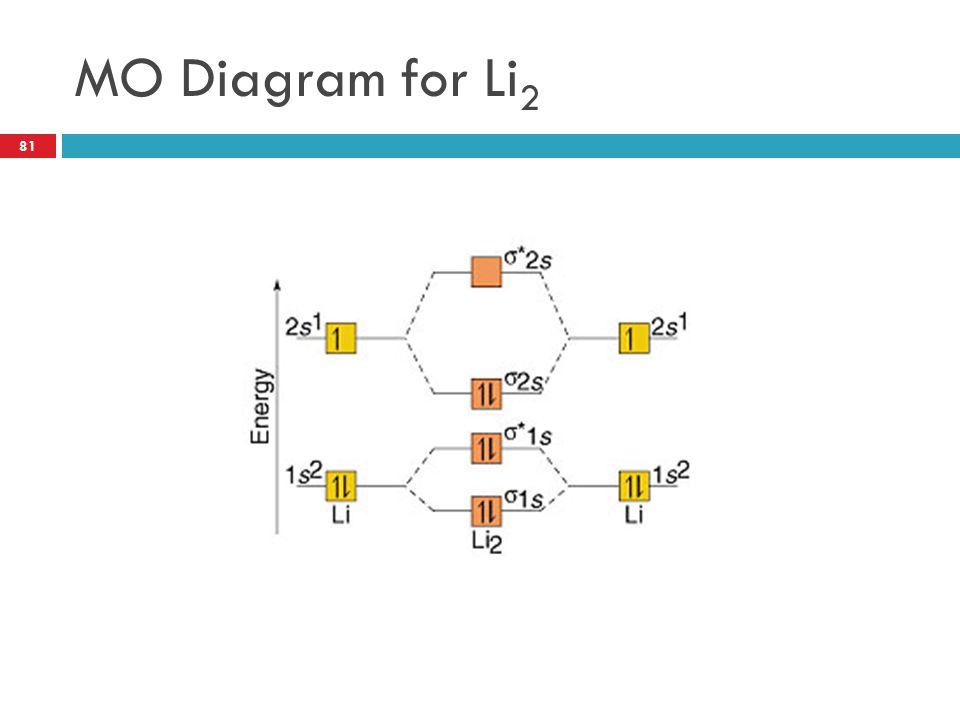
Li2 molecular orbital diagram. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. These doodle notes encourage students to use creativity and both hemispheres of their brain. Its the mot diagram for li2.
This problem has been solved! This is a bond between two lithium atoms, which have an electron configuration of 1s22s1. Compare the atomic and molecular orbital diagrams to identify the member of each of the following pairs that has the highest first ionization energy (the most tightly bound electron). Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry.
The molecular orbital theory (mo) has been introduced for the diatomic hydrogen molecules. Molecular orbital theory and molecular orbital diagram. Valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory. Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory.
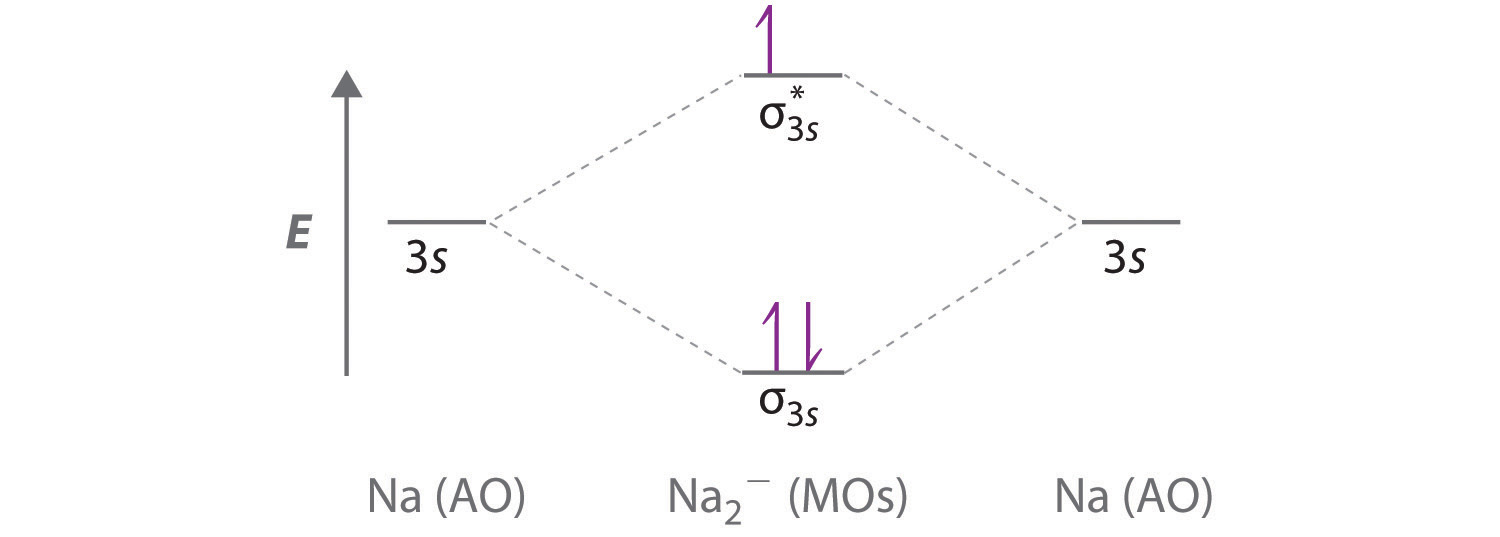
In chemistry molecular orbital (mo) theory is a method for determining molecular. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12. The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a way of looking at the structure of a molecule by using molecular orbitals that belong to the molecule as a whole. Molecular orbital energy level diagrams of li2 according to the molecular orbital theory explains the bond order amd magnetic properties of lithium molecule.
The following molecules are currently available: The molecular orbital diagram shows the creation and filling of mos in a bond. Within the diagram, orbitals are represented by horizontal lines. 1) stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons.
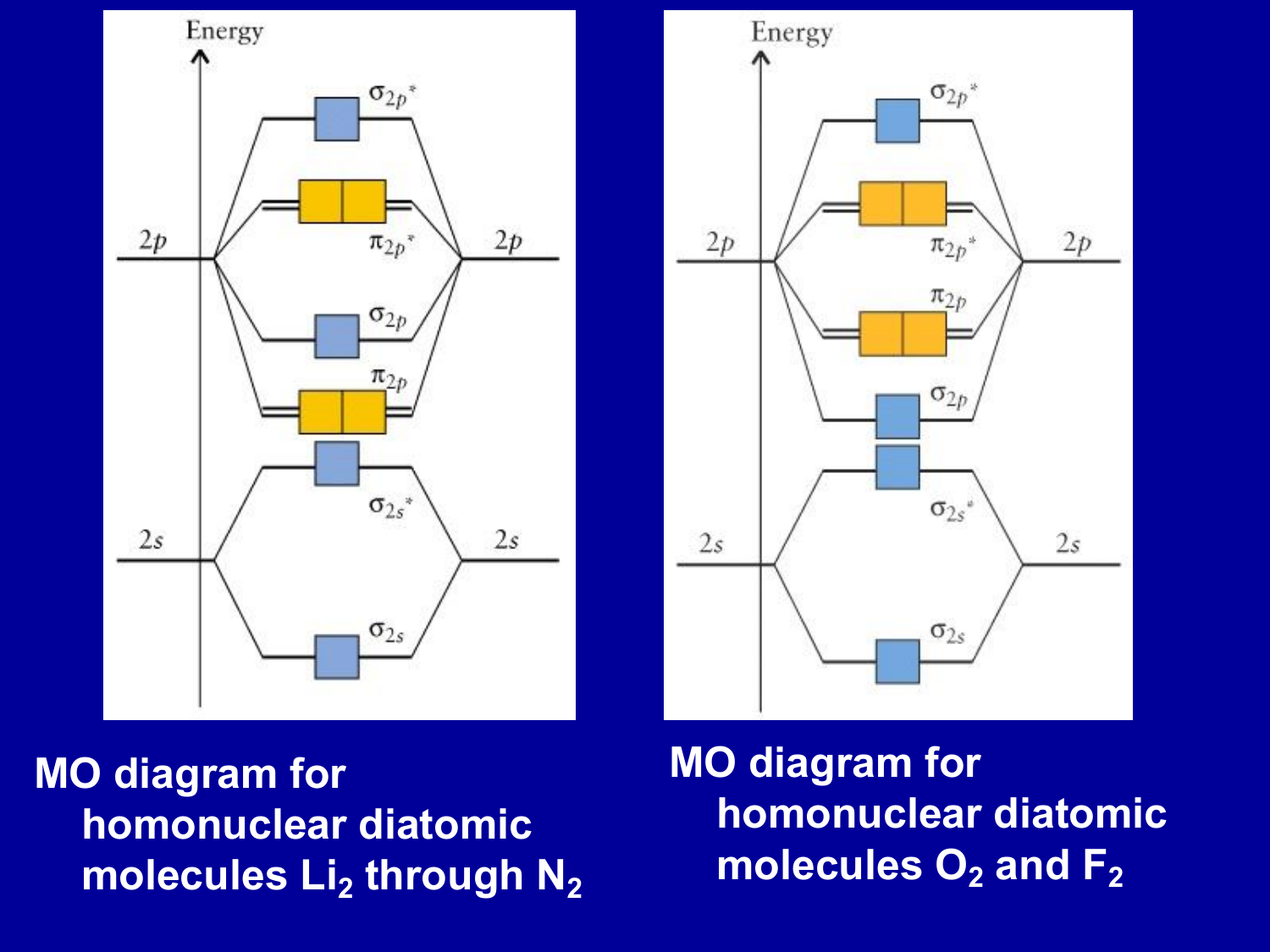
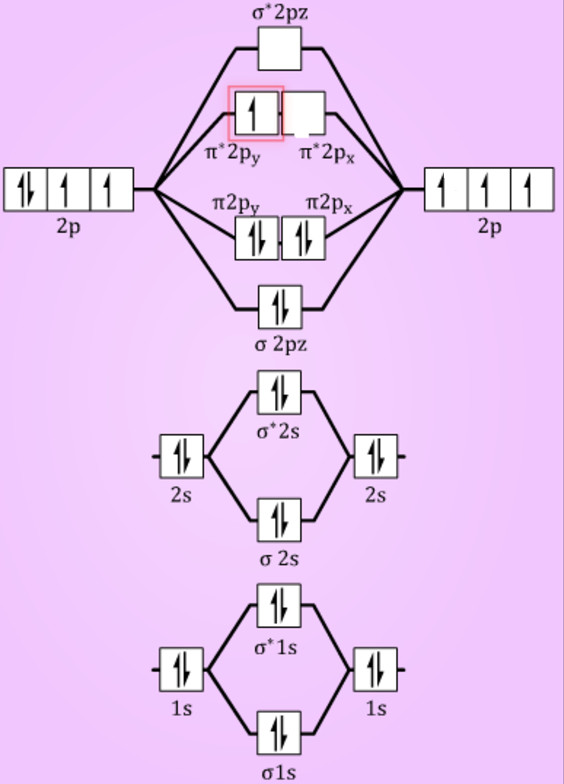
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The homonuclear diatomic molecules li2 to n2 have the molecular orbital diagram in the table below. Li2, be2, b2, c2, n2, o2, f2, and ne2. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories:
Molecules of the first row Molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms, that is, in terms of orbitals, orbital diagrams, and electron configurations. M.ishida, t.nakajima, y.honda, o.kitao, h.nakai, m.klene, x.li, j. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for b₂ and other diatomic molecules from row 2 elements of the.
Answer to 1)complete the atomic orbital (ao) and molecular orbital (mo) energy diagram for li2+ and li2 question: 3) if nb = na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of. Do follow me on unacademy to watch other courses. Unlike most texts on molecular orbital theory and quantum mechanics, this text treats polyatomic molecules before linear molecules before atoms.
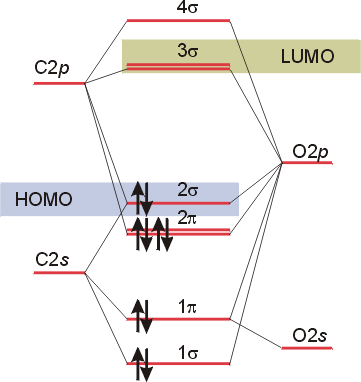
Relationship between electronic configuration and molecular behaviour. As an exercise, please fill electrons in the molecular orbitals of a relative energy level diagram to derive and confirm the above conclusion as well as relative energy levels of molecular orbitals for li2 to n2. Calculate the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in simple molecules. | online chemistry tutorial iit, cbse chemistry, icse chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams molecular orbital diagram of c2 molecule :
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that he2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Bond order 1 = single bond. For example, to give you a glimpse at where we are headed, the following are orbital. Dihydrogen and its ion h2+.
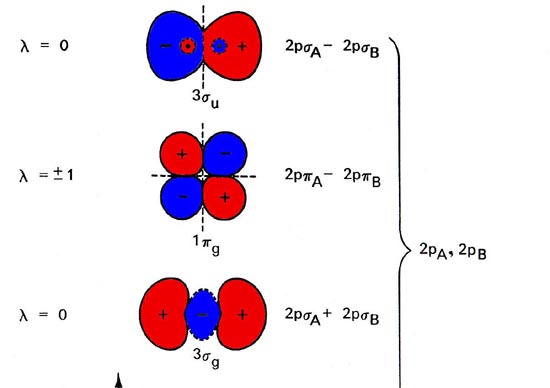
The walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. Valence bond theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. In the molecular orbital theory of h2, we consider the molecular orbitals as made up of the symmetric and antisymmetric combination of the individual 1s atomic orbitals on the two atoms.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, o2. This lecture is for the jee/ neet aspirants and for all those who are interested. B.cross, v.bakken, c.adamo, j.jaramillo, r.gomperts, r.